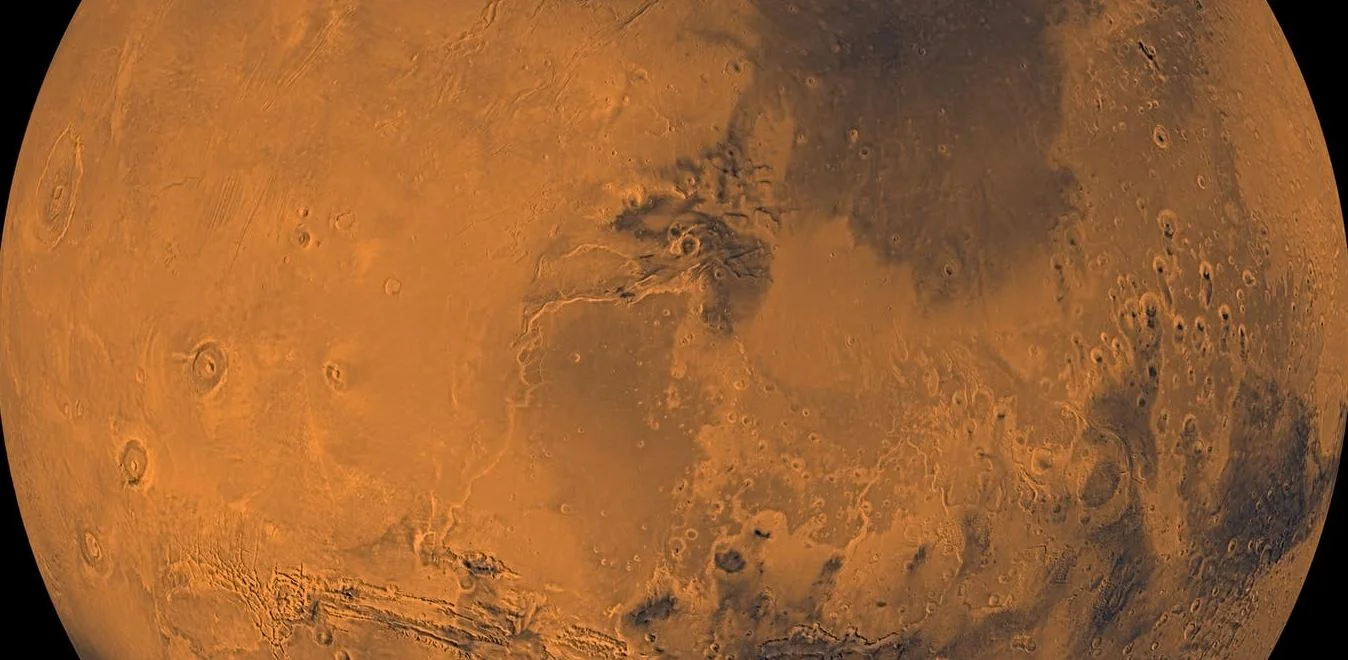
Mars has long been thought of as dry and barren – unable to harbour life. But research over the past few years indicates that there is most likely some briny water present there today, including a possible subsurface lake. This has led to new hopes that there could actually be life on the red planet after all, depending on what the conditions are like in the water.
