If the power goes out in your home, you can usually settle in with some candles, a flashlight, and a good book. You wait it out, because the lights will probably be back on soon.
One of the TRAPPIST-1 planets has an iron core!
In February of 2017, a team of European astronomers announced the discovery of a seven-planet system orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1. Aside from the fact that all seven planets were rocky, there was the added bonus of three of them orbiting within TRAPPIST-1’s habitable zone. Since that time, multiple studies have been conducted to determine whether or not any of these planets could be habitable.
Mining asteroids could unlock untold wealth – here’s how to get started!
Elements from the stars: The unexpected discovery that upended astrophysics 66 years ago
Ancient Galaxy Megamergers - ALMA and APEX discover massive conglomerations of forming galaxies in early Universe
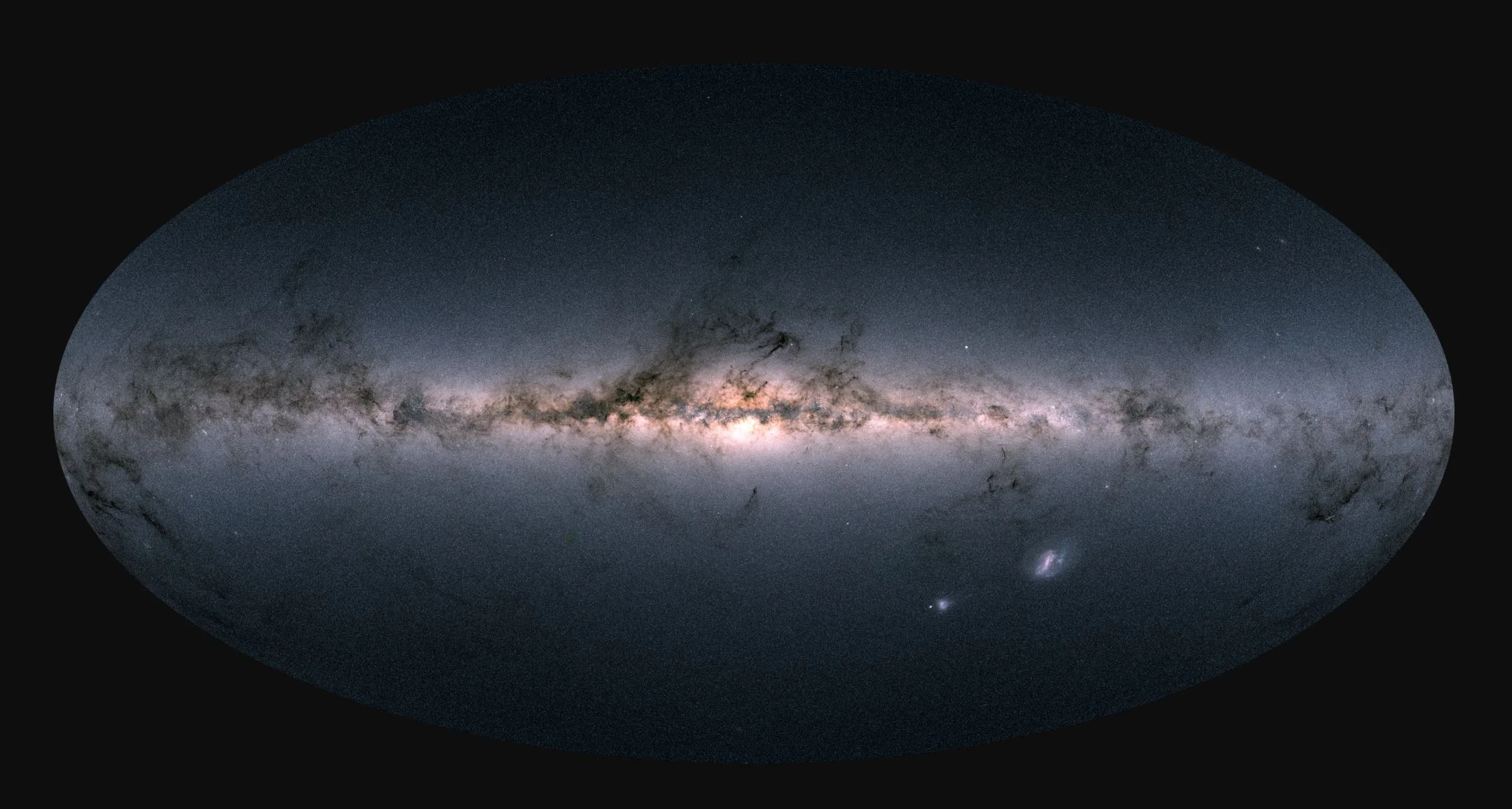
Gaia mission releases map of more than a billion stars – here’s what it can teach us
Most of us have looked up at the night sky and wondered how far away the stars are or in what direction they are moving. The truth is, scientists don’t know the exact positions or velocities of the vast majority of the stars in the Milky Way. But now a new tranche of data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia satellite, aiming to map stars in our galaxy in unprecedented detail, has come in to shed light on the issue.
