Sometimes you run across a grimy, tattered dollar bill that seems like it’s been around since the beginning of time. Assuredly it hasn’t, but the history of human beings using cash currency does go back a long time – 40,000 years.
How would engineers build the Golden Gate Bridge today?
When the Golden Gate Bridge went up, it was the longest suspended bridge span in the world – cables hold up the roadway between two towers, with no intermediate supports. And the setting had a number of inherent challenges. It cost about US$37 million at the time; building the same structure today would cost about a billion dollars. So how has the design held up over the past 80 years – and would we do things differently if we were starting from scratch today?
Here’s how Doctor Who’s time machine measures up with real instruments of space and time
There’s no denying that we’ve seen some absolutely staggering accomplishments in physics in the past year or so, particularly in our ability to measure space and time with unprecedented levels of detail. But being a lifelong “Whovian” excited about Doctor Who returning to our screens once again, I wondered how these accomplishments stacked up to those of the fictional Time Lords.
Paradoxes of probability and other statistical strangeness
3.14 essential reads about π for Pi Day
Five of the most explosive non-nuclear chemicals ever made
Explainer: what is wave-particle duality
Our notion of reality is built on everyday experiences. But wave-particle duality is so strange that we are forced to re-examine our common conceptions. Wave-particle duality refers to the fundamental property of matter where, at one moment it appears like a wave, and yet at another moment it acts like a particle. To understand wave-particle duality it’s worth looking at differences between particles and waves.
If atoms are mostly empty space, why do objects look and feel solid?
Chemist John Dalton proposed the theory that all matter and objects are made up of particles called atoms, and this is still accepted by the scientific community, almost two centuries later. Each of these atoms is each made up of an incredibly small nucleus and even smaller electrons, which move around at quite a distance from the centre.
How Strong Is The Force Of Gravity On Earth?
