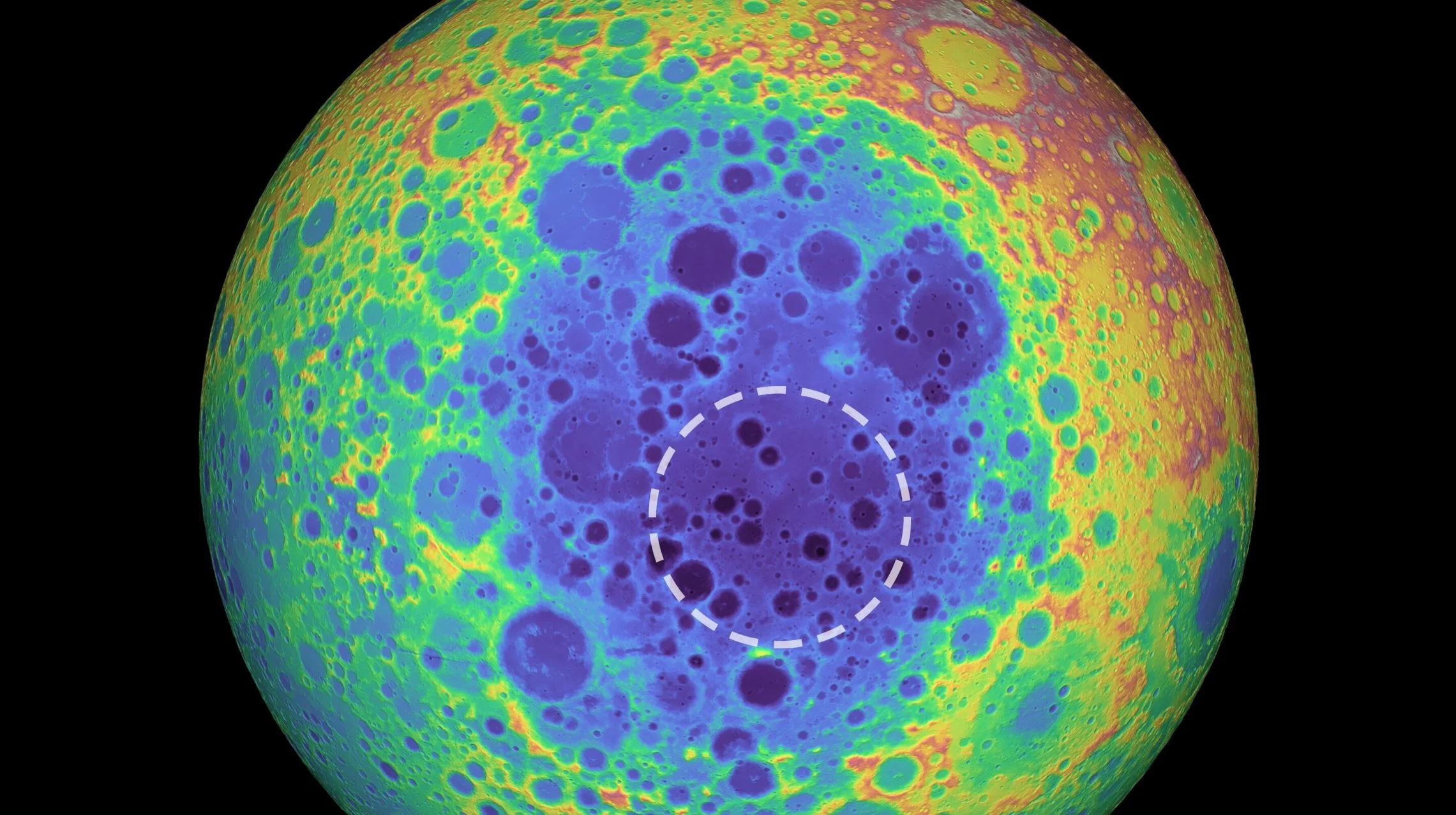
As NASA prepares to return to the Moon by 2024 as part of its Artemis program, the agency is focusing its efforts on exploring the Moon’s polar regions. These are areas of the Moon which seem to have a lot of water mixed in with the regolith.