How many planets is TESS going to find?
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), NASA’s latest exoplanet-hunting space telescope, was launched into space on Wednesday, April 18th, 2018. As the name suggests, this telescope will use the Transit Method to detect terrestrial-mass planets (i.e. rocky) orbiting distant stars. Alongside other next-generation telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), TESS will effectively pick up where telescopes like Hubble and Kepler left off.
Stellar Dust Survey Paves Way for Exoplanet Missions
Veils of dust wrapped around distant stars could make it difficult for scientists to find potentially habitable planets in those star systems. The Hunt for Observable Signatures of Terrestrial Systems, or HOSTS, survey was tasked with learning more about the effect of dust on the search for new worlds. The goal is to help guide the design of future planet-hunting missions. In a new paper published in the Astrophysical Journal, HOSTS scientists report on the survey’s initial findings.
Two Hubble Views of the Same Stellar Nursery
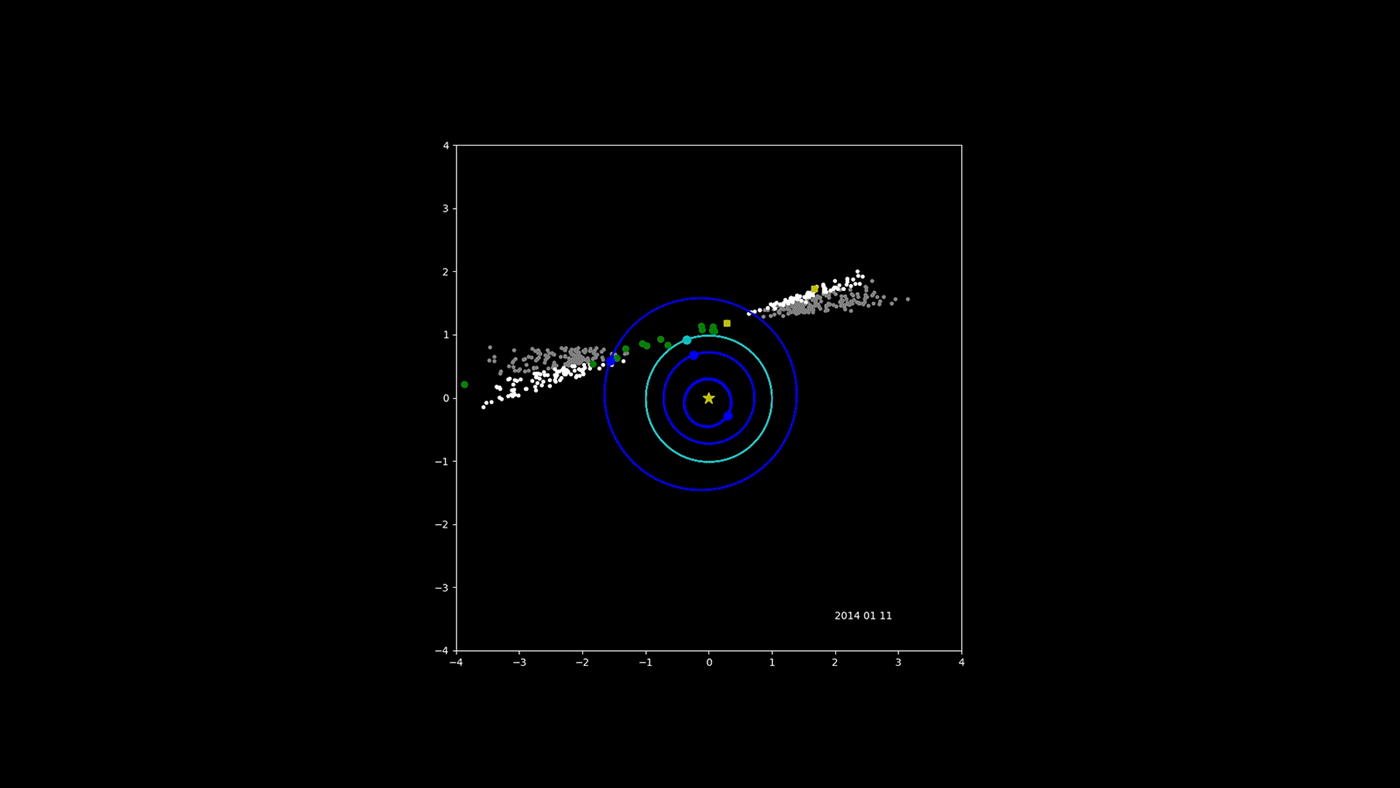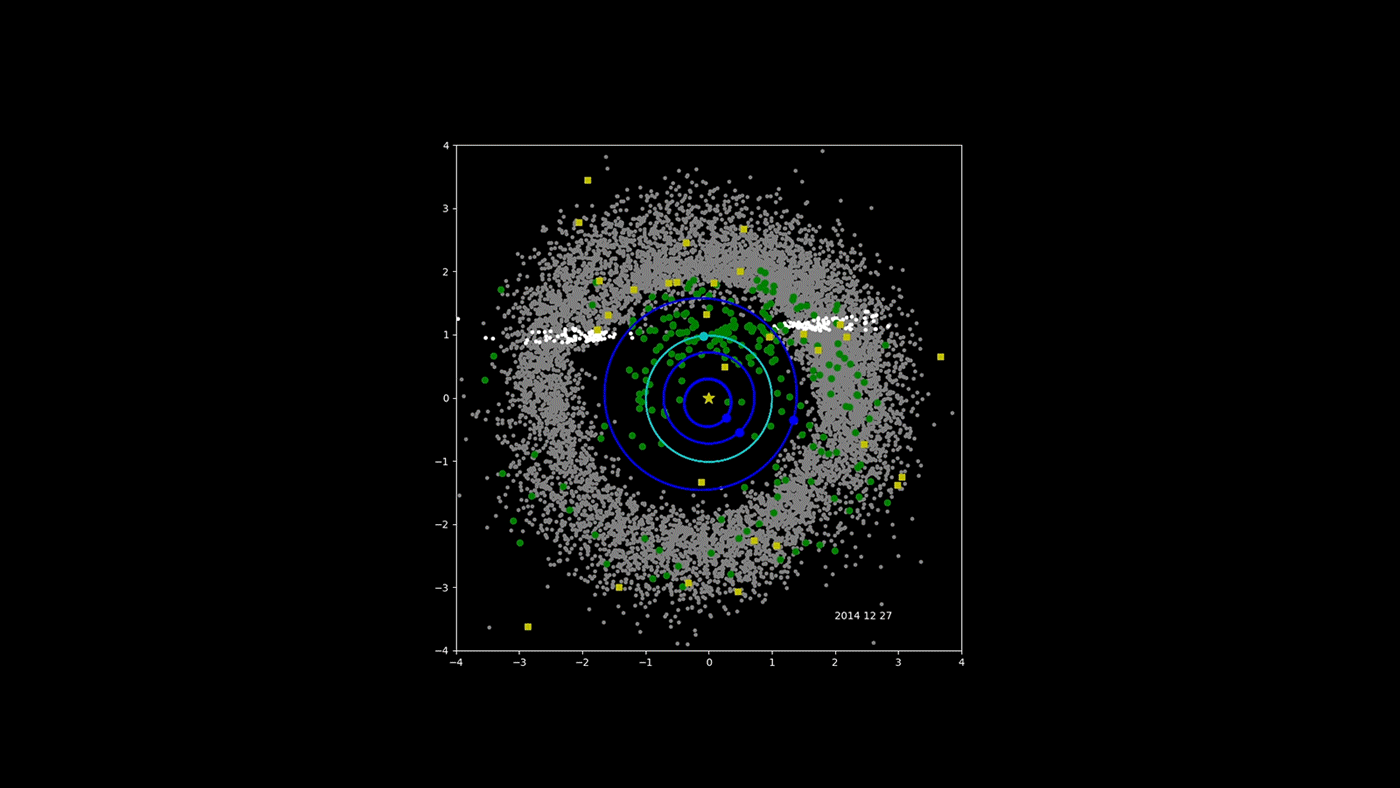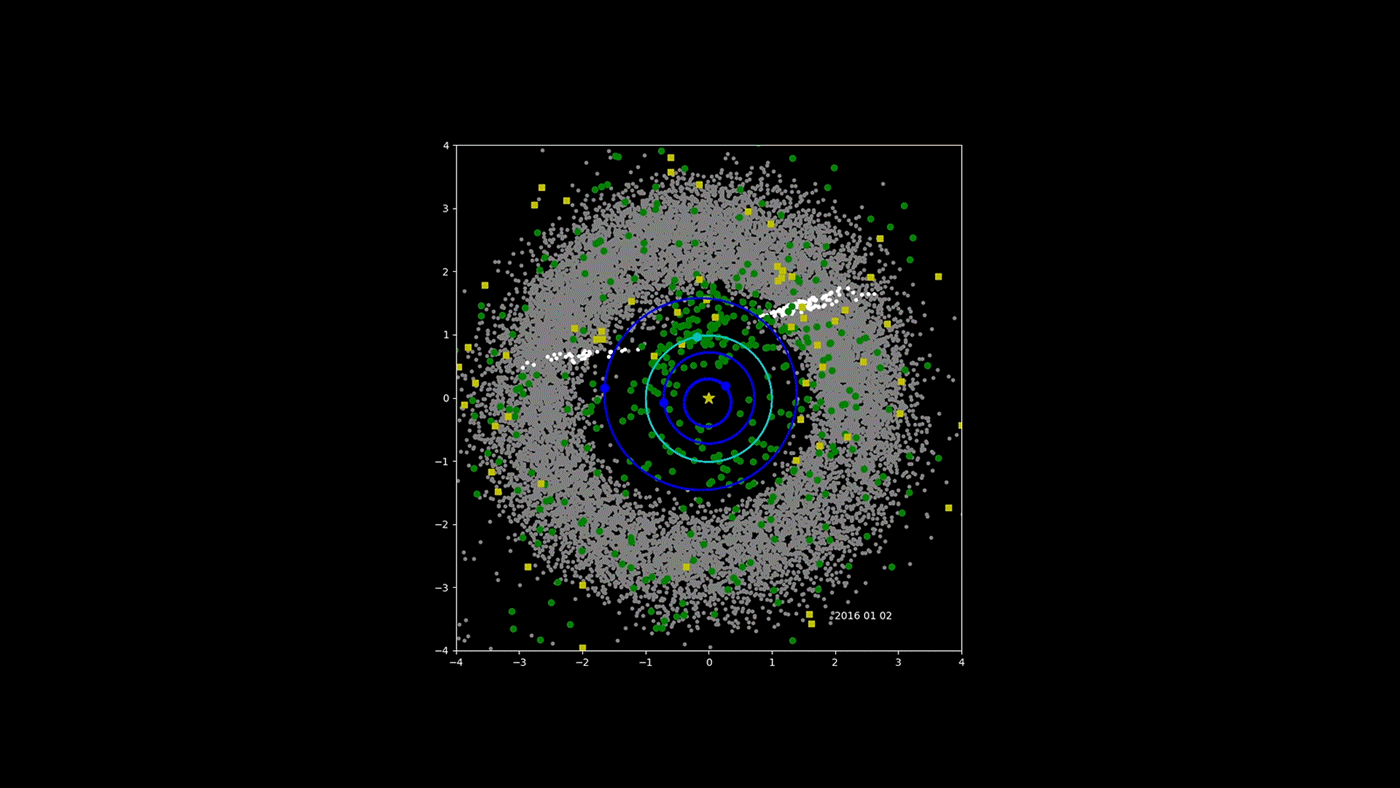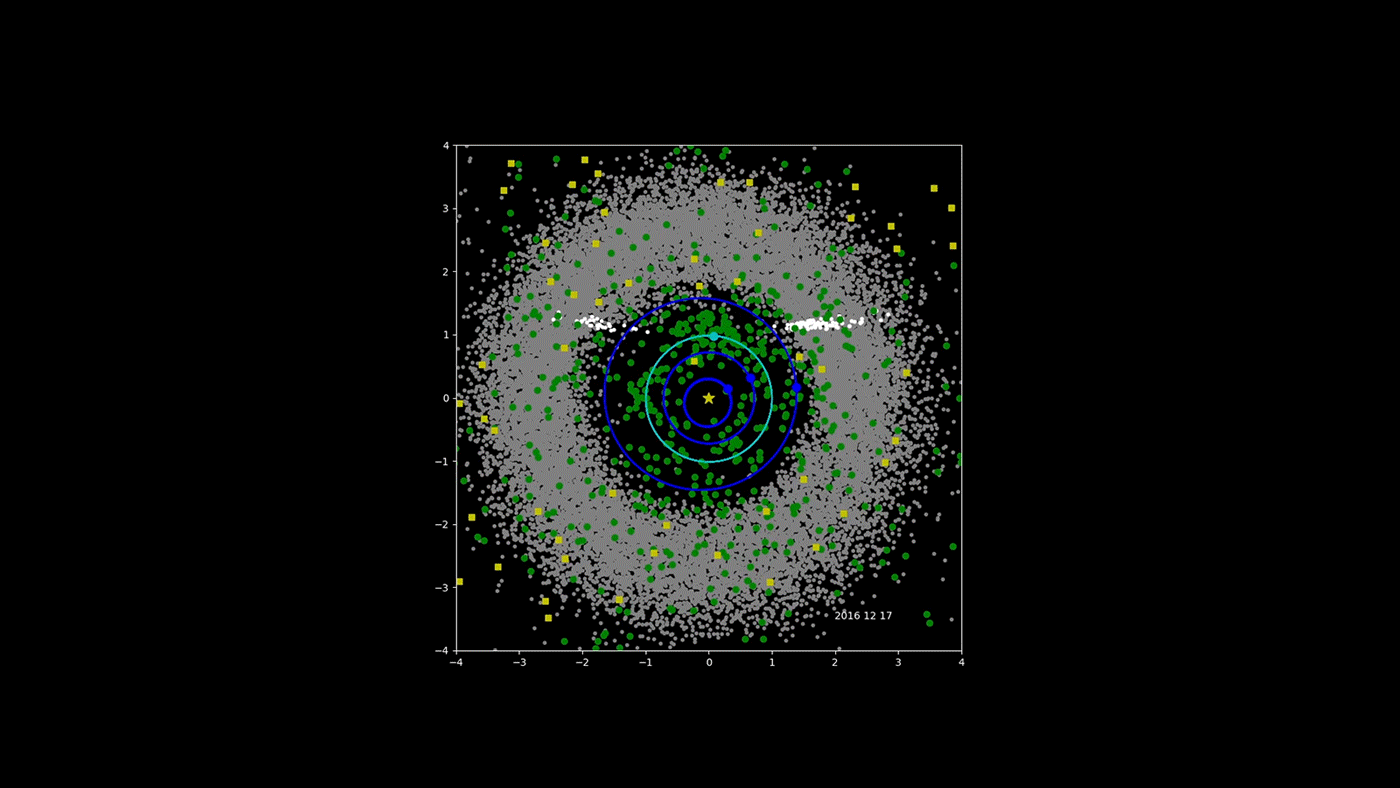
NASA's NEOWISE Asteroid-Hunter Spacecraft -- Four Years of Data