Gravity is a pretty awesome fundamental force. If it wasn’t for the Earth’s comfortable 1 g, which causes objects to fall towards the Earth at a speed of 9.8 m/s², we’d all float off into space. And without it, all us terrestrial species would slowly wither and die as our muscles degenerated, our bones became brittle and weak, and our organs ceased to function properly.
What Is A Magnetic Field?
Everyone knows just how fun magnets can be. As a child, who among us didn’t love to see if we could make our silverware stick together? And how about those little magnetic rocks that we could arrange to form just about any shape because they stuck together? Well, magnetism is not just an endless source of fun or good for scientific experiments; it’s also one of basic physical laws upon which the universe is based.
What exactly does ‘instantaneous’ mean?
How short is an “instant”? Is it a second? A tenth of a second? A microsecond? You might think all of these qualify. What about 100 years? That certainly doesn’t seem like an instant, and to a human being, it isn’t, since we’d be lucky to have a lifespan that long. But to a giant sequoia, say, 100 years is no big deal. And in geological terms it’s practically nothing.
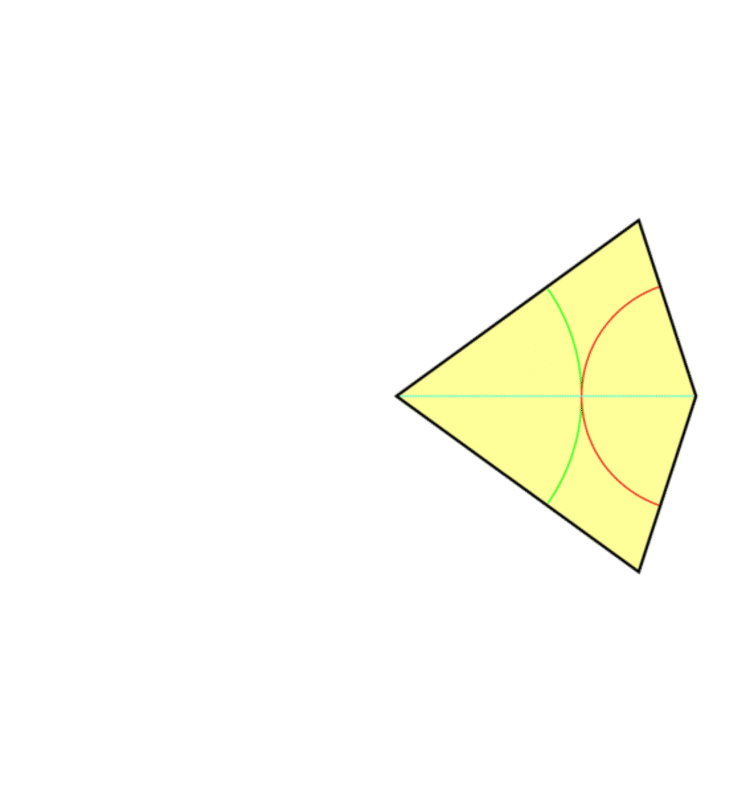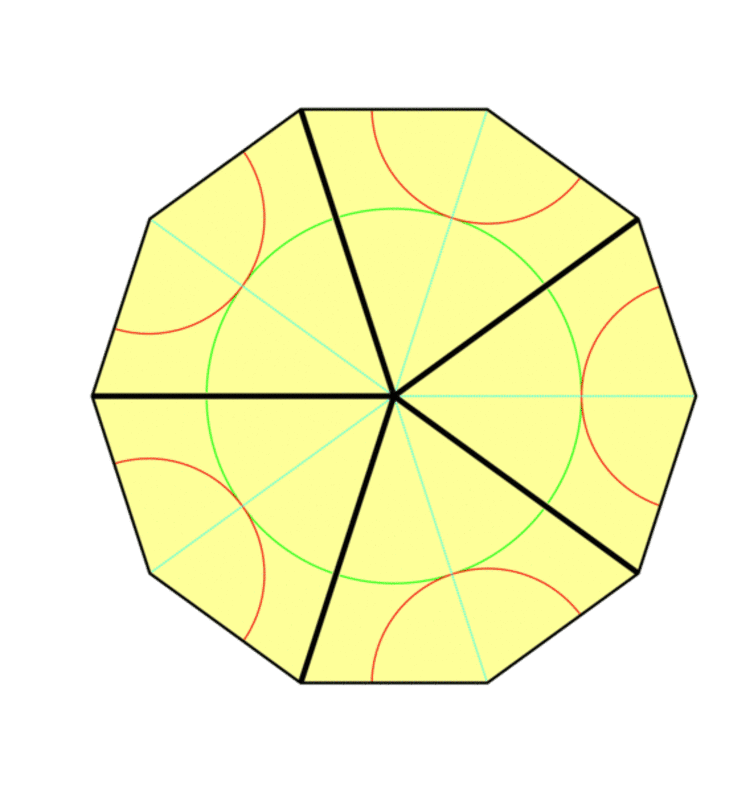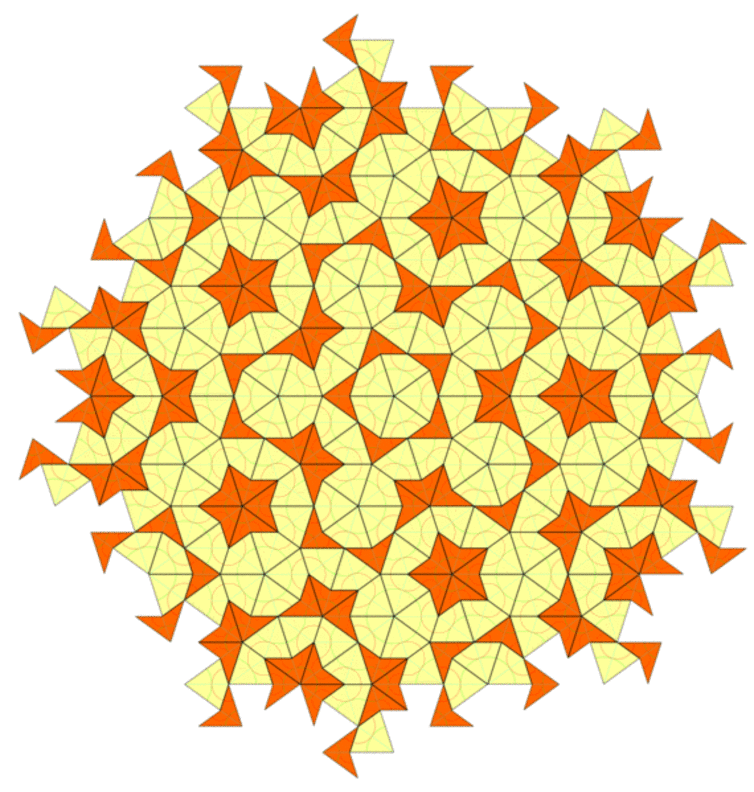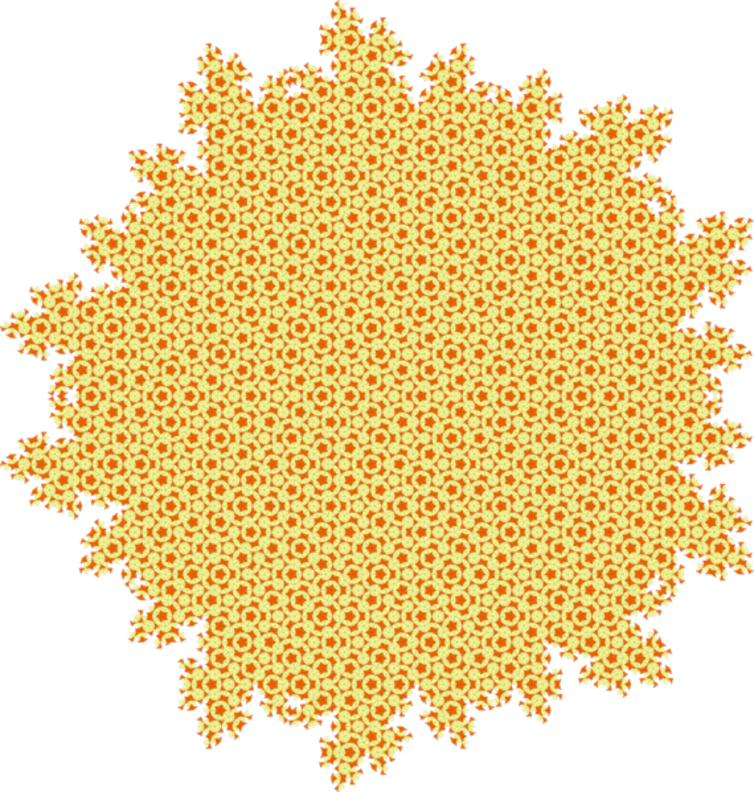
The maths behind ‘impossible’ never-repeating patterns
Remember the graph paper you used at school, the kind that’s covered with tiny squares? It’s the perfect illustration of what mathematicians call a “periodic tiling of space”, with shapes covering an entire area with no overlap or gap. If we moved the whole pattern by the length of a tile (translated it) or rotated it by 90 degrees, we will get the same pattern. That’s because in this case, the whole tiling has the same symmetry as a single tile. But imagine tiling a bathroom with pentagons instead of squares – it’s impossible, because the pentagons won’t fit together without leaving gaps or overlapping one another.
Is every human voice and fingerprint really unique?
Barclays, the UK bank, is to replace the password system on its phone banking service with personal voice recognition. “Unlike a password, each person’s voice is as unique as a fingerprint,” said Steven Cooper, Barclays' head of personal banking. Yet the reality is we have no idea whether either fingerprints or voices are unique at all.