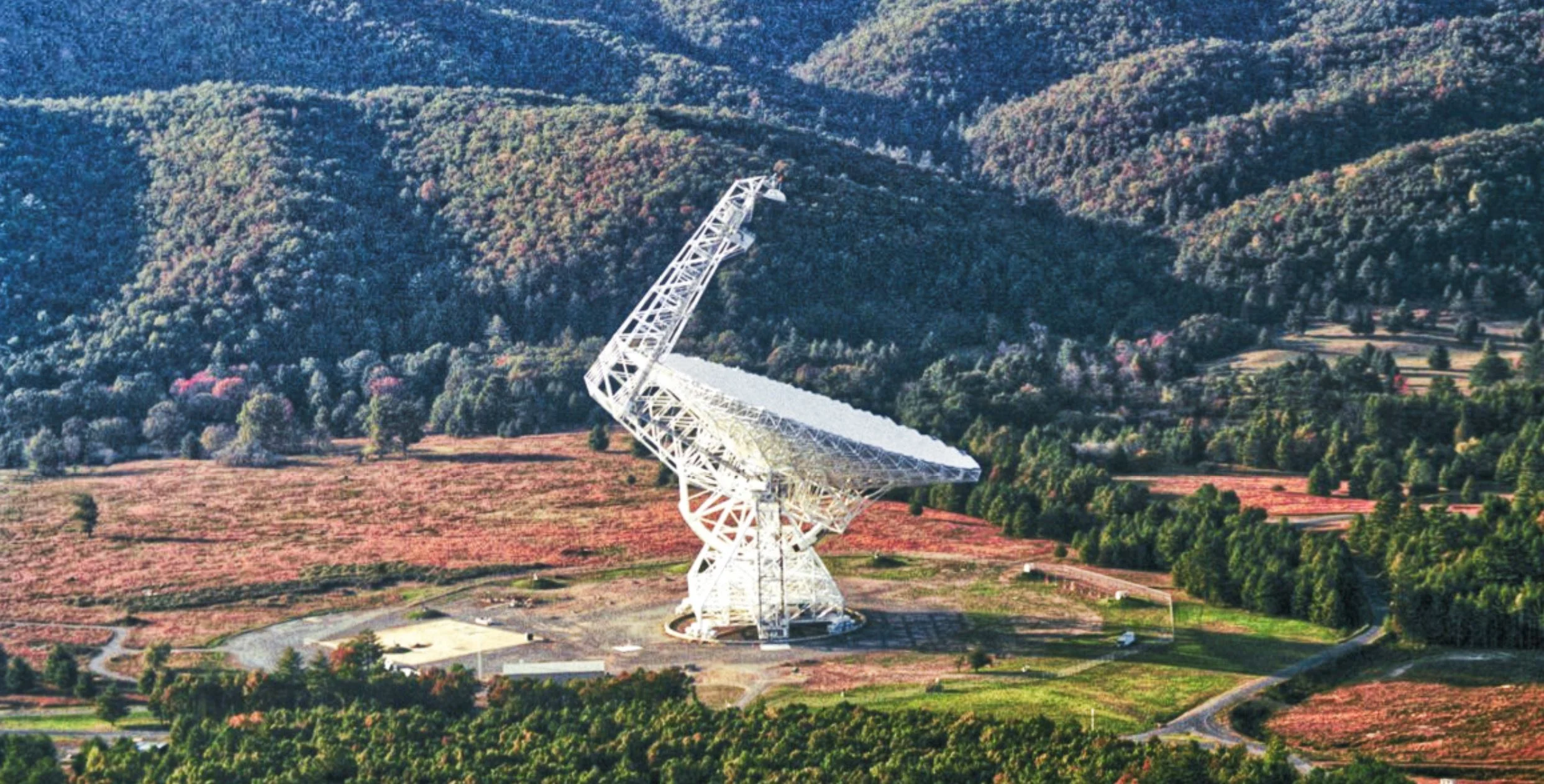
Dead planets can ‘broadcast’ for up to a billion years
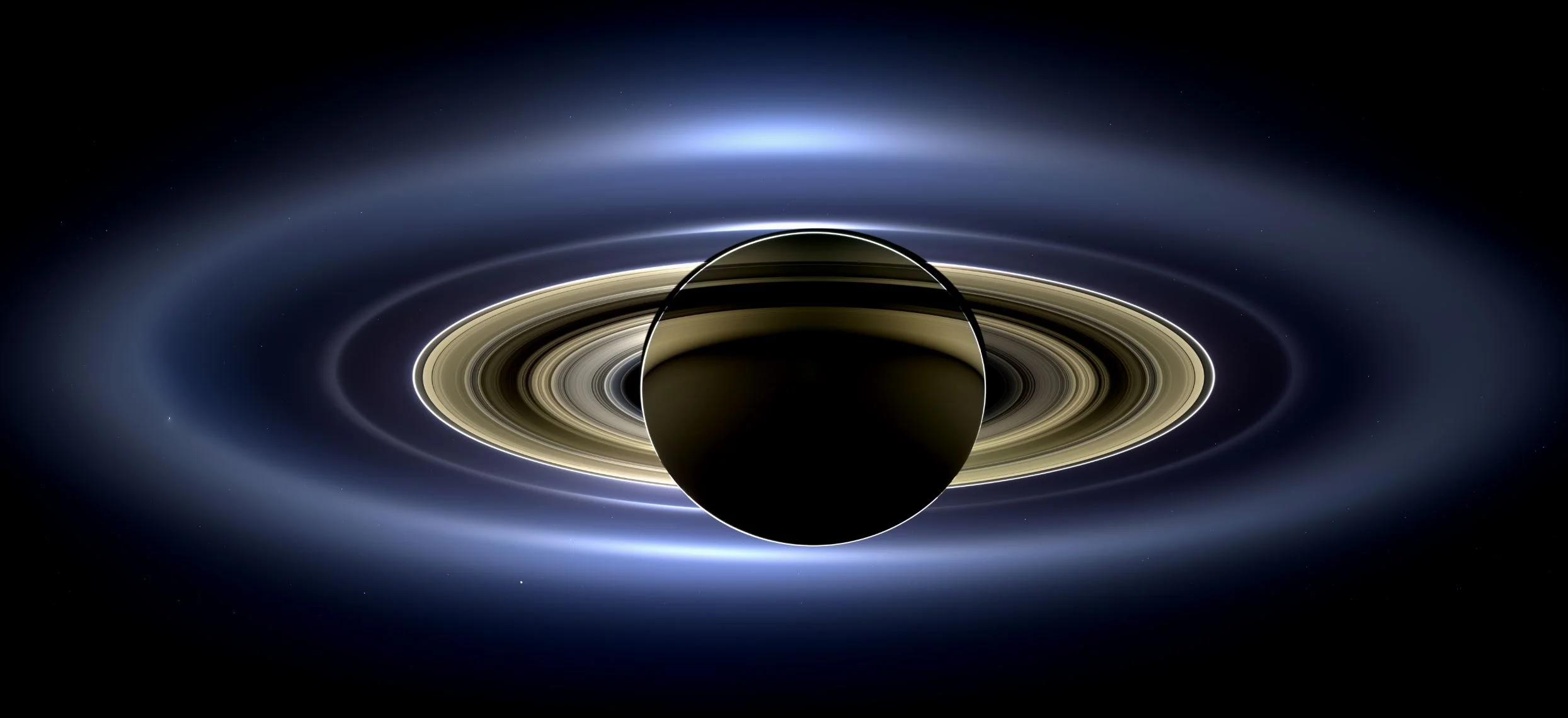
A brief astronomical history of Saturn’s amazing rings
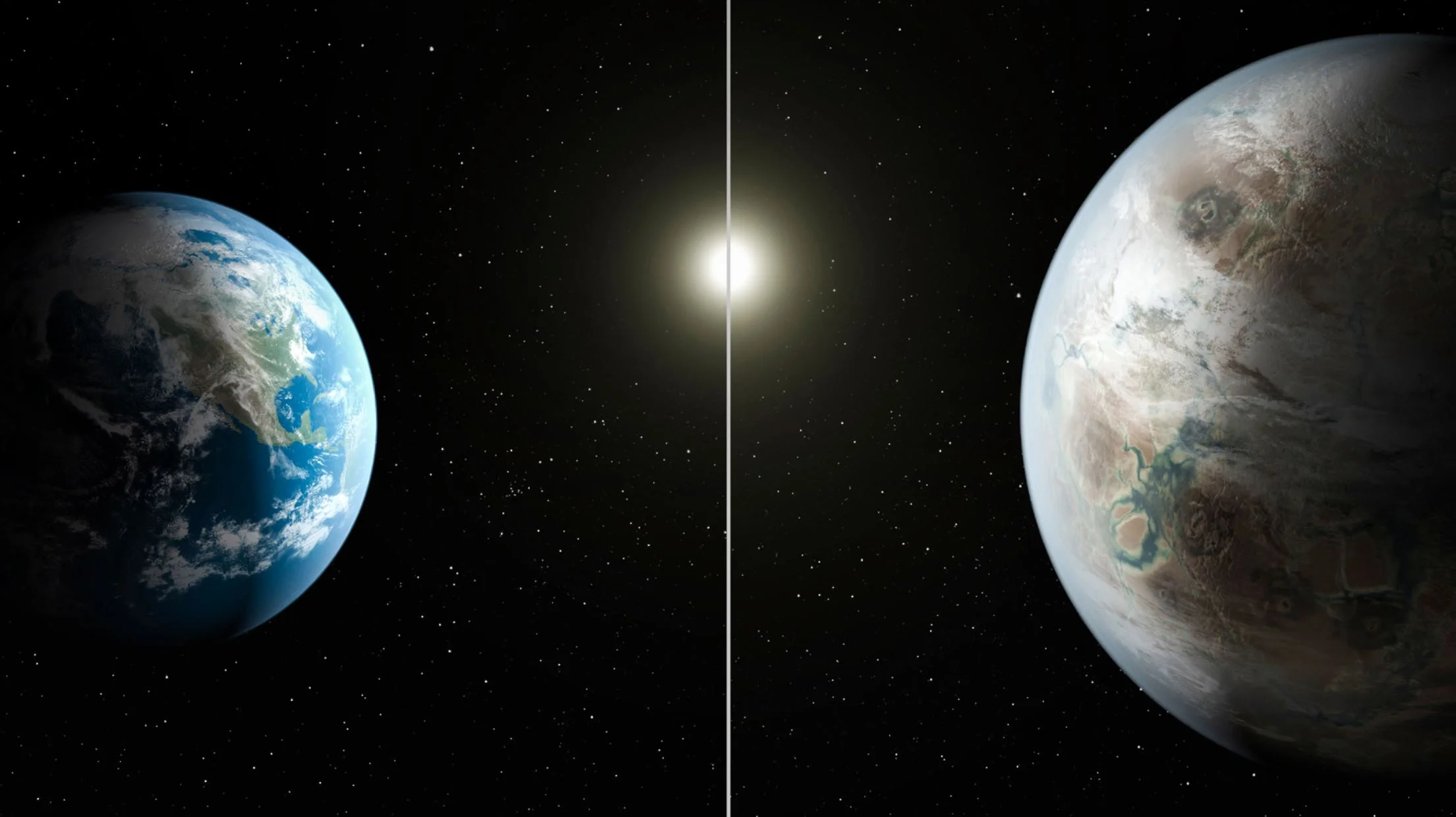
Kepler helps count earth-like planets around sun-like stars to estimate how common we are
The Milky Way’s Black Hole Just Flared, Growing 75 Times as Bright for a Few Hours!
Even though the black hole at the center of the Milky Way is a monster, it’s still rather quiet. Called Sagittarius A*, it’s about 4.6 million times more massive than our Sun. Usually, it’s a brooding behemoth. But scientists observing Sgr. A* with the Keck Telescope just watched as its brightness bloomed to over 75 times normal for a few hours.
