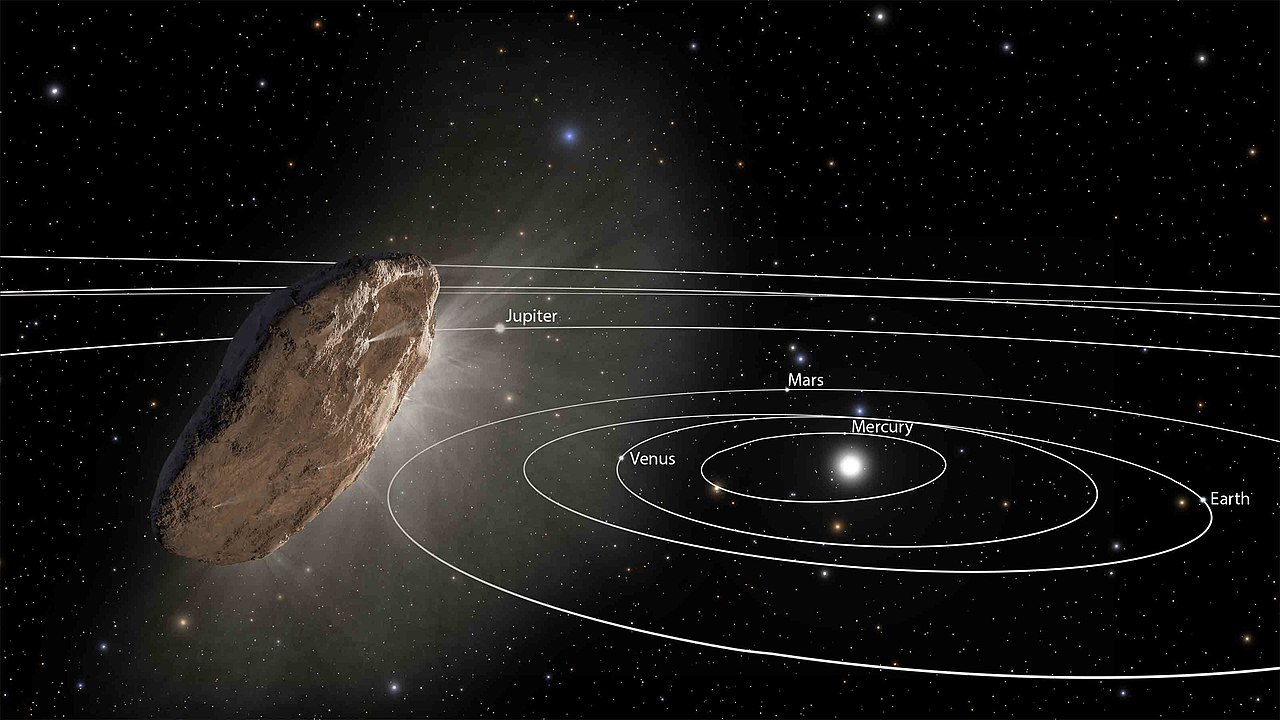
On October 19th, 2017, the Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System-1 (Pan-STARRS-1) in Hawaii announced the first-ever detection of an interstellar asteroid – I/2017 U1 (aka. ‘Oumuamua). Since that time, multiple studies have been conducted to determine the asteroid’s origin, what it encountered in interstellar space, its true nature (is it a comet or an asteroid?), and whether or not it is an alien spacecraft (it’s not).
Our Sun: Two Wavelengths, Two Different Images
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory views our Sun in ten different wavelengths because each wavelength reveals different solar features. This Sept. 21, 2018, view of the Sun uses two selected images taken at virtually the same time but in different wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light. The red-tinted image, which captures material not far above the Sun's surface, is especially good for revealing details along the edge of the Sun, like the small prominence at the ten o'clock position. The brown-tinted image clearly shows two large coronal holes (darker areas) as well as some faint magnetic field lines and hints of solar activity (lighter areas), neither of which are apparent in the red image. This activity is occurring somewhat higher in the Sun's corona. In a way it is like peeling away the layers of an onion, a little at a time.
Inside the Crust of Neutron Stars, There’s Nuclear Pasta; the Hardest Known Substance in the Universe
Ever since they were first discovered in the 1930s, scientists have puzzled over the mystery that is neutron stars. These stars, which are the result of a supernova explosion, are the smallest and densest stars in the Universe. While they typically have a radius of about 10 km (6.2 mi) – about 1.437 x 10-5 times that of the Sun – they also average between 1.4 and 2.16 Solar masses.
