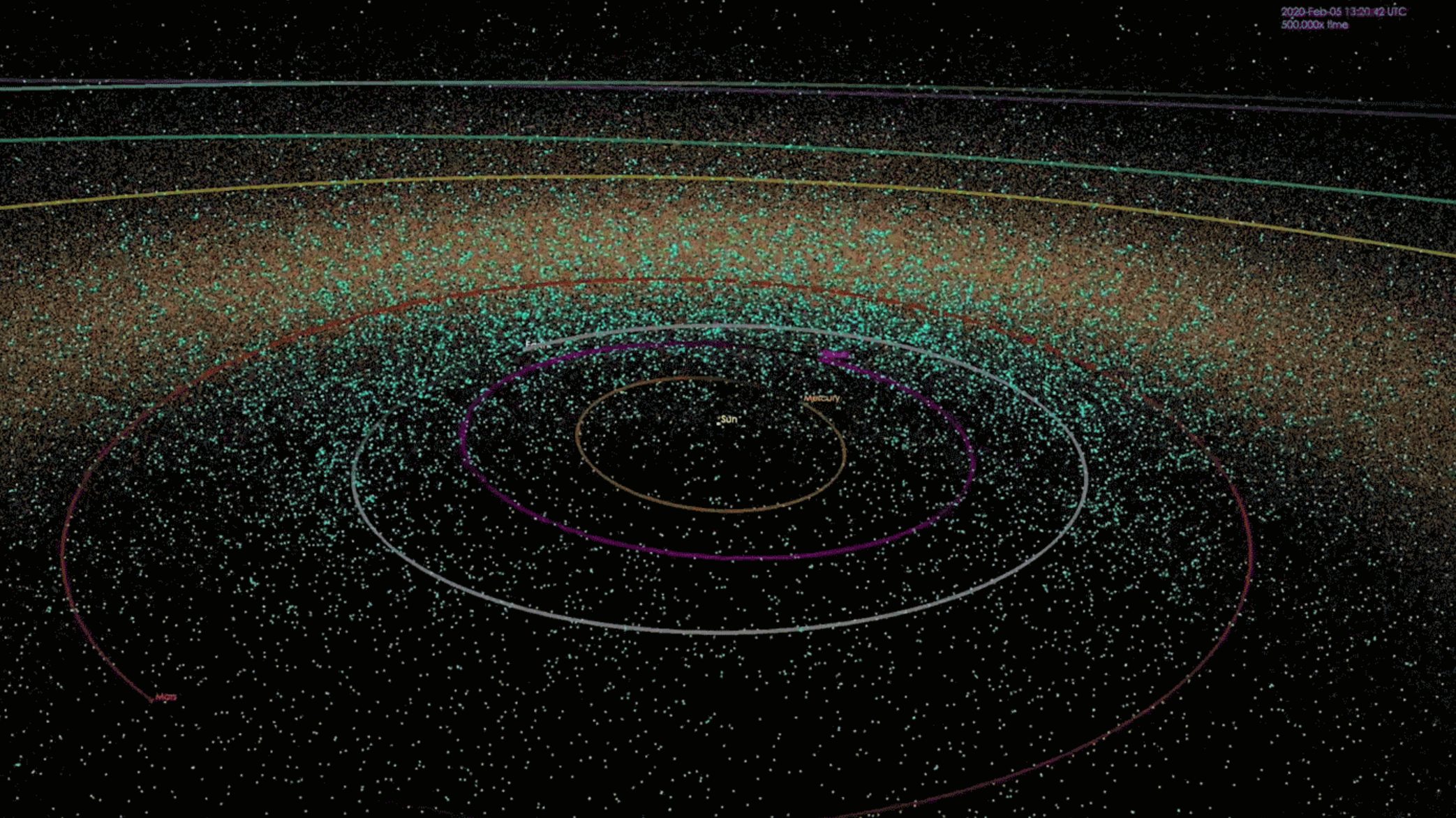
Are we alone in the universe? This question has been with us for thousands of years, but it is only now that science is on the cusp of providing a real answer. We now know of dozens of rocky planets orbiting stars other than our sun where, for all we know, life might exist. And soon, with the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, we will have the first chance to peer into the atmospheres of some of these worlds.