Traces of One of the Oldest Stars in the Universe Found Inside Another Star!
Astronomers Uncover Dozens of Previously Unknown Ancient and Massive Galaxies
For decades, astronomers have been trying to see as far as they can into the deep Universe. By observing the cosmos as it was shortly after the Big Bang, astrophysicists and cosmologists hope to learn all they can about the early formation of the Universe and its subsequent evolution. Thanks to instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have been able to see parts of the Universe that were previously inaccessible.
Virtual 'Universe Machine' Sheds Light on Galaxy Evolution
Cloaked Black Hole Discovered in Early Universe!
Maybe Dark Matter is Warm, Not Cold
Since the “Golden Age of General Relativity” in the 1960s, scientists have held that much of the Universe consists of a mysterious invisible mass known as “Dark Matter“. Since then, scientists have attempted to resolve this mystery with a double-pronged approach. On the one hand, astrophysicists have attempted to find a candidate particle that could account for this mass.
Kepler’s forgotten ideas about symmetry help explain spiral galaxies without the need for dark matter
The 17th-century astronomer Johannes Kepler was the first to muse about the structure of snowflakes. Why are they so symmetrical? How does one side know how long the opposite side has grown? Kepler thought it was all down to what we would now call a “morphogenic field” – that things want to have the form they have. Science has since discounted this idea. But the question of why snowflakes and similar structures are so symmetrical is nevertheless not entirely understood.
Tardigrades: we’re now polluting the moon with near indestructible little creatures
An Israeli spacecraft called Beresheet almost made it to the moon in April. It took a selfie with the lunar surface in the background, but then lost contact with Earth and presumably crashed onto the lunar surface. Now it’s been revealed that the mission was carrying a cargo of dehydrated microscopic lifeforms known as tardigrades.
Space junk: a recycling station could be cleaning up in Earth orbit by 2050
There are about 22,000 large objects orbiting the Earth, including working and broken satellites and bits of old rocket from past space expeditions. If you include all the equipment dropped by astronauts while floating in space and the debris from colliding satellites down to around 1 centimeter in size, there are about one million bits of space junk in Earth’s orbit.
