Every 405,000 years, gravitational tugs from Jupiter and Venus slightly elongate Earth’s orbit, according to new research.
The latest from Juno as Jupiter appears bright in the night sky
NASA Satellite Images Show Fissures from Hawaii Volcano
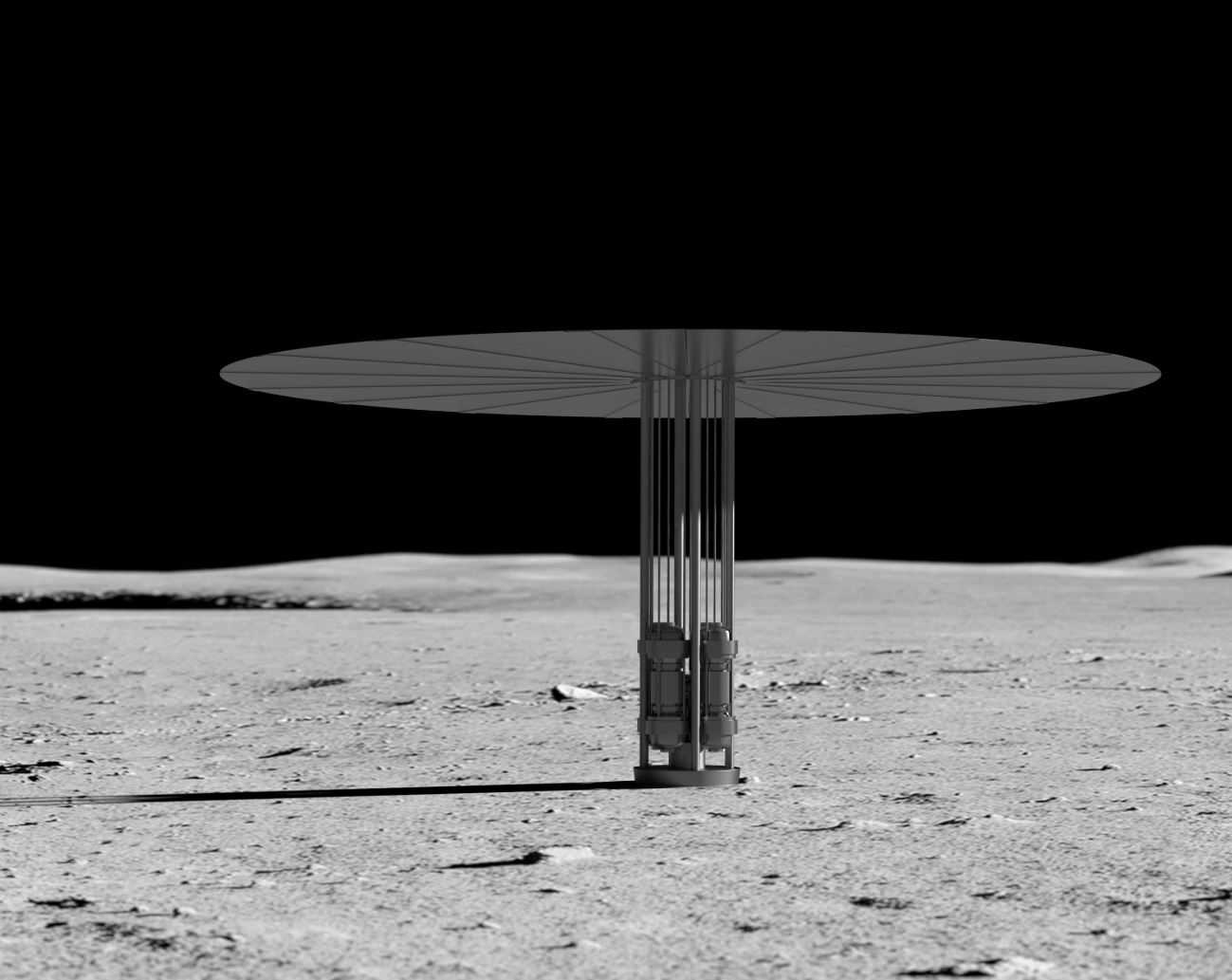
We Now Have A Working Nuclear Reactor for Other Planets — But No Plan For Its Waste
One of the TRAPPIST-1 planets has an iron core!
