Veils of dust wrapped around distant stars could make it difficult for scientists to find potentially habitable planets in those star systems. The Hunt for Observable Signatures of Terrestrial Systems, or HOSTS, survey was tasked with learning more about the effect of dust on the search for new worlds. The goal is to help guide the design of future planet-hunting missions. In a new paper published in the Astrophysical Journal, HOSTS scientists report on the survey’s initial findings.
Two Hubble Views of the Same Stellar Nursery
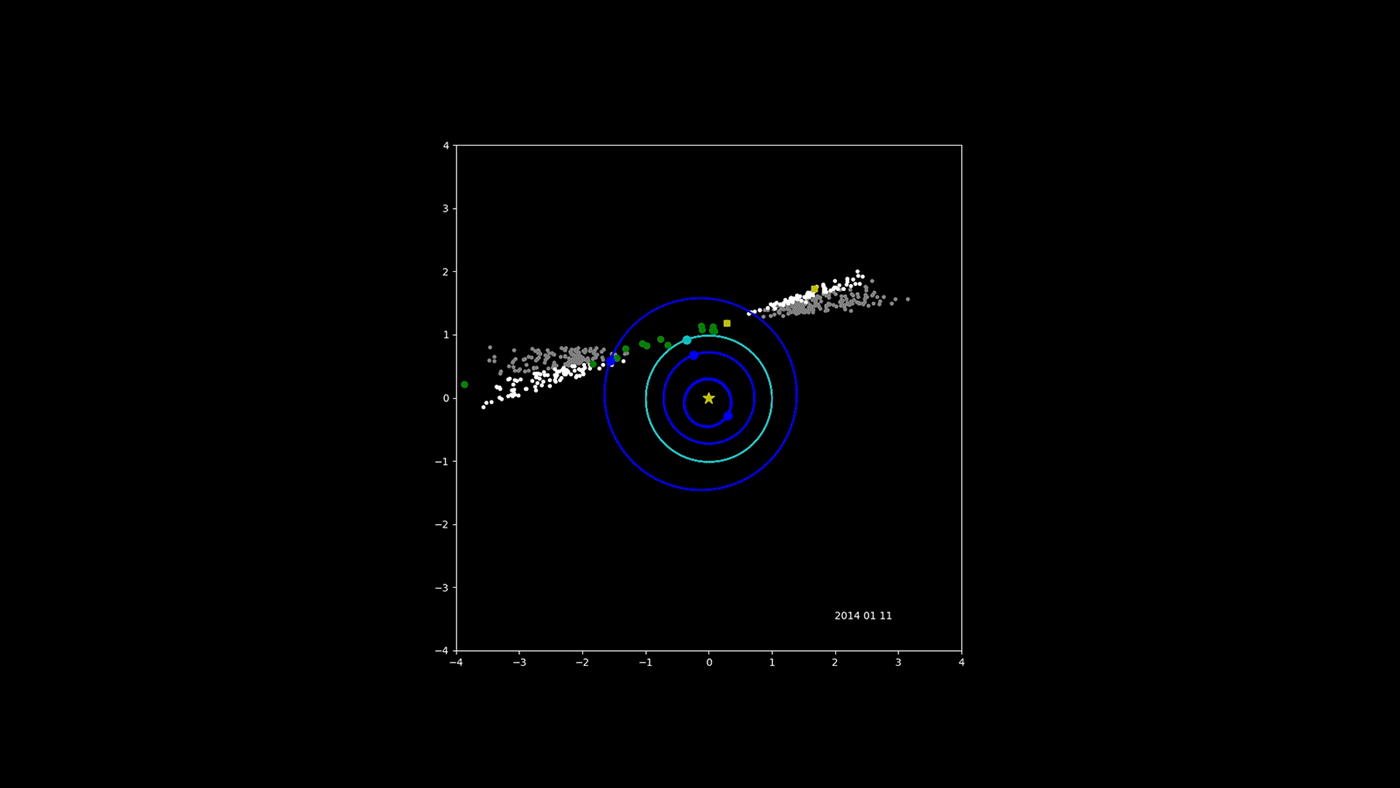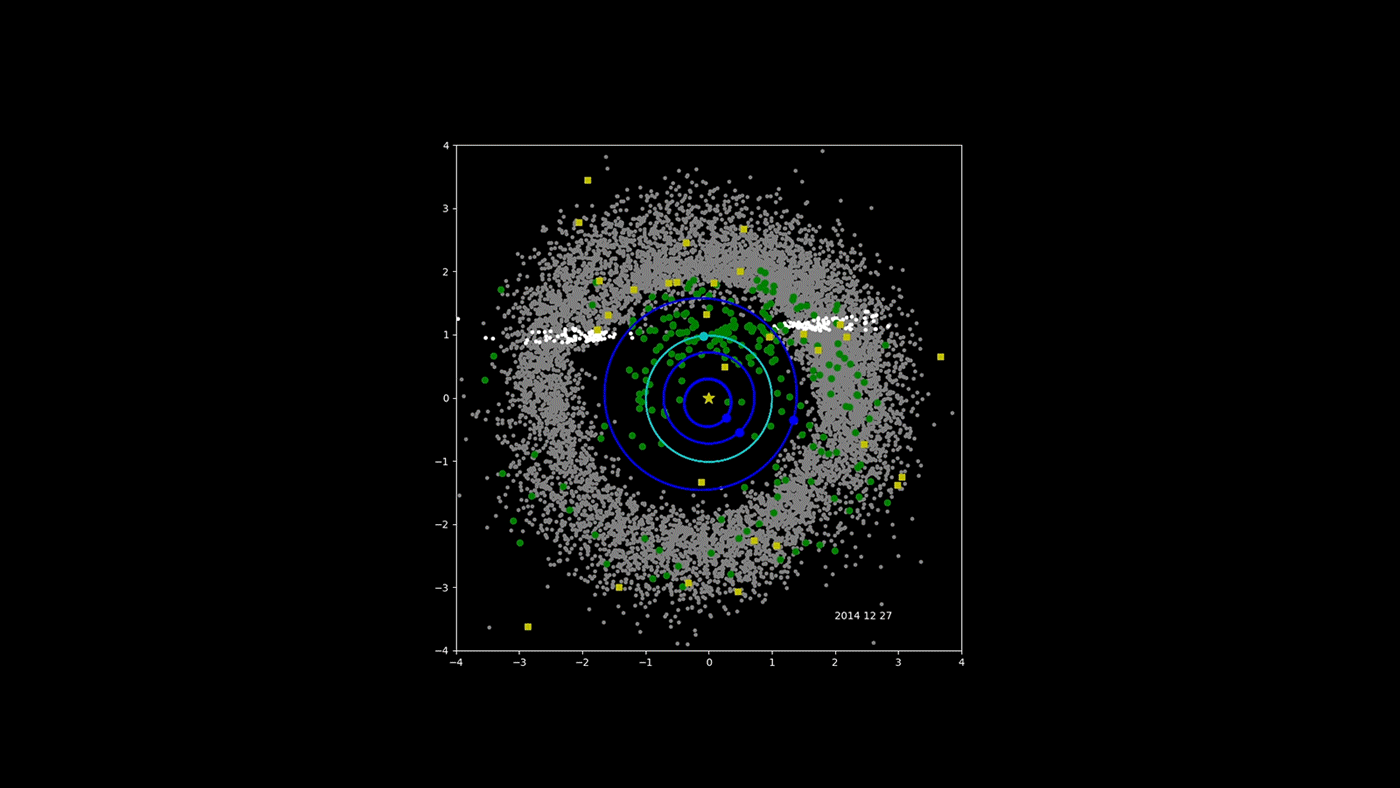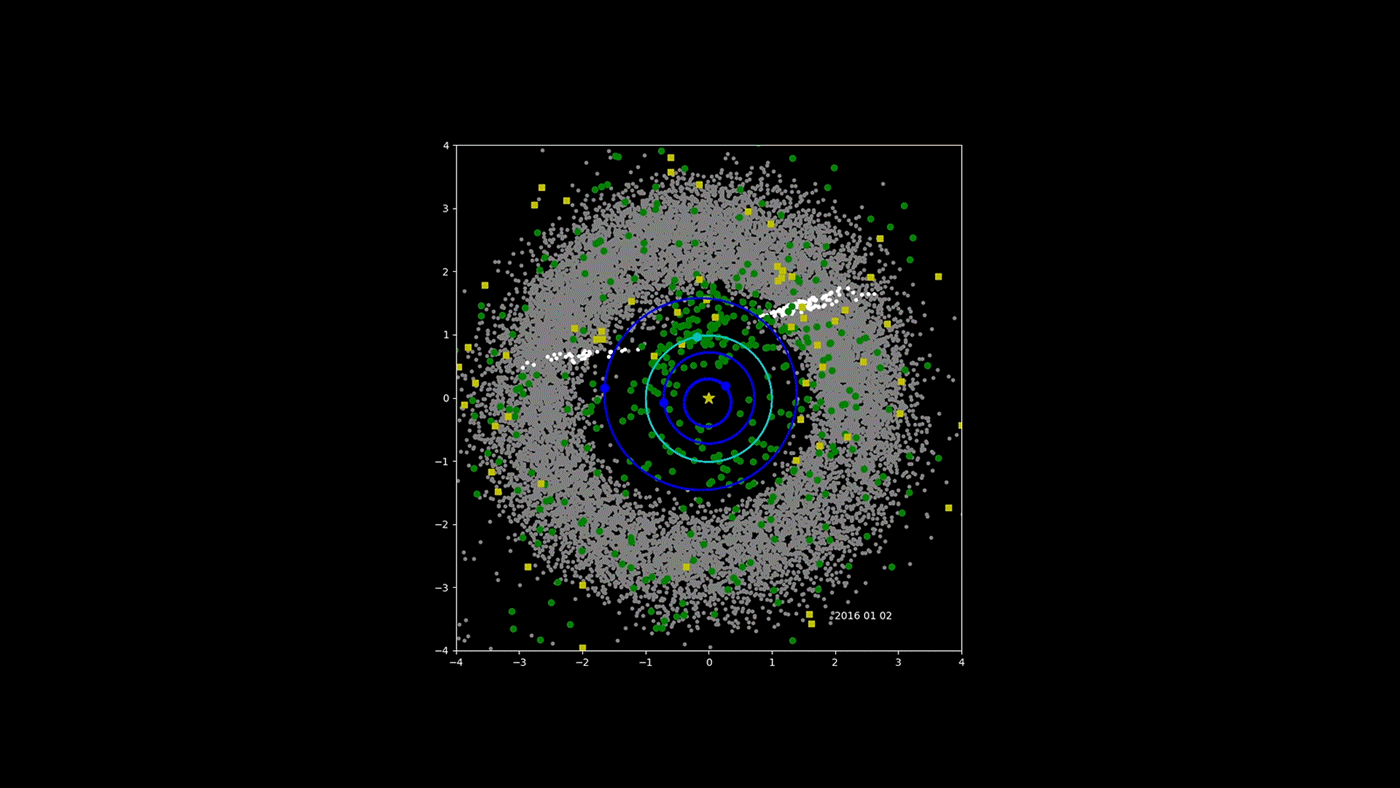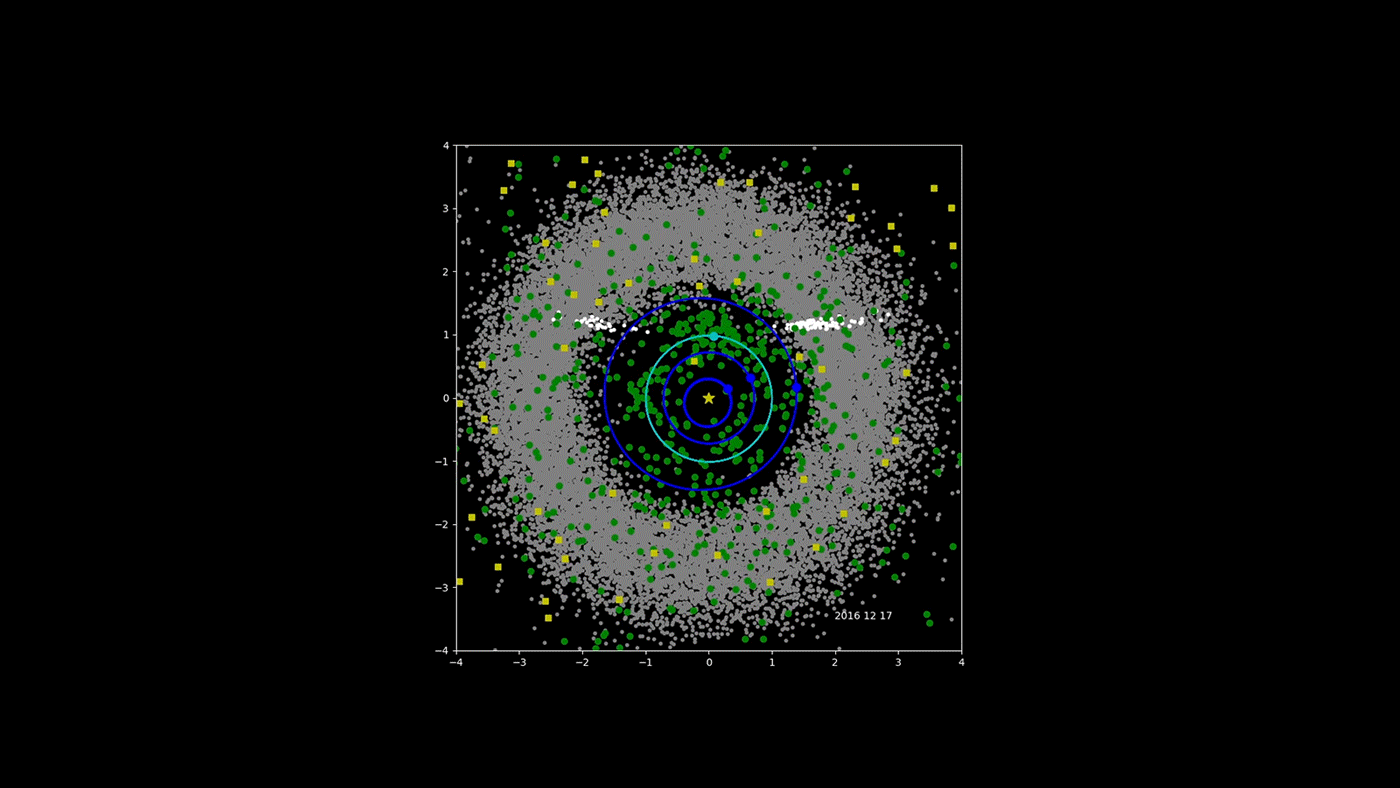
NASA's NEOWISE Asteroid-Hunter Spacecraft -- Four Years of Data
NASA's Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) mission has released its fourth year of survey data. Since the mission was restarted in December 2013, after a period of hibernation, the asteroid- and comet-hunter has completely scanned the skies nearly eight times and has observed and characterized 29,375 objects in four years of operations. This total includes 788 near-Earth objects and 136 comets since the mission restart.