Elon Musk Outlines the Next Few Weeks of Starship Tests
Return to the moon? 3D printing with moondust could be the key to future lunar living
The entire Apollo 11 mission to the moon took just eight days. If we ever want to build permanent bases on the moon, or perhaps even Mars or beyond, then future astronauts will have to spend many more days, months and maybe even years in space without a constant lifeline to Earth. The question is how would they get hold of everything they needed. Using rockets to send all the equipment and supplies for building and maintaining long-term settlements on the moon would be hugely expensive.
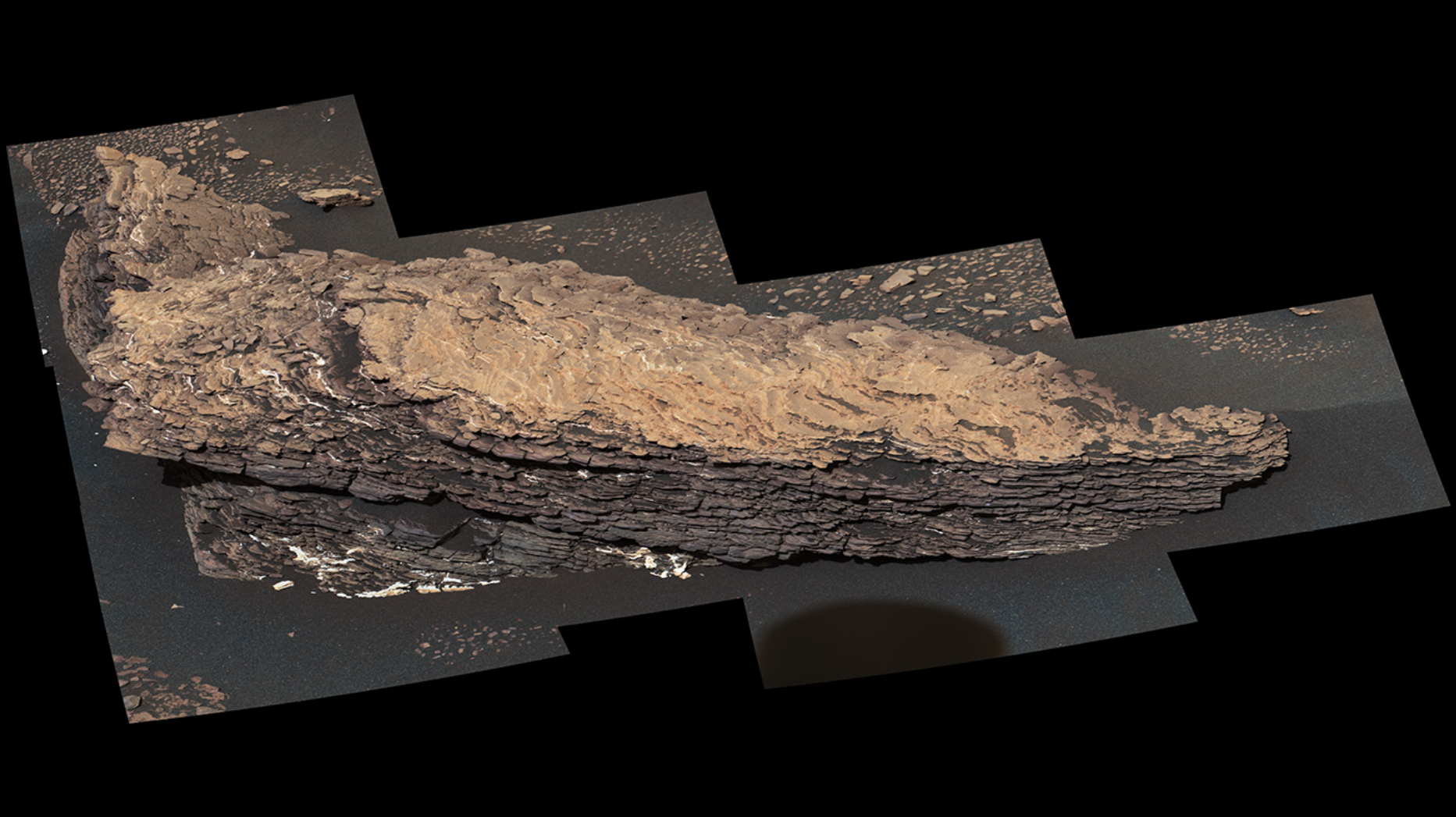
New Finds for Mars Rover, Seven Years After Landing
NASA's Curiosity rover has come a long way since touching down on Mars seven years ago. It has traveled a total of 13 miles (21 kilometers) and ascended 1,207 feet (368 meters) to its current location. Along the way, Curiosity discovered Mars had the conditions to support microbial life in the ancient past, among other things.
Aliens: could light and noise from Earth attract attention from outer space?
Since the first use of electric lamps in the 19th century, society hasn’t looked back. Homes and streets are lit at all hours so that people can go about their business when they’d once have been asleep. Besides the obvious benefits to societies and the economy, there’s growing awareness of the negative impact of artificial light.
Snowball Exoplanets Might Be Better for Life Than We Thought!
When astronomers discover a new exoplanet, one of the first considerations is if the planet is in the habitable zone, or outside of it. That label largely depends on whether or not the temperature of the planet allows liquid water. But of course it’s not that simple. A new study suggests that frozen, icy worlds with completely frozen oceans could actually have livable land areas that remain habitable.
Rock Almost Rolled Into This Crater on the Moon… Almost
The history of the Moon is a tale told by geology, apparent in its rocks, craters, and other surface features. For centuries, astronomers have studied the Moon from afar and for the past few decades, it has been visited by countless robotic missions. Between 1969 and 1972, a total of twelve astronauts walked on its surface, conducted lunar science, and brought samples of lunar rock back to Earth for study.