In February of 2017, a team of European astronomers announced the discovery of a seven-planet system orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1. Aside from the fact that all seven planets were rocky, there was the added bonus of three of them orbiting within TRAPPIST-1’s habitable zone. Since that time, multiple studies have been conducted to determine whether or not any of these planets could be habitable.
Mining asteroids could unlock untold wealth – here’s how to get started!
A virus ‘cocktail’ could one day treat food poisoning
Water-based battery stores green energy for later
Five amazing ways redesigning biological cells could help us fight cancer
Want to eat better? You might be able to train yourself to change your tastes
Elements from the stars: The unexpected discovery that upended astrophysics 66 years ago
Ancient Galaxy Megamergers - ALMA and APEX discover massive conglomerations of forming galaxies in early Universe
Scientists discover how to harness the power of quantum spookiness by entangling clouds of atoms
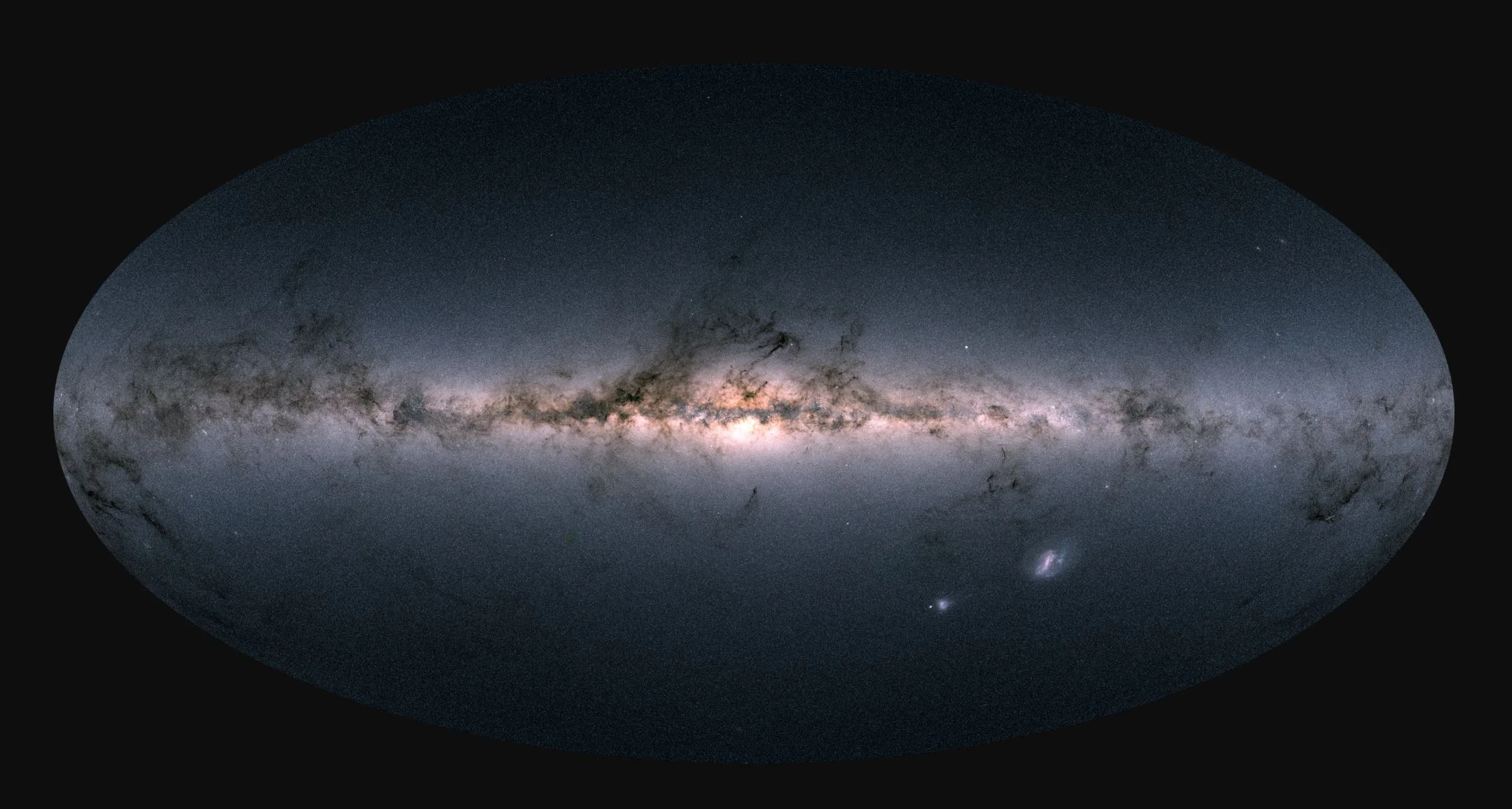
Gaia mission releases map of more than a billion stars – here’s what it can teach us
Most of us have looked up at the night sky and wondered how far away the stars are or in what direction they are moving. The truth is, scientists don’t know the exact positions or velocities of the vast majority of the stars in the Milky Way. But now a new tranche of data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia satellite, aiming to map stars in our galaxy in unprecedented detail, has come in to shed light on the issue.