Space Station Experiment Reaches Ultracold Milestone
The International Space Station is officially home to the coolest experiment in space.
NASA's Cold Atom Laboratory (CAL) was installed in the station's U.S. science lab in late May and is now producing clouds of ultracold atoms known as Bose-Einstein condensates. These "BECs" reach temperatures just above absolute zero, the point at which atoms should theoretically stop moving entirely. This is the first time BECs have ever been produced in orbit.
How to grow crops on Mars if we are to live on the red planet
First Successful Test of Einstein’s General Relativity Near Supermassive Black Hole
Observations made with ESO’s Very Large Telescope have for the first time revealed the effects predicted by Einstein’s general relativity on the motion of a star passing through the extreme gravitational field near the supermassive black hole in the centre of the Milky Way. This long-sought result represents the climax of a 26-year-long observation campaign using ESO’s telescopes in Chile.
Discovered: a huge liquid water lake beneath the southern pole of Mars!
Life on Europa would be protected by just a few centimeters of ice
Ever since the Galileo probe provided compelling evidence for the existence of a global ocean beneath the surface of Europa in the 1990s, scientists have wondered when we might be able to send another mission to this icy moon and search for possible signs of life. Most of these mission concepts call for an orbiter or lander than will study Europa’s surface, searching the icy sheet for signs of biosignatures turned up from the interior.