To Find Evidence of Life on Exoplanets, Scientists Should Search for “Purple Earths”
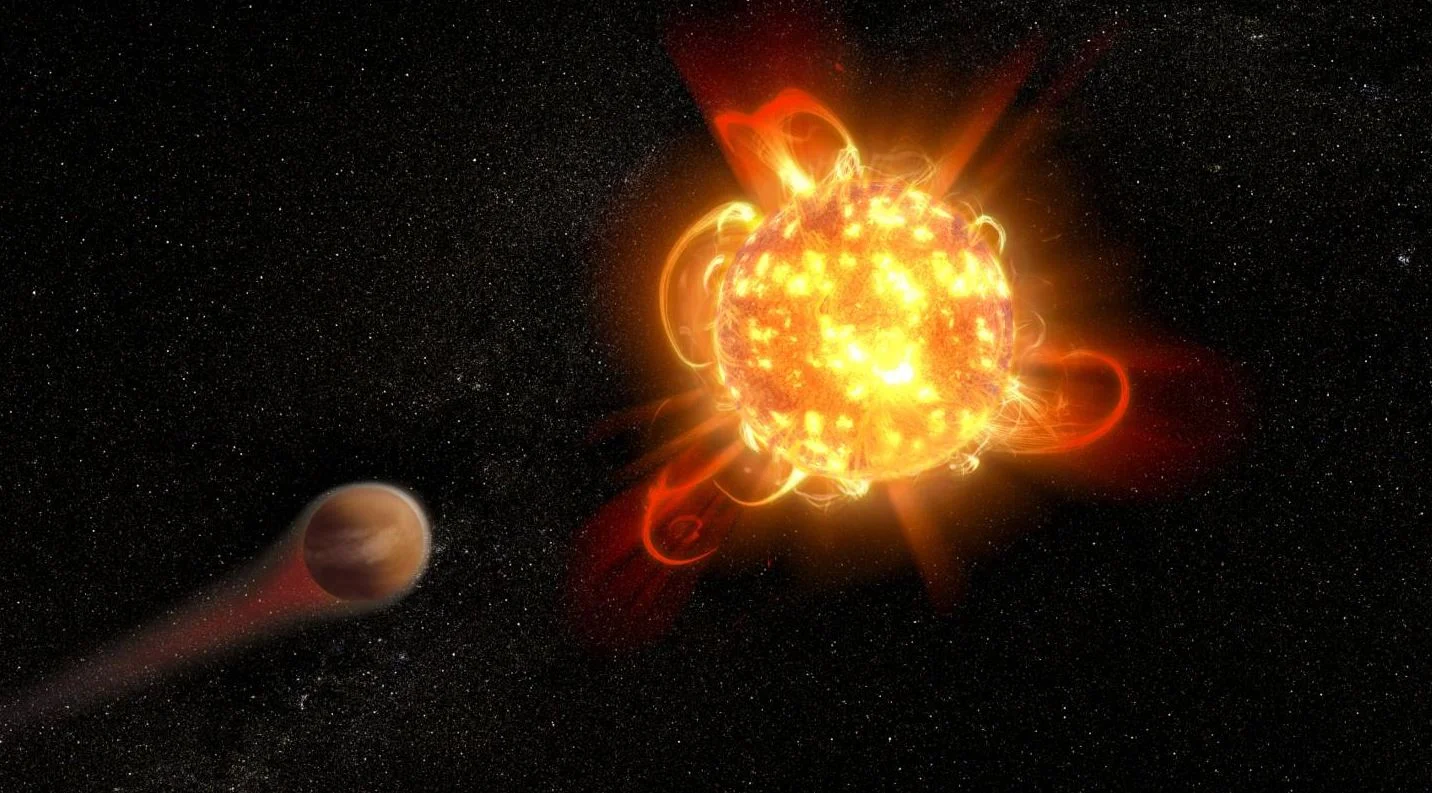
A Red Dwarf Blasts off a Superflare. Any Life on its Planets Would Have a Very Bad Day
A Goblin could guide us to a mystery planet thought to exist in the Solar system