How many planets is TESS going to find?
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), NASA’s latest exoplanet-hunting space telescope, was launched into space on Wednesday, April 18th, 2018. As the name suggests, this telescope will use the Transit Method to detect terrestrial-mass planets (i.e. rocky) orbiting distant stars. Alongside other next-generation telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), TESS will effectively pick up where telescopes like Hubble and Kepler left off.
End of ageing and cancer? Scientists unveil structure of the ‘immortality’ enzyme telomerase
Making a drug is like trying to pick a lock at the molecular level. There are two ways in which you can proceed. You can try thousands of different keys at random, hopefully finding one that fits. The pharmaceutical industry does this all the time – sometimes screening hundreds of thousands of compounds to see if they interact with a certain enzyme or protein. But unfortunately it’s not always efficient – there are more drug molecule shapes than seconds have passed since the beginning of the universe.
Stellar Dust Survey Paves Way for Exoplanet Missions
Veils of dust wrapped around distant stars could make it difficult for scientists to find potentially habitable planets in those star systems. The Hunt for Observable Signatures of Terrestrial Systems, or HOSTS, survey was tasked with learning more about the effect of dust on the search for new worlds. The goal is to help guide the design of future planet-hunting missions. In a new paper published in the Astrophysical Journal, HOSTS scientists report on the survey’s initial findings.
Two Hubble Views of the Same Stellar Nursery