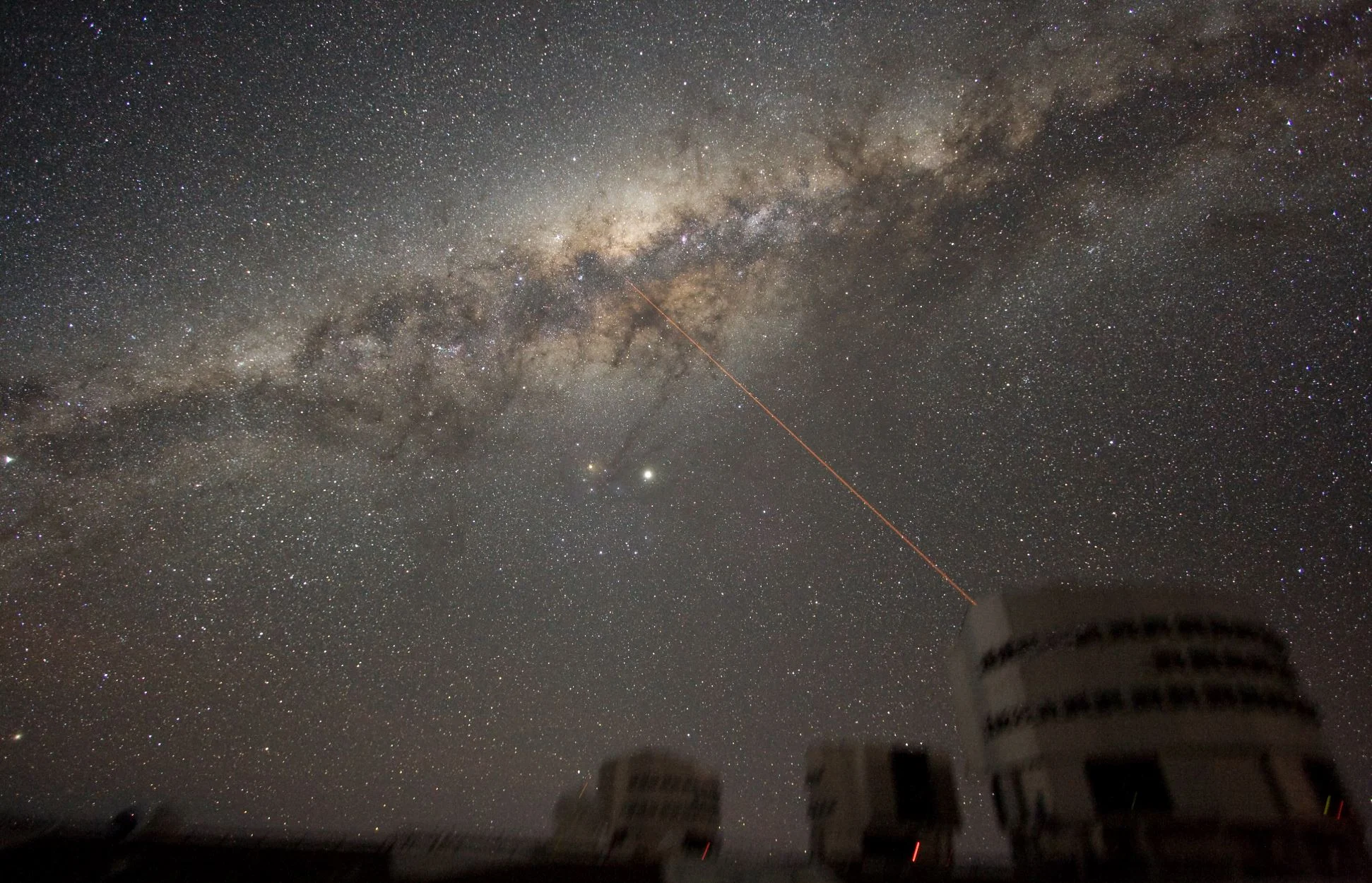
Narrowing Down the Mass of the Milky Way
Since the birth of modern astronomy, scientists have sought to determine the full extent of the Milky Way galaxy and learn more about its structure, formation and evolution. At present, astronomers estimate that it is 100,000 to 180,000 light-years in diameter and consists of 100 to 400 billion stars – though some estimates say there could be as many as 1 trillion.