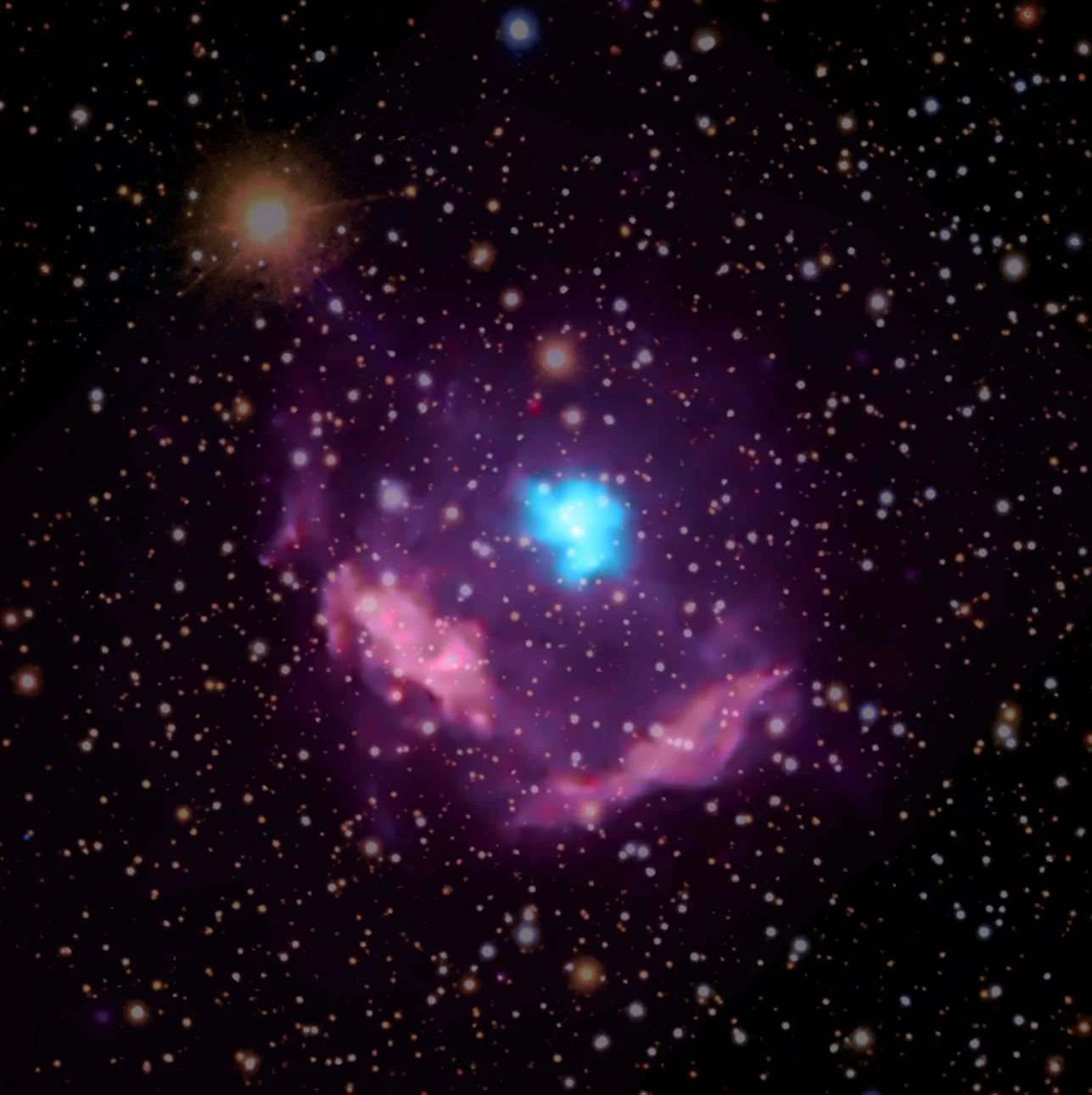
Kes 75: Milky Way's Youngest Pulsar Exposes Secrets of Star's Demise
NASA Calls for Instruments, Technologies for Delivery to the Moon
Would a Space Force mean the end of NASA?