Health Check: is there an optimal time of day to work out?
Delivering VR in perfect focus with nanostructure meta-lenses
If wearing a virtual reality or augmented reality headset is ever to become commonplace, hardware manufacturers will need to figure out how to make the devices small and lightweight while ensuring their images are sharp and clear. Unfortunately, this task faces a key limitation in optics: Conventional lenses are curved glass objects that focus different wavelengths of light in different locations, which would show viewers blurry images. As a result, pretty much anything with a lens – from tiny smartphone cameras to large-scale projectors – uses multiple lenses, which add weight, thickness and complexity, increasing cost.
The challenges of an alien spaceflight program: escaping super earths and red dwarf stars
Since the beginning of the Space Age, humans have relied on chemical rockets to get into space. While this method is certainly effective, it is also very expensive and requires a considerable amount of resources. As we look to more efficient means of getting out into space, one has to wonder if similarly-advanced species on other planets (where conditions would be different) would rely on similar methods.
Mysterious red spots on Mercury get names – but what are they?
Mercury is the closest planet to the sun, but far from being a dull cinder of a world, it has instead turned out to be a real eye opener for geologists. Among the revelations by NASA’s MESSENGER probe, which first flew past Mercury in 2008 and orbited it between 2011 and 2015, is the discovery of a hundred or so bright red spots scattered across the globe. Now they are at last being named.
Did you know the earth has a second magnetic field? Its oceans
Earth’s magnetic field is one of the most mysterious features of our planet. It is also essential to life as we know it, ensuring that our atmosphere is not stripped away by solar wind and shielding life on Earth from harmful radiation. For some time, scientists have theorized that it is the result of a dynamo action in our core, where the liquid outer core revolves around the solid inner core and in the opposite direction of the Earth’s rotation.
Overeating? It may be a brain glitch
How the lowly mushroom is becoming a nutritional star
The way you see colour depends on what language you speak
Research Check: is it true pasta doesn’t make you gain weight, and could even help you lose it?
Health check: why do we get muscle cramps?
Explainer: how do we make hydrogen from coal, and is it really a clean fuel?
What in the World is an ‘Exoplanet?’
Supercontinent formation may be linked to a cycle of supertides
Earth’s crust is made up of fractured slabs of rock, like a broken shell on an egg. These plates move around at speeds of about 5cm per year – and eventually this movement brings all the continents together and form what is known as a supercontinent. The last supercontinent on Earth was Pangaea, which existed between 300-180m years ago.
Living underground on other worlds. Exploring lava tubes
‘Junk DNA’ isn’t so useless after all
Io afire with volcanoes under Juno’s gaze
Volcanic activity on Io was discovered by Voyager 1 imaging scientist Linda Morabito. She spotted a little bump on Io’s limb while analyzing a Voyager image and thought at first it was an undiscovered moon. Moments later she realized that wasn’t possible — it would have been seen by earthbound telescopes long ago. Morabito and the Voyager team soon came to realize they were seeing a volcanic plume rising 190 miles (300 km) off the surface of Io. It was the first time in history that an active volcano had been detected beyond the Earth.