Graphene isn’t the only Lego in the materials-science toy box
You may have heard of graphene, a sheet of pure carbon, one atom thick, that’s all the rage in materials-science circles, and getting plenty of media hype as well. Reports have trumpeted graphene as an ultra-thin, super-strong, super-conductive, super-flexible material. You could be excused for thinking it might even save all of humanity from certain doom.
Explainer: how dangerous is turbulence… and can it bring down a plane?
Why lightsabers would be far more lethal than George Lucas envisioned
Research is an unpredictable process. Sometimes you end up making a really cool discovery that you didn’t see coming. I recently uncovered a fundamental property of lightsabers (that’s right – the awesome weapons from Star Wars) while doing my regular plasma physics research. I found that, while it is in theory possible to build a lightsaber, it’s likely it would be the most dangerous weapon ever created – both for the perpetrator and the victim.
How to build a time machine
Every now and again, we all indulge in dreams about travelling in time. Wouldn’t it be wonderful to return to that specific point in the past to change a bad decision or relive an experience – those halcyon days of childhood, that night you won an Oscar – or to zip ahead to see how things turn out in the far future.
What is time – and why does it move forward?
Imagine time running backwards. People would grow younger instead of older and, after a long life of gradual rejuvenation – unlearning everything they know – they would end as a twinkle in their parents' eyes. That’s time as represented in a novel by science fiction writer Philip K Dick but, surprisingly, time’s direction is also an issue that cosmologists are grappling with.
Timeline: the history of gravity
Corals, crochet and the cosmos: how hyperbolic geometry pervades the universe
We have built a world of largely straight lines – the houses we live in, the skyscrapers we work in and the streets we drive on our daily commutes. Yet outside our boxes, nature teams with frilly, crenellated forms, from the fluted surfaces of lettuces and fungi to the frilled skirts of sea slugs and the gorgeous undulations of corals.