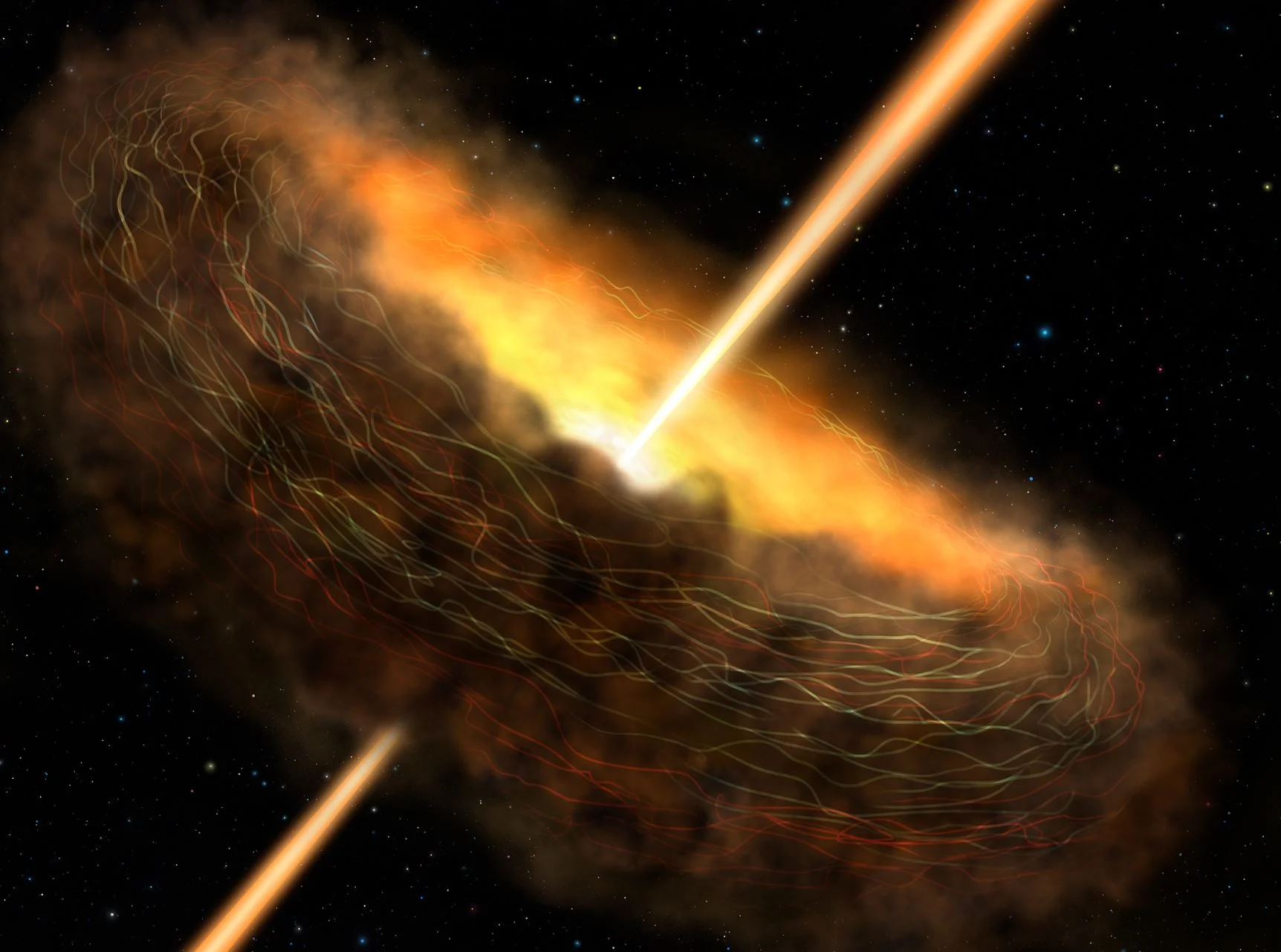
Magnetic Fields May Be the Key to Black Hole Activity
Parallel jets provide astronomers with some of the most powerful evidence that a supermassive black hole lurks in the heart of most galaxies. Some of these black holes appear to be active, gobbling up material from their surroundings and launching jets at ultra-high speeds, while others are quiescent, even dormant.
Largest Galaxy Proto-Supercluster Found - Astronomers using ESO’s Very Large Telescope uncover a cosmic titan lurking in the early Universe
An international team of astronomers using the VIMOS instrument of ESO’s Very Large Telescope have uncovered a titanic structure in the early Universe. This galaxy proto-supercluster — which they nickname Hyperion — was unveiled by new measurements and a complex examination of archive data. This is the largest and most massive structure yet found at such a remote time and distance — merely 2 billion years after the Big Bang.
Surprising Discovery. Four Giant Planets Found Around a Very Young Star
What exactly is a “normal” solar system? If we thought we had some idea in the past, we definitely don’t now. And a new study led by astronomers at Cambridge University has reinforced this fact. The new study found four gas giant planets, similar to our own Jupiter and Saturn, orbiting a very young star called CI Tau. And one of the planets has an extreme orbit that takes it more than a thousand times more distant from the star than the innermost planet.