How to Know Once and For All if the Universe Began With a Bang or a Bounce
According to the Big Bang cosmological model, our Universe began 13.8 billion years ago when all the matter and energy in the cosmos began expanding. This period of “cosmic inflation” is believed to be what accounts for the large-scale structure of the Universe and why space and the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) appear to be largely uniform in all directions.
To Avoid Vision Problems in Space, Astronauts Will Need Some Kind of Artificial Gravity
Ever since astronauts began going to space for extended periods of time, it has been known that long-term exposure to zero-gravity or microgravity comes with its share of health effects. These include muscle atrophy and loss of bone density, but also extend to other areas of the body leading to diminished organ function, circulation, and even genetic changes.
NASA’s TESS Shares First Science Image in Hunt to Find New Worlds
NASA’s newest planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), is now providing valuable data to help scientists discover and study exciting new exoplanets, or planets beyond our solar system. Part of the data from TESS’ initial science orbit includes a detailed picture of the southern sky taken with all four of the spacecraft’s wide-field cameras. This “first light” science image captures a wealth of stars and other objects, including systems previously known to have exoplanets.
The Closest Planet Ever Discovered Outside the Solar System Could be Habitable With a Dayside Ocean
In of August of 2016, astronomers from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) confirmed the existence of an Earth-like planet around Proxima Centauri – the closest star to our Solar System. In addition, they confirmed that this planet (Proxima b) orbited within its star’s habitable zone. Since that time, multiple studies have been conducted to determine if Proxima b could in fact be habitable.
Hubble Uncovers Never-Before-Seen Features Around a Neutron Star
An unusual infrared light emission from a nearby neutron star detected by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope could indicate new features never before seen. One possibility is that there is a dusty disk surrounding the neutron star; another is that there is an energetic wind coming off the object and slamming into gas in interstellar space the neutron star is plowing through.
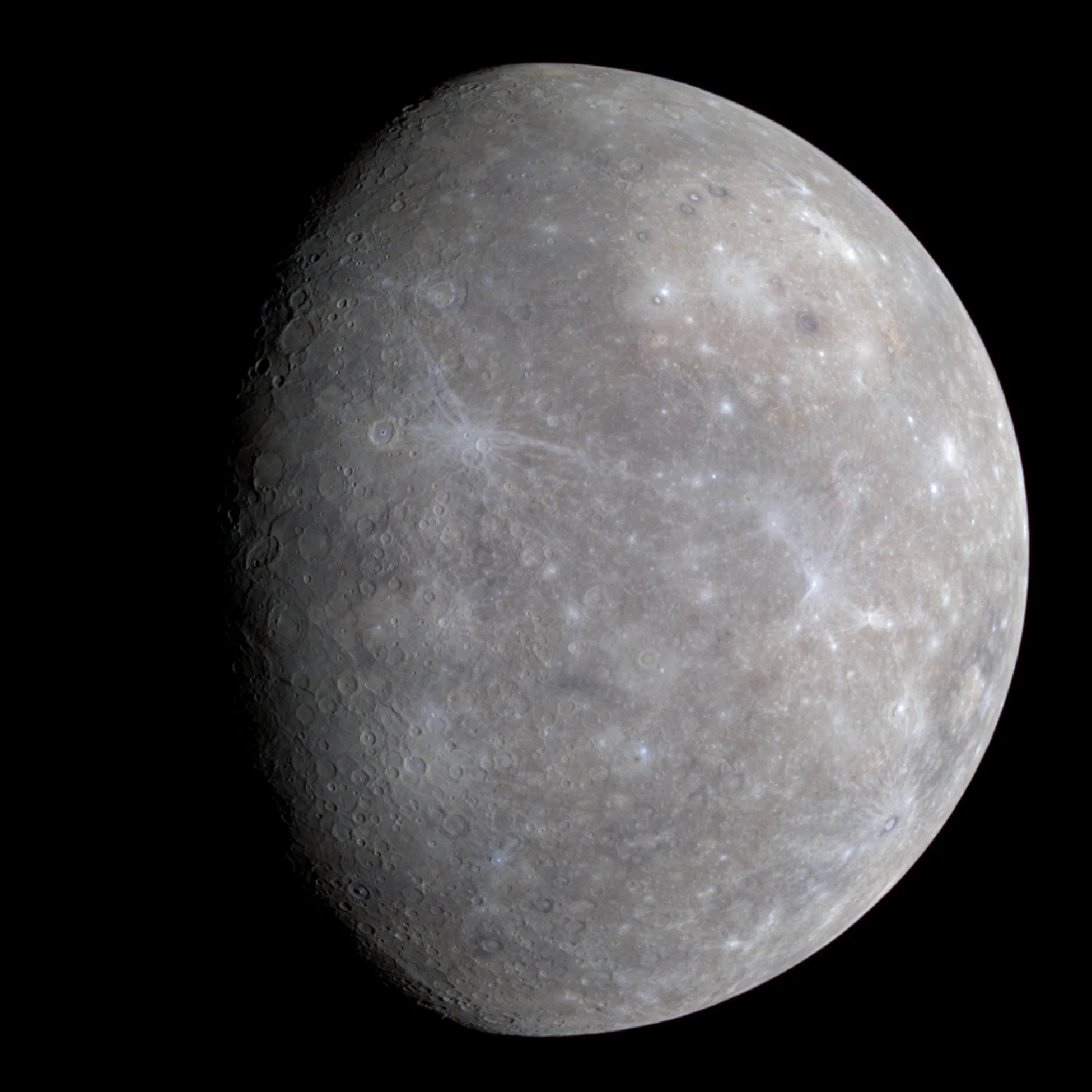
Forming Dense Metal Planets like Mercury is Probably Pretty Difficult and Rare in the Universe
The planet Mercury, the closet planet to our Sun, is something of an exercise in extremes. Its days last longer than its years and at any given time, its sun-facing side is scorching hot while its dark side is freezing cold. It is also one of the least understood planets in our Solar System. While it is a terrestrial (i.e. rocky) planet like Earth, Venus and Mars, it has a significantly higher iron-to-rock ratio than the others.
A Galactic Gem
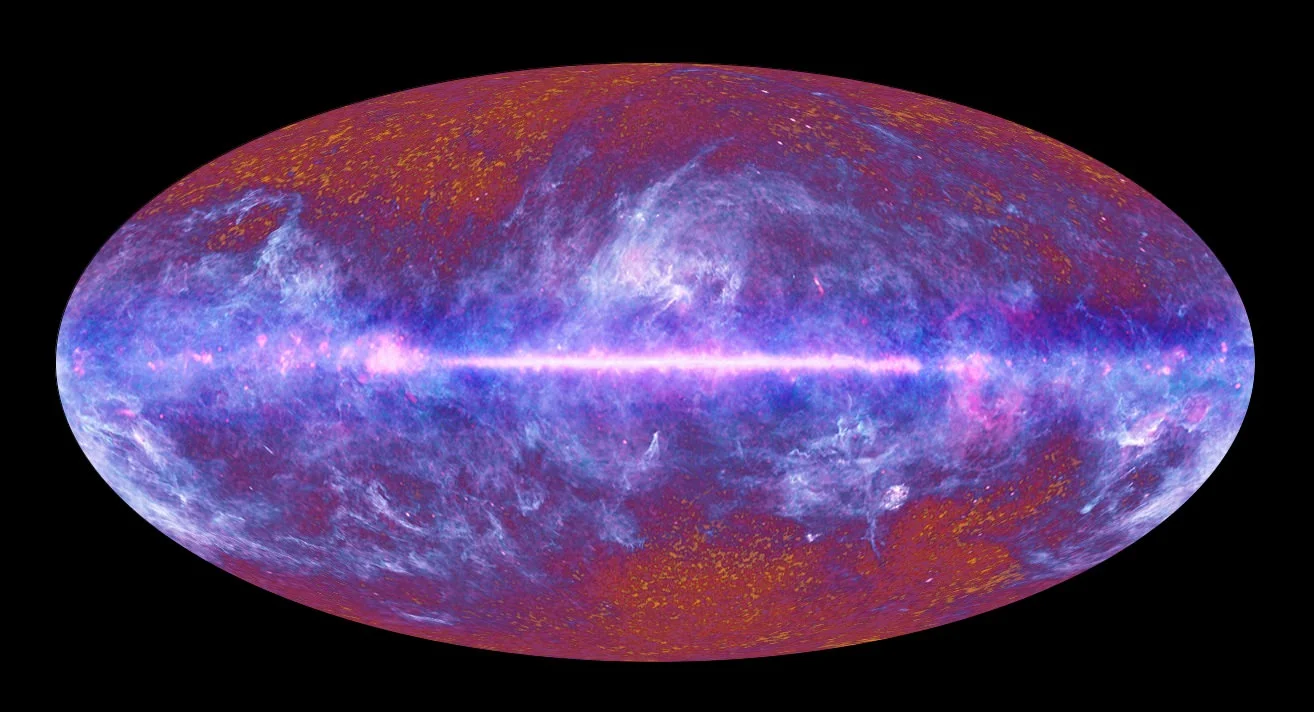
What is the Cosmic Microwave Background?