Iceberg Towers Over Greenland Village
Twenty Years of Planetary Defense
NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies Enters Third Decade.
On March 11, 1998, asteroid astronomers around the world received an ominous message: new observational data on the recently discovered asteroid 1997 XF11 suggested there was a chance that the half-mile-wide (nearly one kilometer) object could hit Earth in 2028.
Who owns the moon? A space lawyer answers
Most likely, this is the best-known picture of a flag ever taken: Buzz Aldrin standing next to the first U.S. flag planted on the Moon. For those who knew their world history, it also rang some alarm bells. Only less than a century ago, back on Earth, planting a national flag in another part of the world still amounted to claiming that territory for the fatherland. Did the Stars and Stripes on the moon signify the establishment of an American colony?
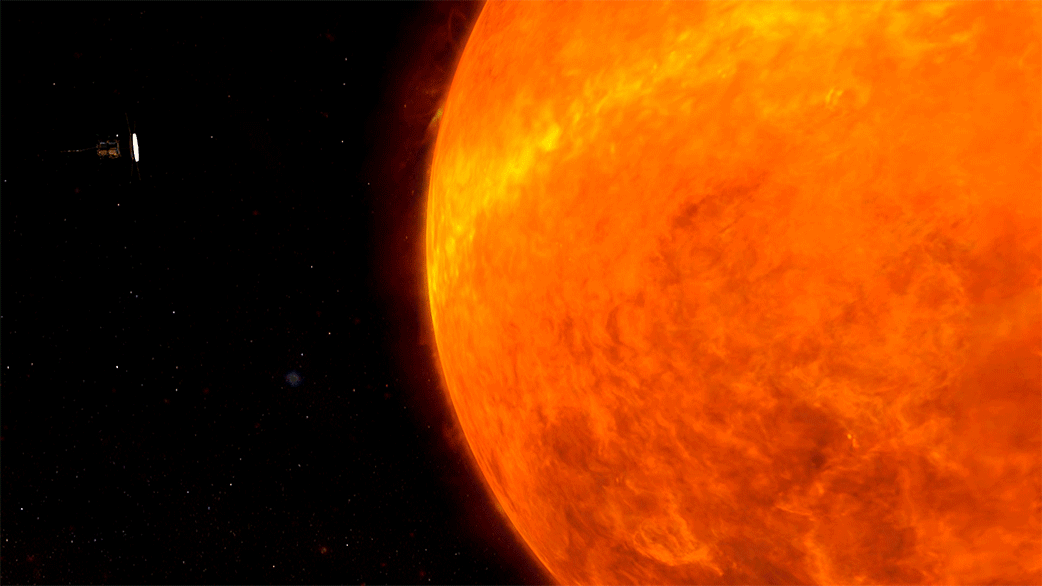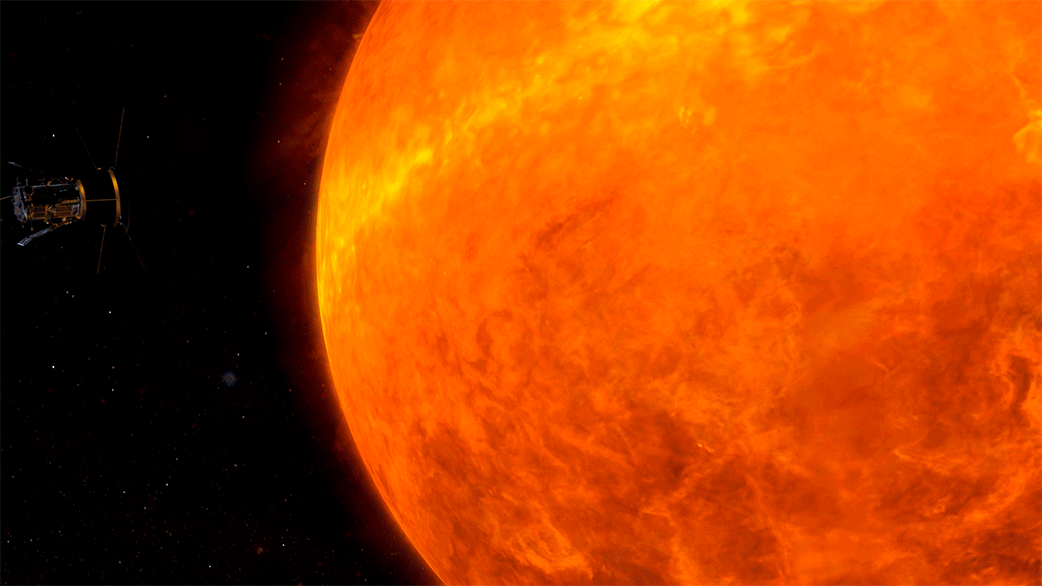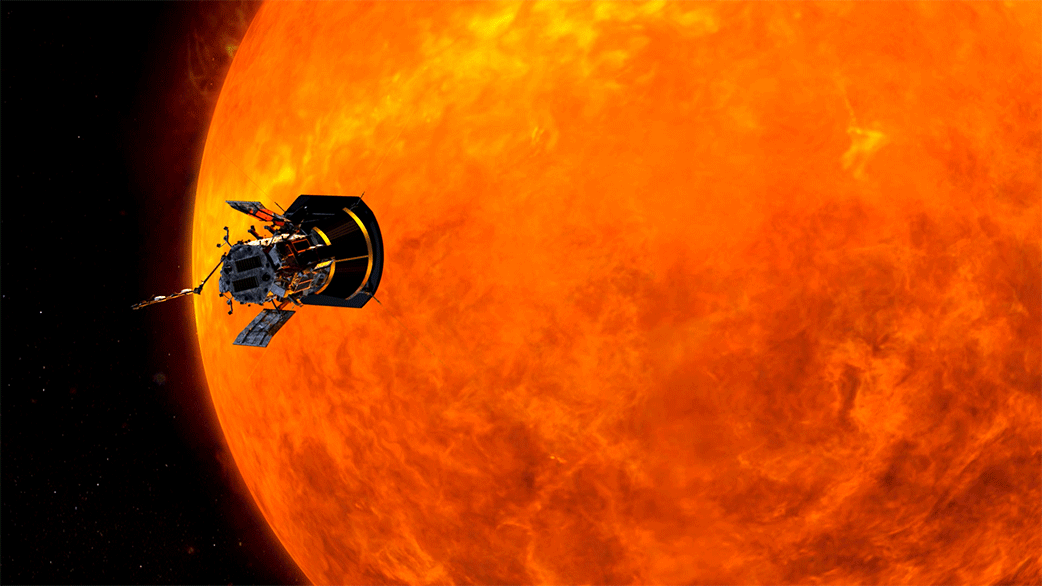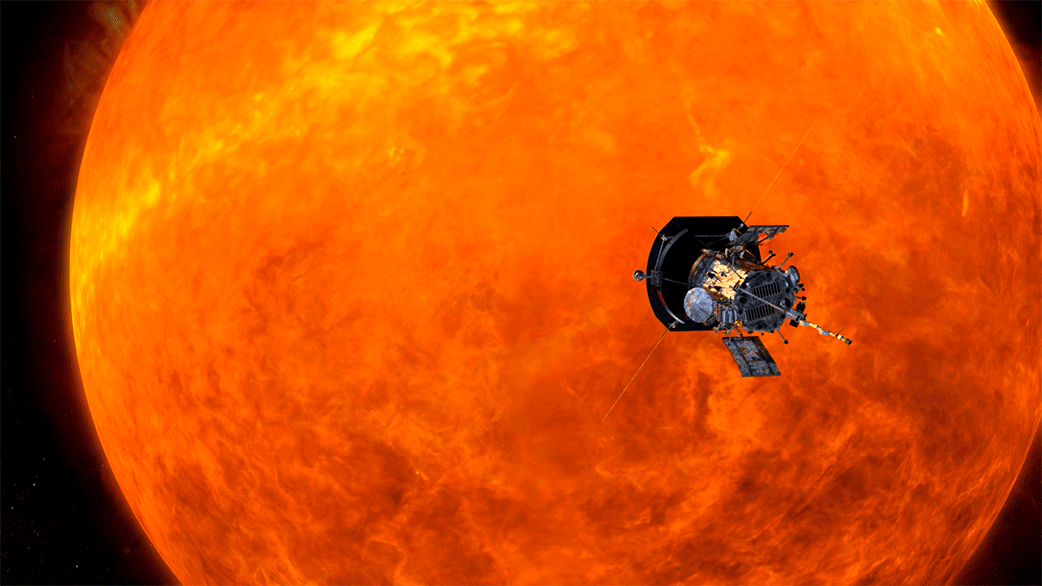
Traveling to the Sun: Why Won’t Parker Solar Probe Melt?
High-Altitude Jovian Clouds
Nasa’s James Webb Space Telescope will inspect the atmospheres of distant gas giants
The James Webb Space Telescope is like the party of the century that keeps getting postponed. Due to its sheer complexity and some anomalous readings that were detected during vibration testing, the launch date of this telescope has been pushed back many times – it is currently expected to launch sometime in 2021. But for obvious reasons, NASA remains committed to seeing this mission through.
New VLT Adaptive Optics Generarte Super-Crisp Images of Neptune Showing How Far Our Telescopes Have Come
ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) has achieved first light with a new adaptive optics mode called laser tomography — and has captured remarkably sharp test images of the planet Neptune, star clusters and other objects. The pioneering MUSE instrument in Narrow-Field Mode, working with the GALACSI adaptive optics module, can now use this new technique to correct for turbulence at different altitudes in the atmosphere. It is now possible to capture images from the ground at visible wavelengths that are sharper than those from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. The combination of exquisite image sharpness and the spectroscopic capabilities of MUSE will enable astronomers to study the properties of astronomical objects in much greater detail than was possible before.
NASA simulation shows how Europa’s “fossil ocean” rises to the surface over time
In the 1970s, the Jupiter system was explored by a succession of robotic missions, beginning with the Pioneer 10 and 11 missions in 1972/73 and the Voyager 1 and 2 missions in 1979. In addition to other scientific objectives, these missions also captured images of Europa’s icy surface features, which gave rise to the theory that the moon had an interior ocean that could possibly harbor life.