Even Ganymede is Showing Tectonic Activity. We’re Going to Need Another Icy Moon Orbiter
Ganymede was shaped by pronounced periods of tectonic activity in the past, according to a new paper. It’s no longer active and its surface is more-or-less frozen in place now. But this discovery opens the door to better planning for future missions to Jupiter’s other frozen moon Europa. Unlike Ganymede, Europa is still tectonically active, and understanding past geological activity on Ganymede helps us understand present-day Europa.
Artist is Planning to Launch a Giant, Unfolding Structure That’ll be Bright in the Sky For a Few Months
One of the most cited reasons and benefits of space exploration is the way it brings people together. Think of iconic moments, like the Moon Landing or the launch of Yuri Gagarin (the first man to go into space), and the impact they had on their respective generations. Looking to the future, there are many who hope to use space exploration to bring people from all walks of life and nationalities together again.
How we solved a centuries-old mystery by discovering a rare form of star collision
A bright new star appeared in the sky in June, 1670. It was seen by the Carthusian monk Père Dom Anthelme in Dijon, France, and astronomer Johannes Hevelius in Gdansk, Poland. Over the next few months, it slowly faded to invisibility. But in March 1671, it reappeared – now even more luminous and among the 100 brightest stars in the sky. Again it faded, and by the end of the summer it was gone. Then in 1672, it put in a third appearance, now only barely visible to the naked eye. After a few months it was gone again and hasn’t been seen since.
The Milky Way Could Be Spreading Life From Star to Star
For almost two centuries, scientists have theorized that life may be distributed throughout the Universe by meteoroids, asteroids, planetoids, and other astronomical objects. This theory, known as Panspermia, is based on the idea that microorganisms and the chemical precursors of life are able to survive being transported from one star system to the next.
Next Generation Telescopes Could Use “Teleportation” to Take Better Images