For thousands of years, human being have been contemplating the Universe and seeking to determine its true extent. And whereas ancient philosophers believed that the world consisted of a disk, a ziggurat or a cube surrounded by celestial oceans or some kind of ether, the development of modern astronomy opened their eyes to new frontiers. By the 20th century, scientists began to understand just how vast (and maybe even unending) the Universe really is.
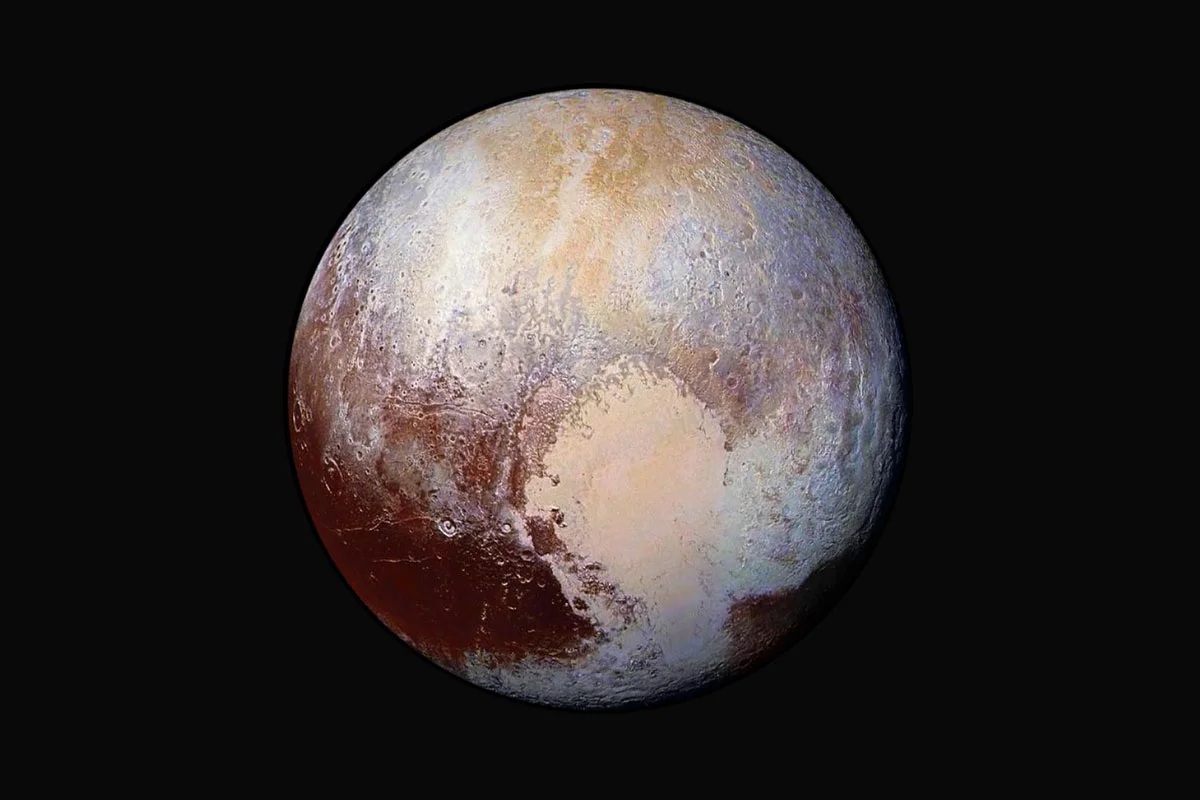
New Reasons why Pluto Should be Considered a Planet After All
In 2006, during their 26th General Assembly, the International Astronomic Union (IAU) passed a resolution to adopt a formal definition for the term “planet”. According to this definition, bodies that orbit the Sun, are spherical, do not orbit other bodies, and have cleared their orbits were designated planets. Pluto, and other such bodies that did not meet all of these requirements, would thereafter be designated as “dwarf planets”.