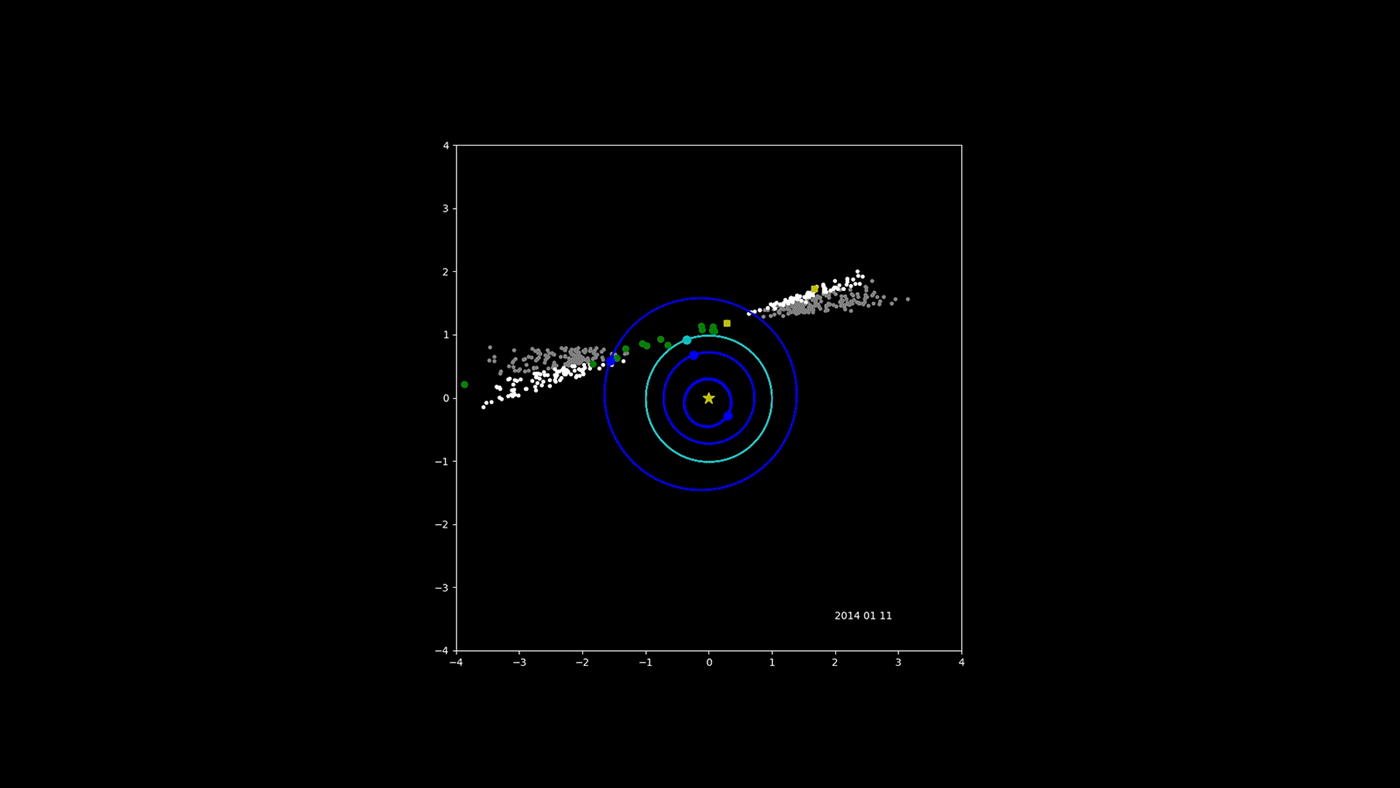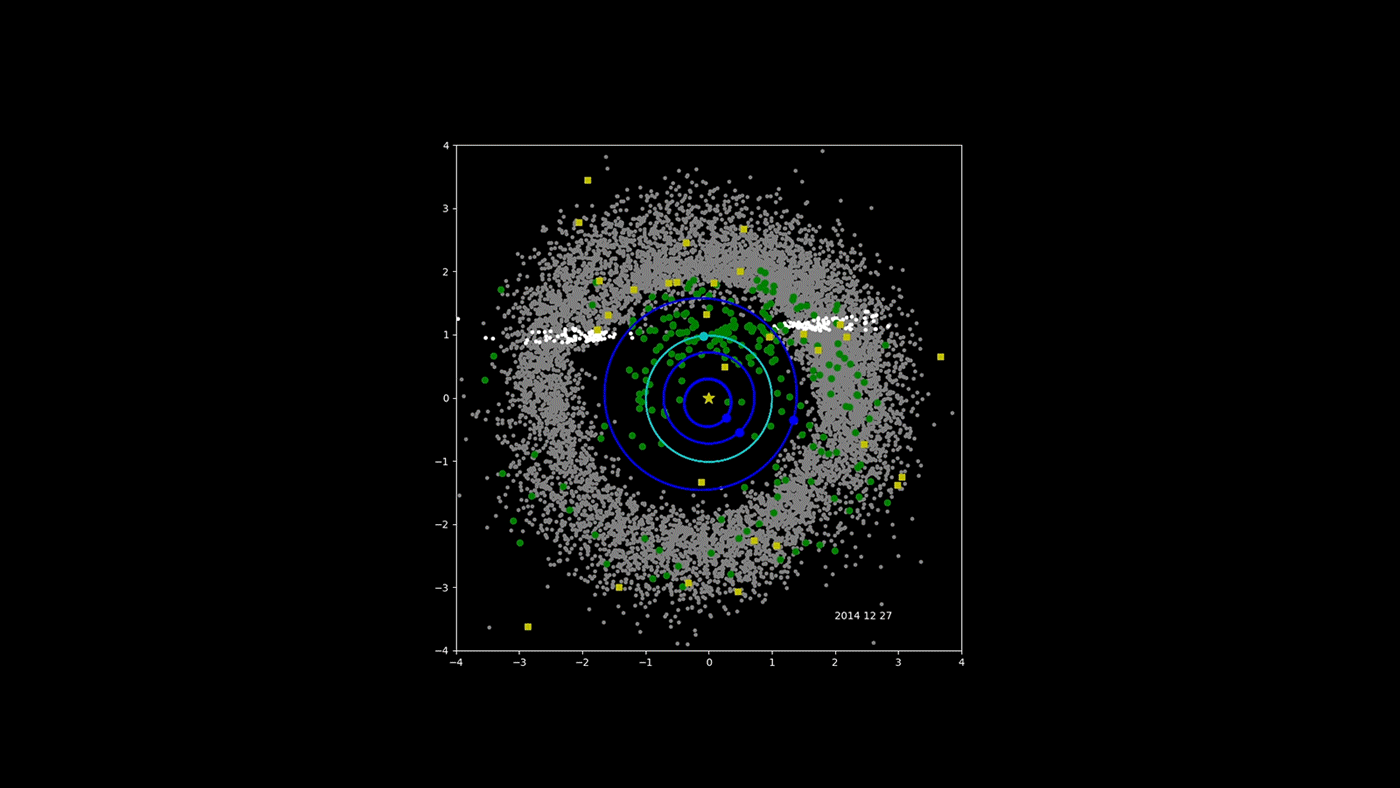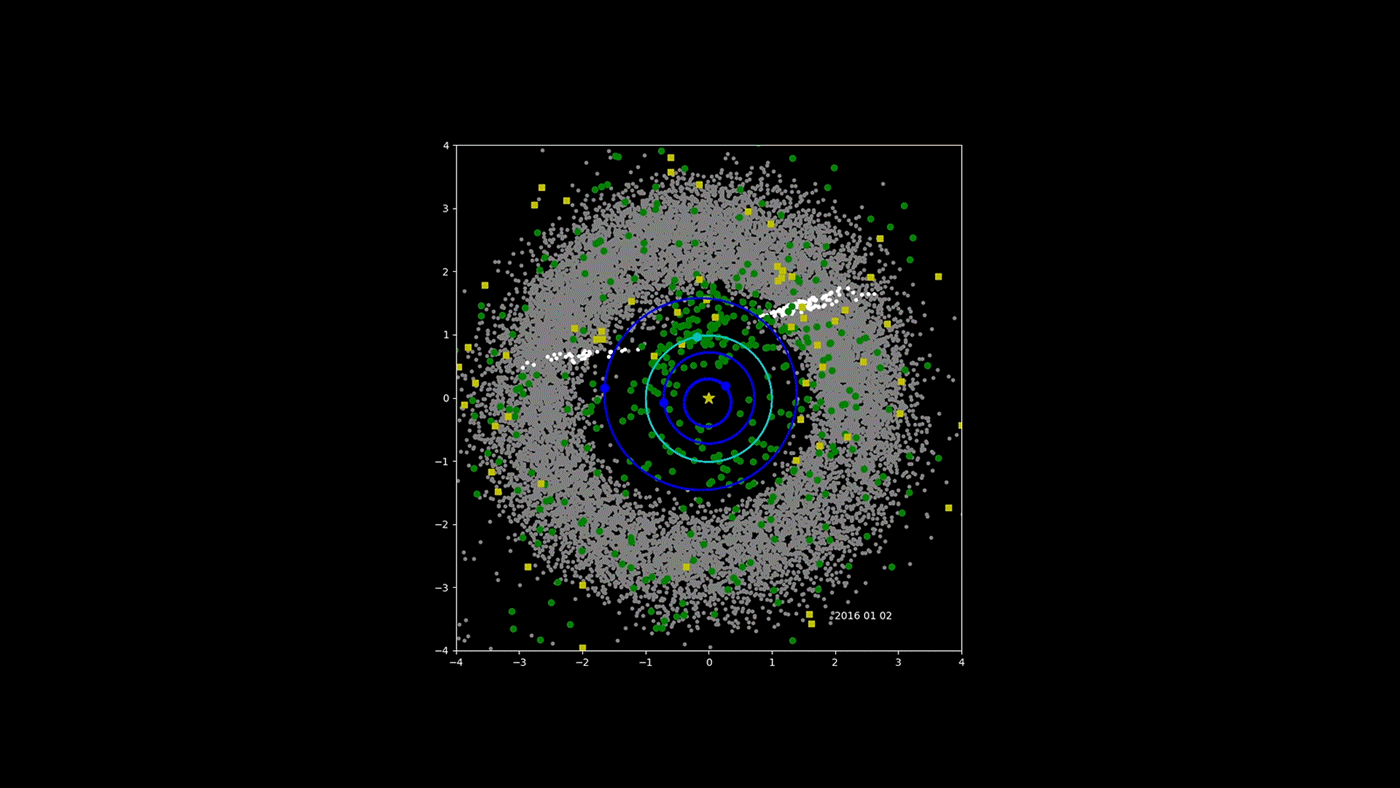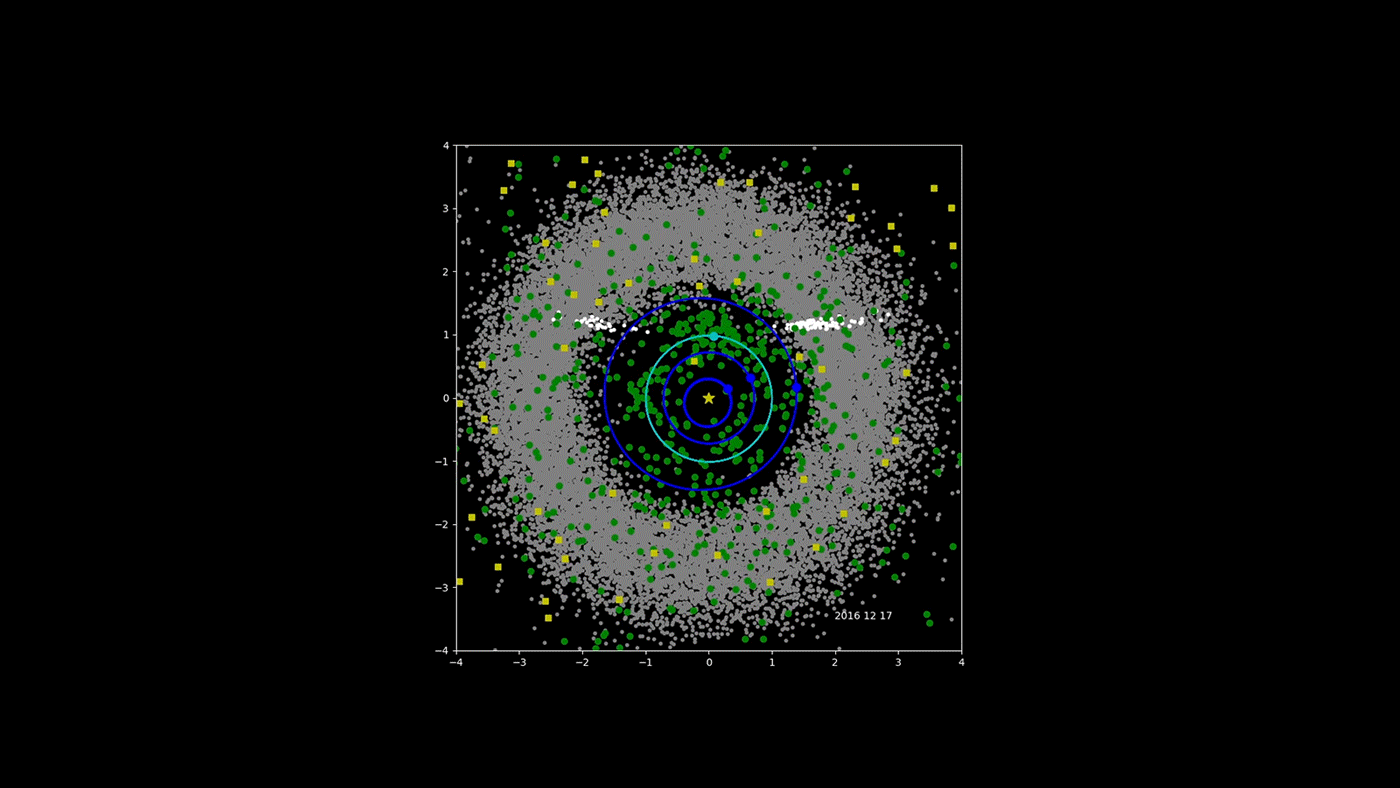
NASA's NEOWISE Asteroid-Hunter Spacecraft -- Four Years of Data
NASA's Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) mission has released its fourth year of survey data. Since the mission was restarted in December 2013, after a period of hibernation, the asteroid- and comet-hunter has completely scanned the skies nearly eight times and has observed and characterized 29,375 objects in four years of operations. This total includes 788 near-Earth objects and 136 comets since the mission restart.