Telescopes have come a long way in the past few centuries. From the comparatively modest devices built by astronomers like Galileo Galilei and Johannes Kepler, telescopes have evolved to become massive instruments that require an entire facility to house them and a full crew and network of computers to run them. And in the coming years, much larger observatories will be constructed that can do even more.
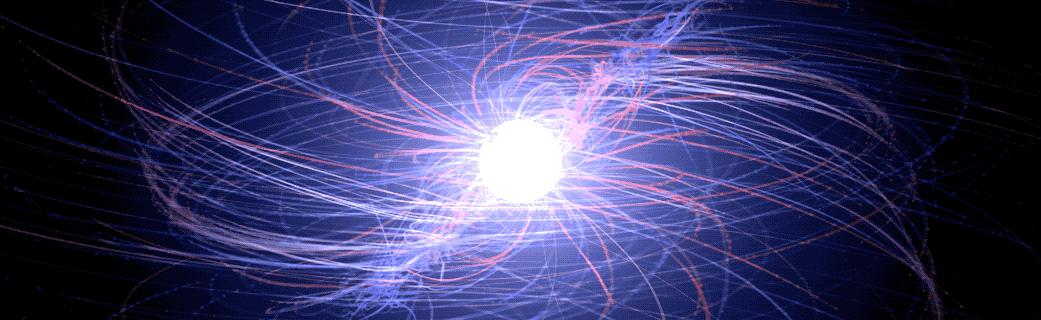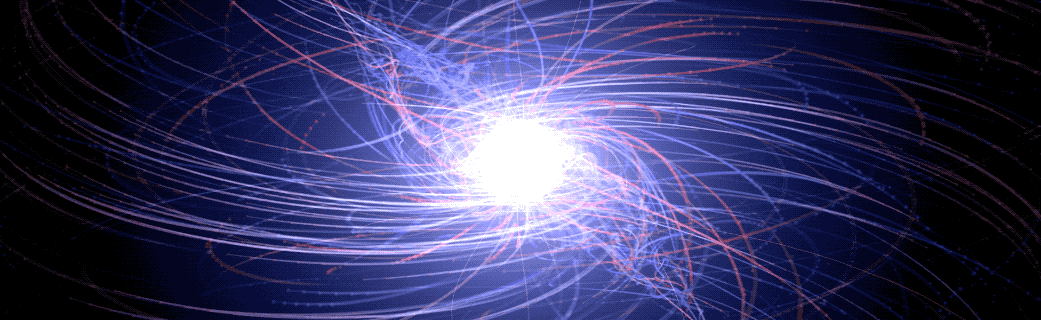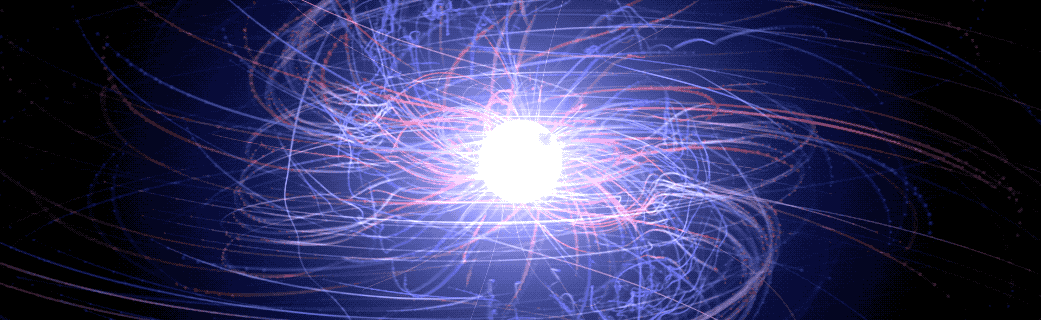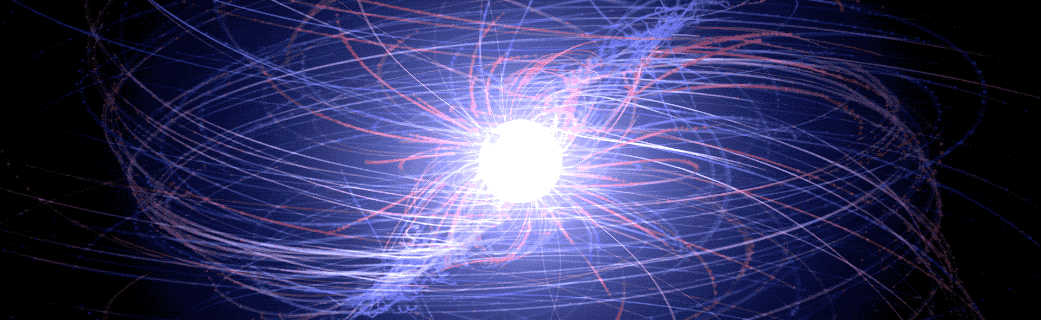
‘Pulsar in a Box’ Reveals Surprising Picture of a Neutron Star’s Surroundings
An international team of scientists studying what amounts to a computer-simulated “pulsar in a box” are gaining a more detailed understanding of the complex, high-energy environment around spinning neutron stars, also called pulsars. The model traces the paths of charged particles in magnetic and electric fields near the neutron star, revealing behaviors that may help explain how pulsars emit gamma-ray and radio pulses with ultra precise timing.
NASA Voyager 2 Could Be Nearing Interstellar Space
NASA's Voyager 2 probe, currently on a journey toward interstellar space, has detected an increase in cosmic rays that originate outside our solar system. Launched in 1977, Voyager 2 is a little less than 11 billion miles (about 17.7 billion kilometers) from Earth, or more than 118 times the distance from Earth to the Sun.
New Image Shows the Rugged Landscape of Comet 67P
In March of 2004, the European Space Agency’s Rosetta spacecraft blasted off from French Guiana aboard an Ariane 5 rocket. After ten years, by November of 2014, the spacecraft rendezvoused with its target – Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (67P/C-G). Over the more than two years that followed, the spacecraft remained in orbit of this comet, gathering information on its surface, interior, and gas and dust environment.
Dark Matter Isn’t Made From Black Holes
In February of 2016, scientists working for the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) made history when they announced the first-ever detection of gravitational waves. Since that time, multiple detections have taken place and scientific collaborations between observatories – like Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo – are allowing for unprecedented levels of sensitivity and data sharing.