Europan Space Whales Anyone? Planets Covered by Deep Oceans Can Still Have Life on Them
In recent decades, astronomers have discovered many planets that they believe are “Earth-like” in nature, meaning that they appear to be terrestrial (i.e. rocky) and orbit their stars at the right distance to support the existence of liquid water on their surfaces. Unfortunately, recent research has indicated that many of these planets may in fact be “water worlds“, where water makes up a significant proportion of the planet’s mass.
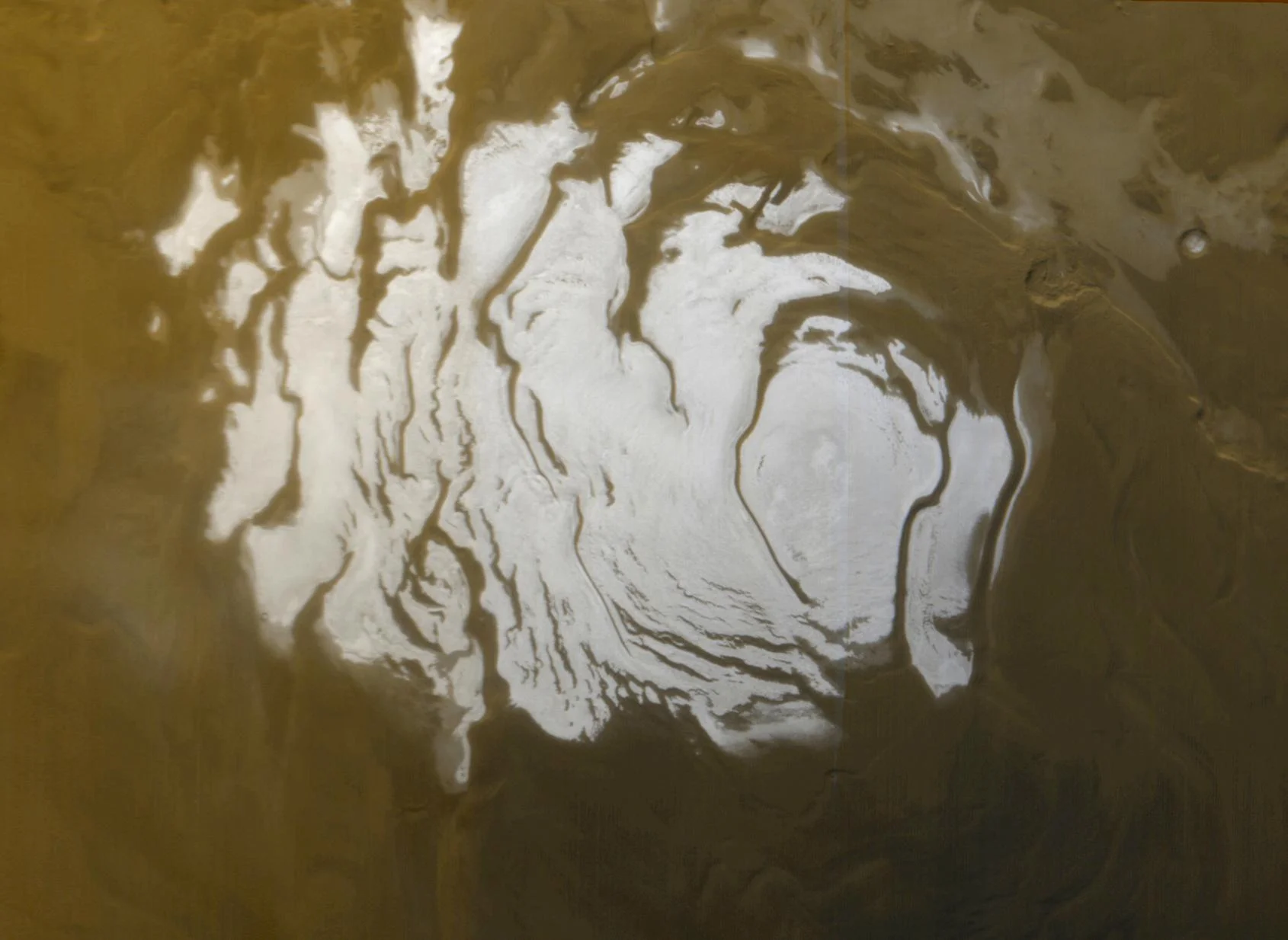
What on Earth could live in a salt water lake on Mars? An expert explains
Tantalizing new evidence has suggested that there may be a salty lake below a glacier on Mars. While brine at freezing temperatures does not sound like the most hospitable of environments, it is difficult to resist pondering whether organic life could survive – or even make some kind of living – there
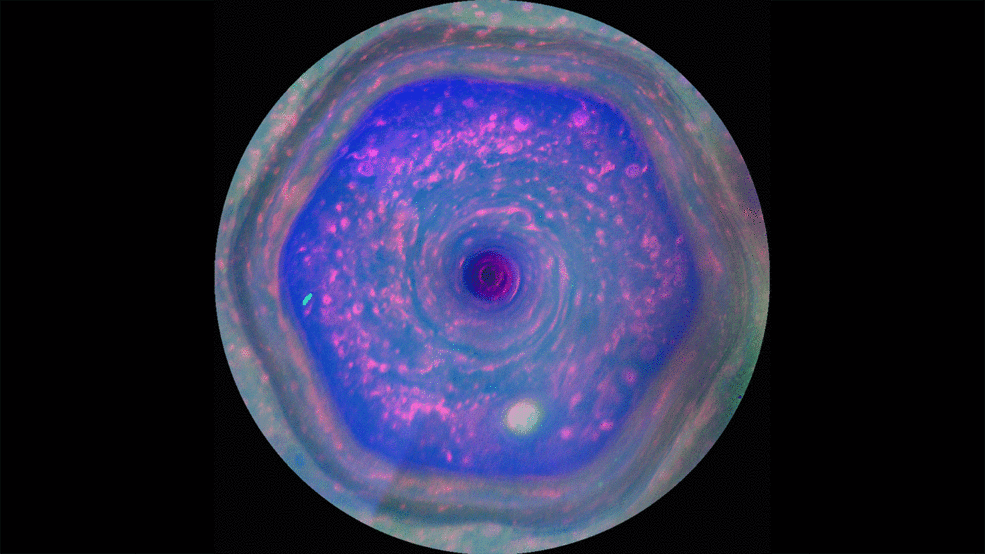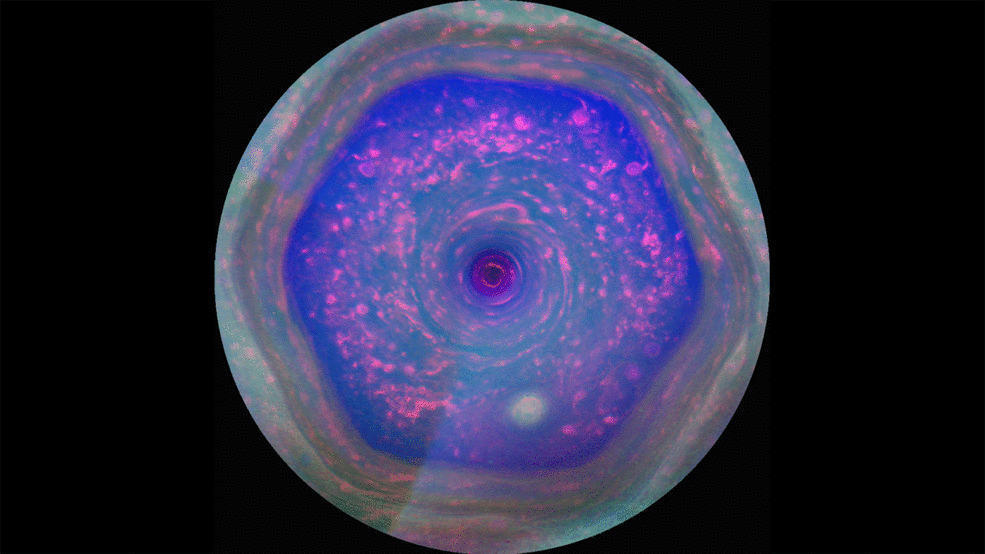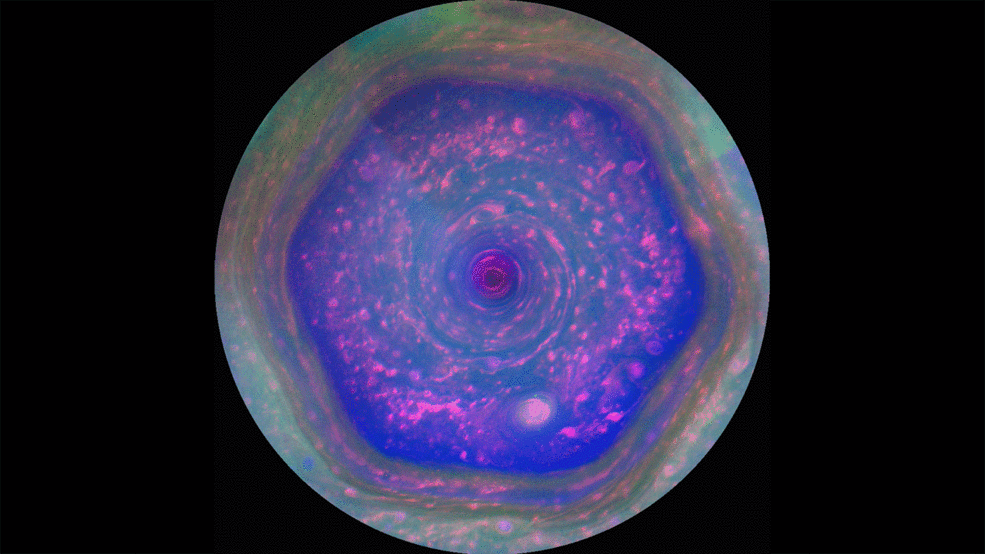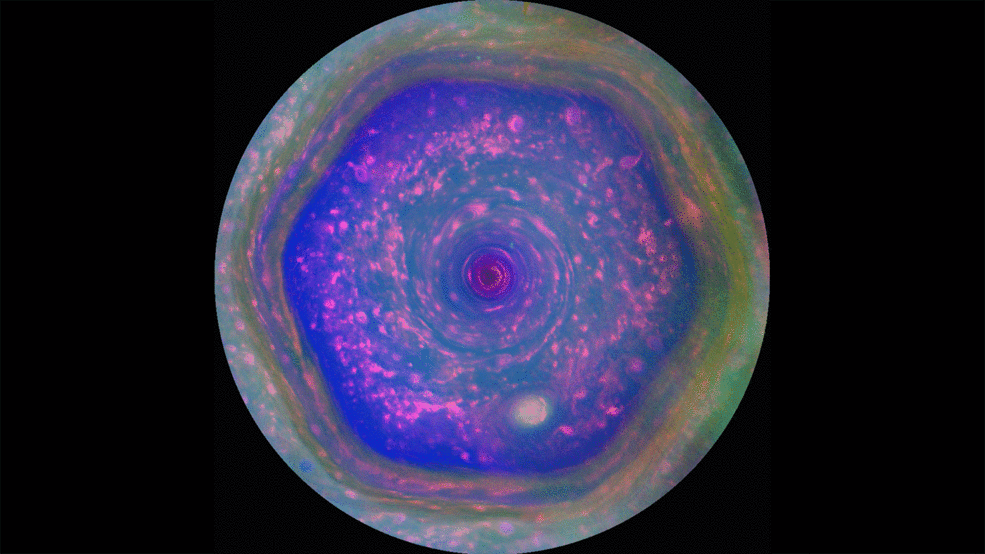