NASA's Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) mission has released its fourth year of survey data. Since the mission was restarted in December 2013, after a period of hibernation, the asteroid- and comet-hunter has completely scanned the skies nearly eight times and has observed and characterized 29,375 objects in four years of operations. This total includes 788 near-Earth objects and 136 comets since the mission restart.
The challenges of an alien spaceflight program: escaping super earths and red dwarf stars
Since the beginning of the Space Age, humans have relied on chemical rockets to get into space. While this method is certainly effective, it is also very expensive and requires a considerable amount of resources. As we look to more efficient means of getting out into space, one has to wonder if similarly-advanced species on other planets (where conditions would be different) would rely on similar methods.
Mysterious red spots on Mercury get names – but what are they?
Mercury is the closest planet to the sun, but far from being a dull cinder of a world, it has instead turned out to be a real eye opener for geologists. Among the revelations by NASA’s MESSENGER probe, which first flew past Mercury in 2008 and orbited it between 2011 and 2015, is the discovery of a hundred or so bright red spots scattered across the globe. Now they are at last being named.
Did you know the earth has a second magnetic field? Its oceans
Earth’s magnetic field is one of the most mysterious features of our planet. It is also essential to life as we know it, ensuring that our atmosphere is not stripped away by solar wind and shielding life on Earth from harmful radiation. For some time, scientists have theorized that it is the result of a dynamo action in our core, where the liquid outer core revolves around the solid inner core and in the opposite direction of the Earth’s rotation.
What in the World is an ‘Exoplanet?’
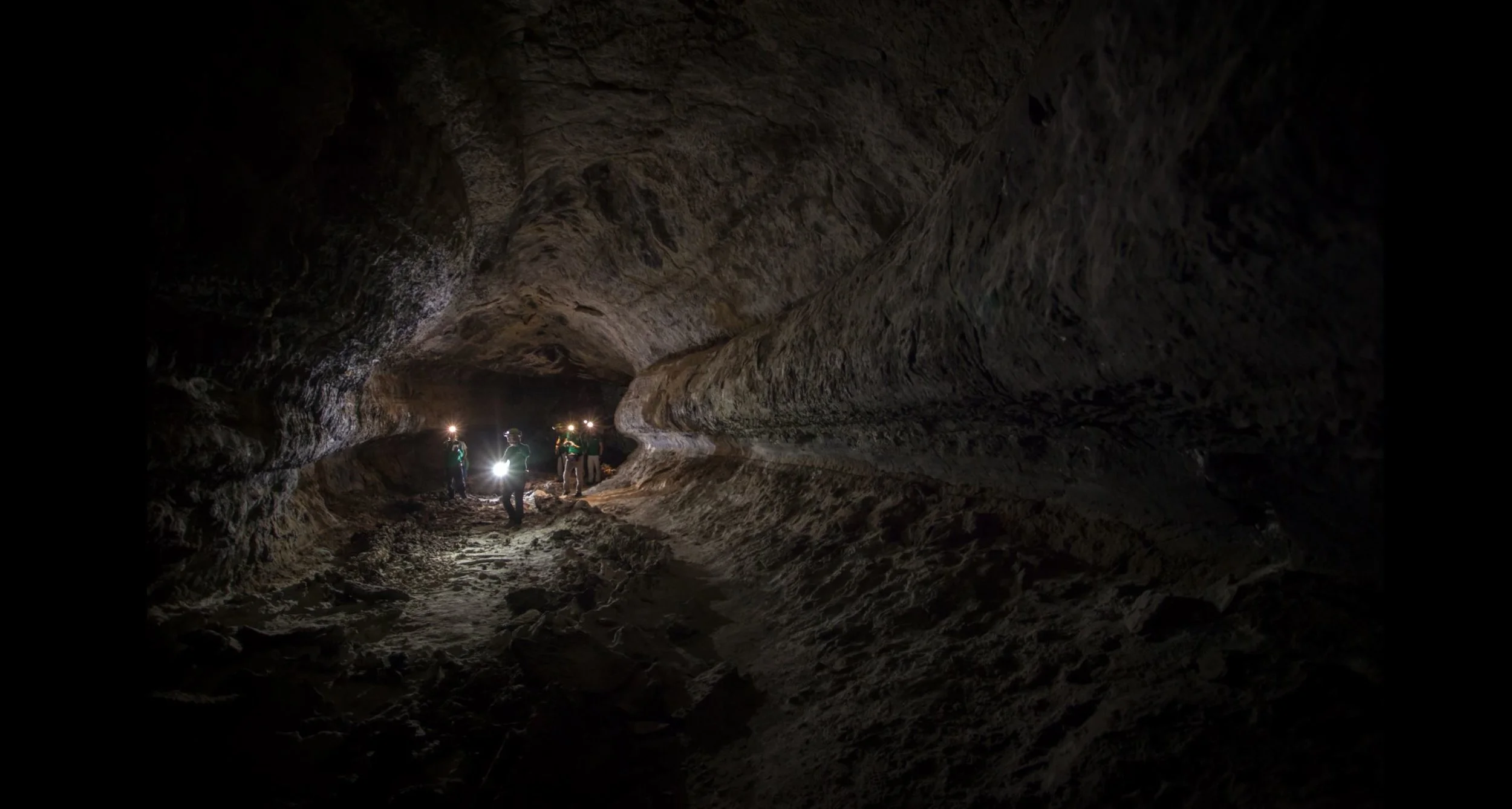
Living underground on other worlds. Exploring lava tubes
Io afire with volcanoes under Juno’s gaze
Volcanic activity on Io was discovered by Voyager 1 imaging scientist Linda Morabito. She spotted a little bump on Io’s limb while analyzing a Voyager image and thought at first it was an undiscovered moon. Moments later she realized that wasn’t possible — it would have been seen by earthbound telescopes long ago. Morabito and the Voyager team soon came to realize they were seeing a volcanic plume rising 190 miles (300 km) off the surface of Io. It was the first time in history that an active volcano had been detected beyond the Earth.