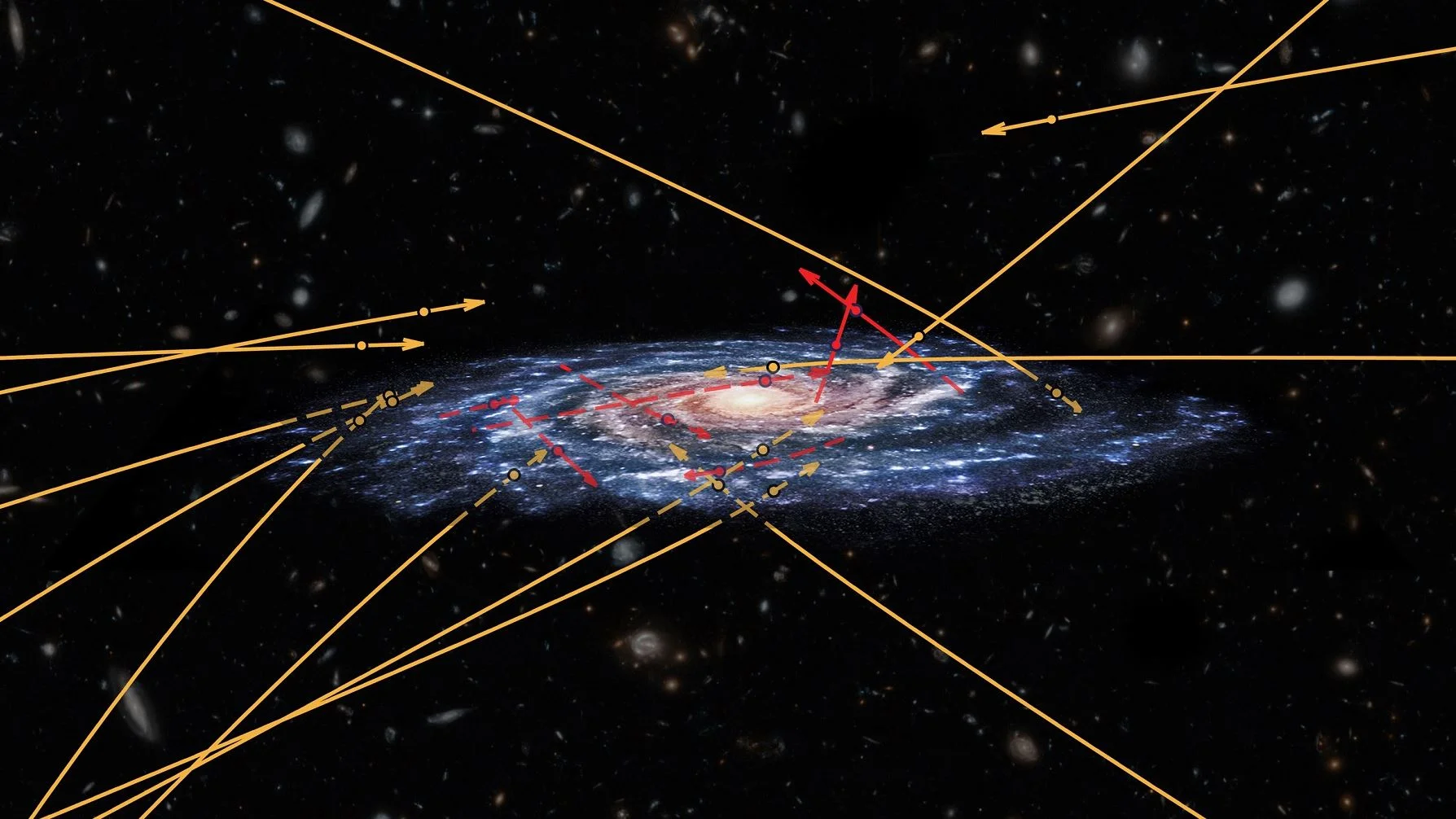
Gaia Sees Stars Out in Deep Space, Flying Between Galaxies
In December of 2013, the European Space Agency (ESA) launched the Gaia mission. Since that time, this space observatory has been busy observing over 1 billion astronomical objects in our galaxy and beyond – including stars, planets, comets, asteroids, quasars, etc. – all for the sake of creating the largest and most precise 3D space catalog ever made.