Saturn's Famous Hexagon May Tower Above the Clouds
How the next generation of ground-based super-telescopes will directly observe exoplanets
Over the past few decades, the number of extra-solar planets that have been detected and confirmed has grown exponentially. At present, the existence of 3,778 exoplanets have been confirmed in 2,818 planetary systems, with an additional 2,737 candidates awaiting confirmation. With this volume of planets available for study, the focus of exoplanet research has started to shift from detection towards characterization.
Hubble observes energetic lightshow at Saturn’s north pole
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space telescope have taken a series of spectacular images featuring the fluttering auroras at the north pole of Saturn. The observations were taken in ultraviolet light and the resulting images provide astronomers with the most comprehensive picture so far of Saturn’s northern aurora.
Telescope pierces into one of the biggest nebulae in the milky way to reveal its newly forming (and nearly dying) stars
Located about 7500 light-years from Earth, in the constellation of Carina, lies a star-forming region known as the Carina Nebula. This dynamic, evolving cloud of interstellar gas and dust measures about 300 light-years in diameter and is one of the Milky Way’s largest star-forming regions. It is also an exercise in contrasts, consisting of bright regions of gas illuminated by intense stellar radiation and dark pillars of dust that obscure star formation.
Building bricks on the moon from lunar dust
In the coming decades, many space agencies hope to conduct crewed missions to the Moon and even establish outposts there. In fact, between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), Roscosmos, and the Indian and Chinese space agencies, there are no shortages of plans to construct lunar bases and settlements. These will not only establish a human presence on the Moon, but facilitate missions to Mars and deeper into space.