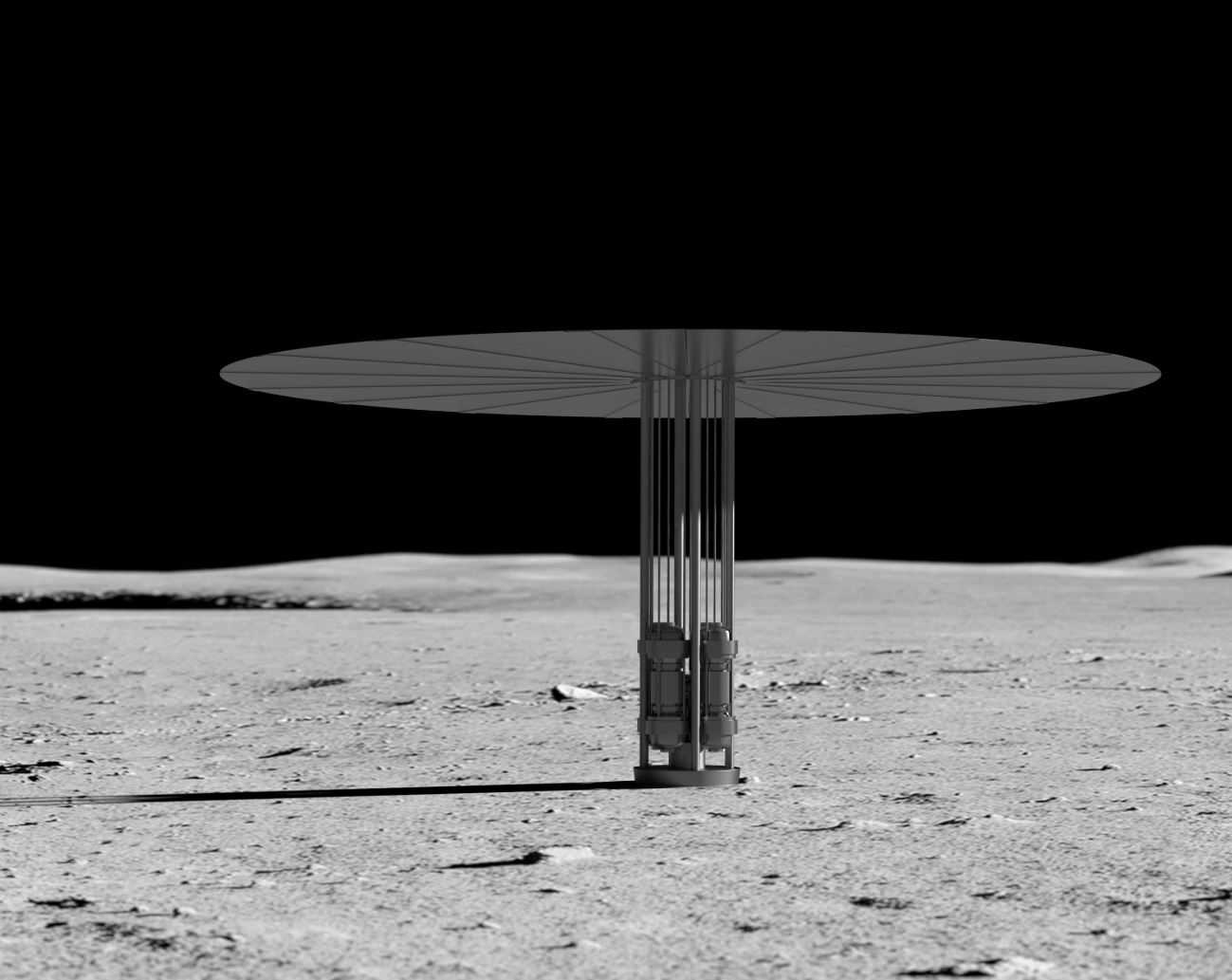
Mining the moon for rocket fuel to get us to Mars
Simulated View of a Newly Forming Planetary System with Rings and Gaps
When searching for extra-solar planets, astronomers most often rely on a number of indirect techniques. Of these, the Transit Method (aka. Transit Photometry) and the Radial Velocity Method(aka. Doppler Spectroscopy) are the two most effective and reliable (especially when used in combination). Unfortunately, direct imaging is rare since it is very difficult to spot a faint exoplanet amidst the glare of its host star.
Look up – it’s a satellite!
Could there be life in the cloud tops of Venus?
In the search for life beyond Earth, scientists have turned up some very interesting possibilities and clues. On Mars, there are currently eight functioning robotic missions on the surface of or in orbit investigating the possibility of past (and possibly present) microbial life. Multiple missions are also being planned to explore moons like Titan, Europa, and Enceladus for signs of methanogenic or extreme life.