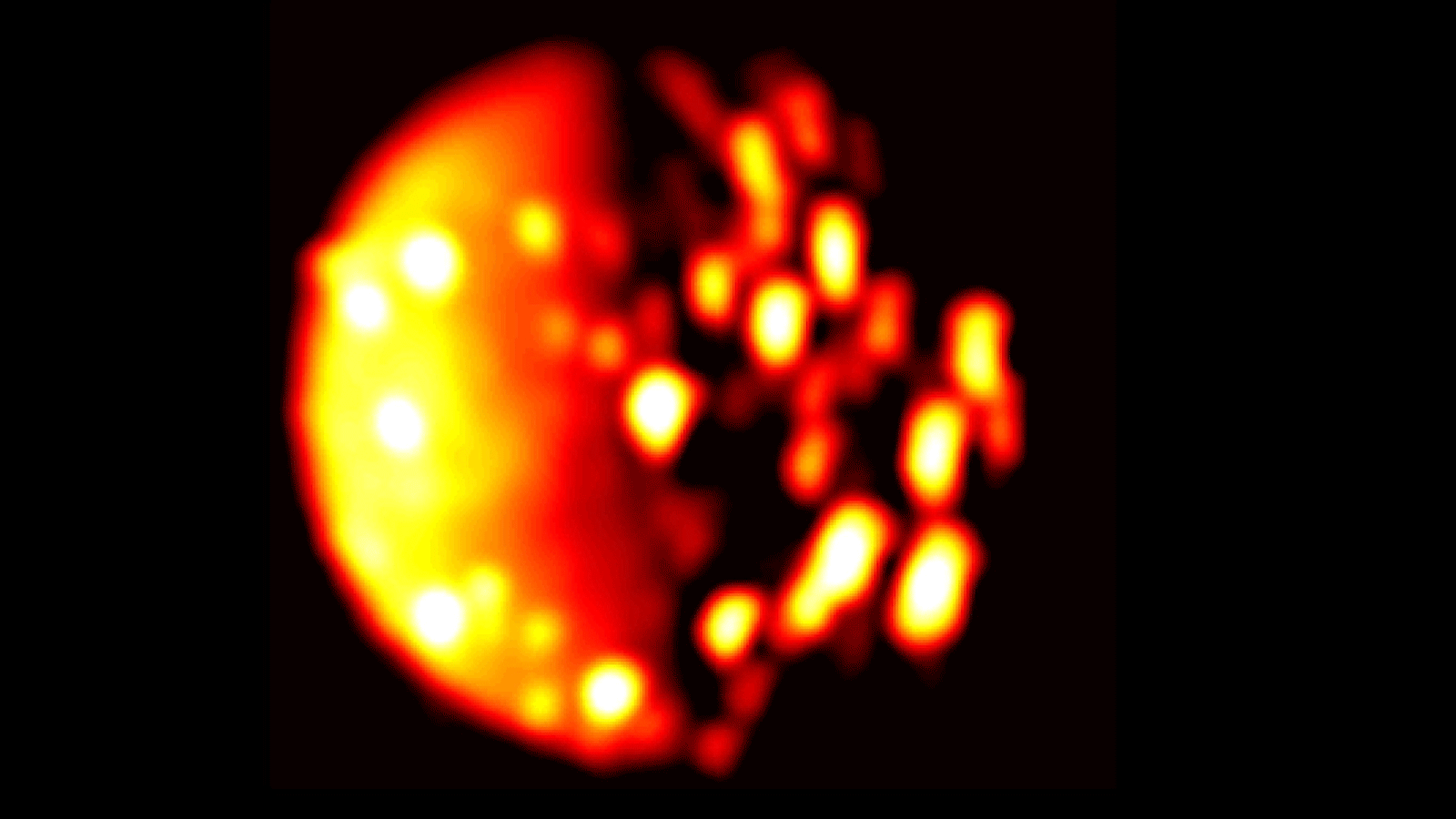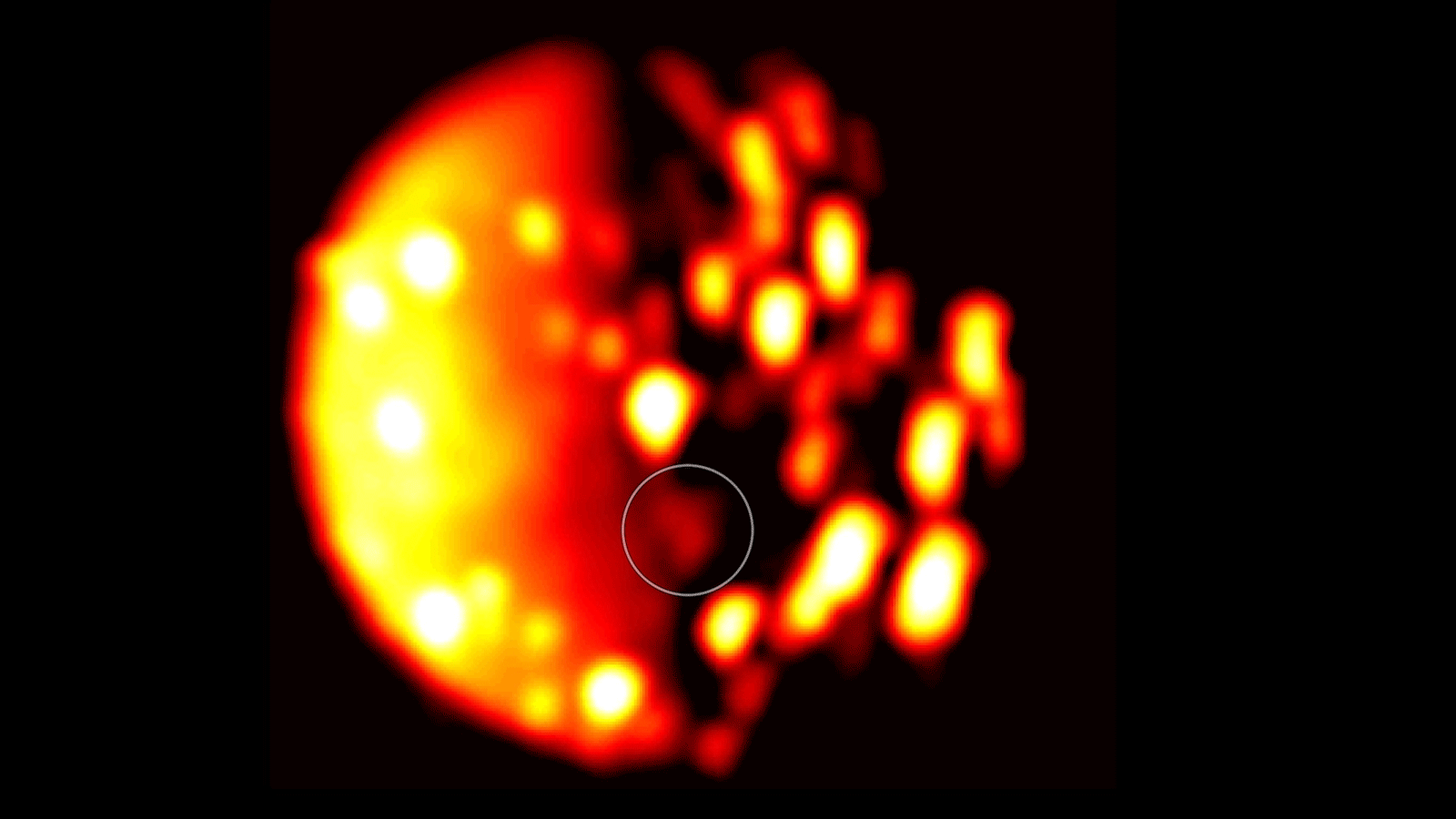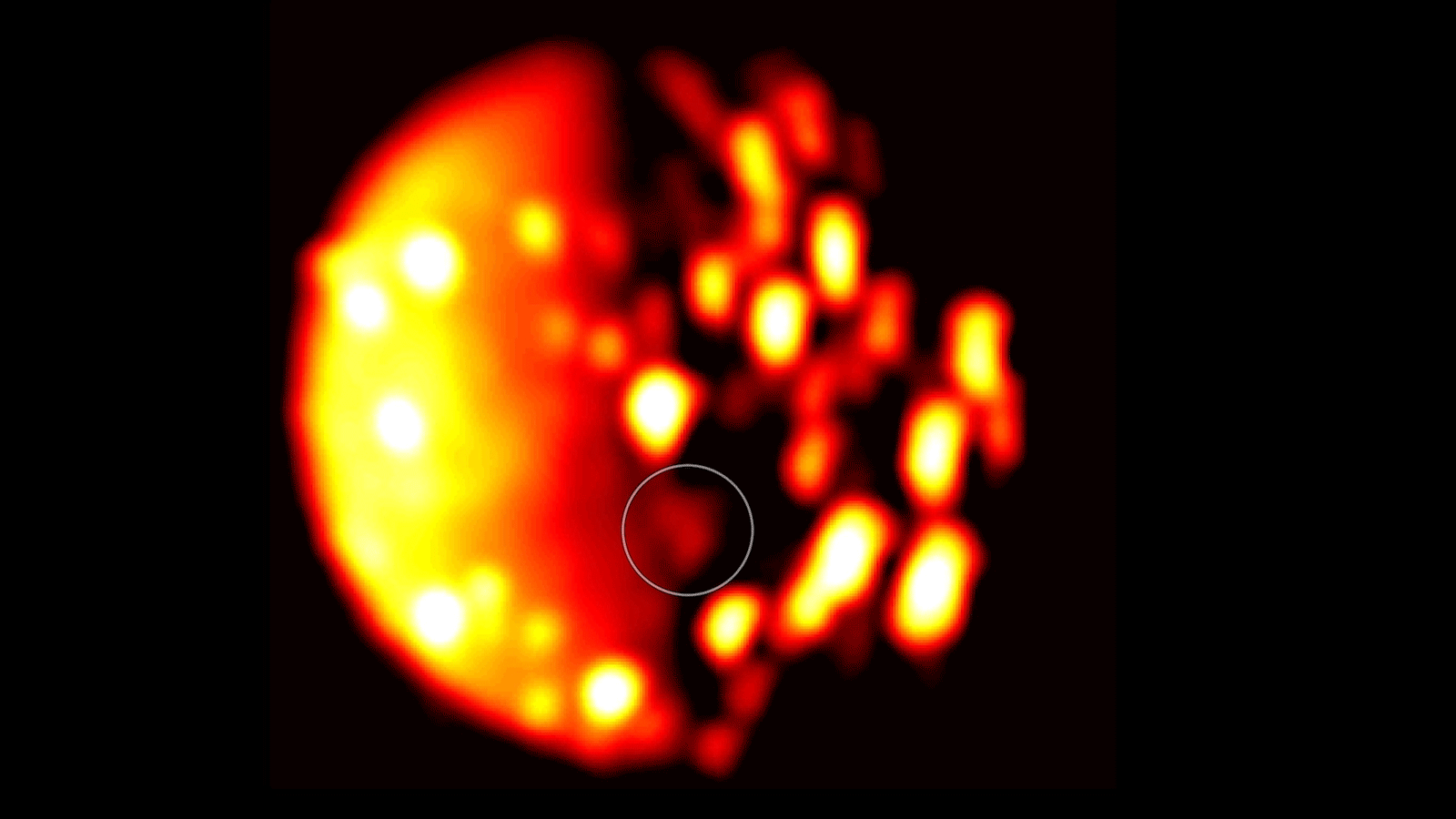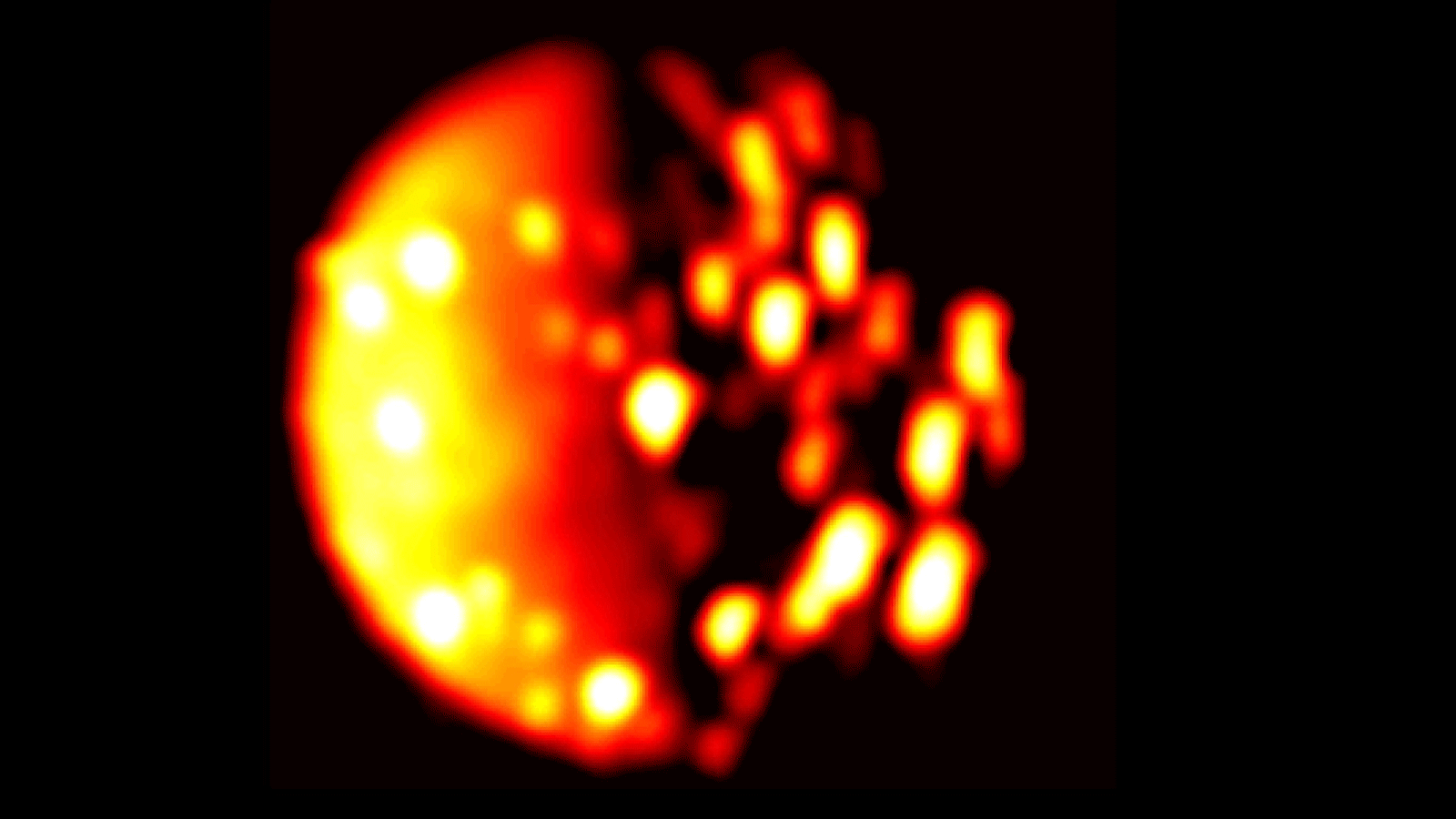
NASA Juno Data Indicate Another Possible Volcano on Jupiter Moon Io
Data collected by NASA’s Juno spacecraft using its Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument point to a new heat source close to the south pole of Io that could indicate a previously undiscovered volcano on the small moon of Jupiter. The infrared data were collected on Dec. 16, 2017, when Juno was about 290,000 miles (470,000 kilometers) away from the moon.
New insights into what might have smashed Uranus over onto its side
The gas/ice giant Uranus has long been a source of mystery to astronomers. In addition to presenting some thermal anomalies and a magnetic field that is off-center, the planet is also unique in that it is the only one in the Solar System to rotate on its side. With an axial tilt of 98°, the planet experiences radical seasons and a day-night cycle at the poles where a single day and night last 42 years each.
Instead of building single monster scopes like james webb, what about swarms of space telescopes working together?
In the coming decade, a number of next-generation instruments will take to space and begin observing the Universe. These will include the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), which is likely to be followed by concepts like the Large Ultraviolet/Optical/Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR), the Origins Space Telescope (OST), the Habitable Exoplanet Imager (HabEx) and the Lynx X-ray Surveyor.
Juno data shows that some of jupiter’s moons are leaving “footprints” in its aurora
Since it arrived in orbit around Jupiter in July of 2016, the Junomission has been sending back vital information about the gas giant’s atmosphere, magnetic field and weather patterns. With every passing orbit – known as perijoves, which take place every 53 days – the probe has revealed things about Jupiter that scientists will rely on to learn more about its formation and evolution.