Located about 7500 light-years from Earth, in the constellation of Carina, lies a star-forming region known as the Carina Nebula. This dynamic, evolving cloud of interstellar gas and dust measures about 300 light-years in diameter and is one of the Milky Way’s largest star-forming regions. It is also an exercise in contrasts, consisting of bright regions of gas illuminated by intense stellar radiation and dark pillars of dust that obscure star formation.
Math shows how DNA twists, turns and unzips
Building bricks on the moon from lunar dust
In the coming decades, many space agencies hope to conduct crewed missions to the Moon and even establish outposts there. In fact, between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), Roscosmos, and the Indian and Chinese space agencies, there are no shortages of plans to construct lunar bases and settlements. These will not only establish a human presence on the Moon, but facilitate missions to Mars and deeper into space.
The hidden costs of a hangover
Ten strategies to lose weight – backed by research
Everybody knows that to lose weight you should eat less and move more. But, of course, it’s not that simple; the combination of today’s environment and human biology can make it really, really hard to shed pounds. To reduce diseases caused by being overweight or obese, society needs to change, but those changes will be slow to come. We need effective weight-loss strategies now.
Hubble’s Lucky Observation of an Enigmatic Cloud
The little-known nebula IRAS 05437+2502 billows out among the bright stars and dark dust clouds that surround it in this striking image from the Hubble Space Telescope. It is located in the constellation of Taurus (the Bull), close to the central plane of our Milky Way galaxy. Unlike many of Hubble’s targets, this object has not been studied in detail and its exact nature is unclear.
How a NASA Scientist Looks in the Depths of the Great Red Spot to Find Water on Jupiter
For centuries, scientists have worked to understand the makeup of Jupiter. It’s no wonder: this mysterious planet is the biggest one in our solar system by far, and chemically, the closest relative to the Sun. Understanding Jupiter is key to learning more about how our solar system formed, and even about how other solar systems develop.
Why you can smell rain
15 of Spitzer's Greatest Discoveries From 15 Years in Space
There are so many water-worlds out there
Ever since the first exoplanet was confirmed in 1992, astronomers have found thousands of worlds beyond our Solar System. With more and more discoveries happening all the time, the focus of exoplanet research has begun to slowly shift from exoplanet discovery to exoplanet characterization. Essentially, scientists are now looking to determine the composition of exoplanets to determine whether or not they could support life.
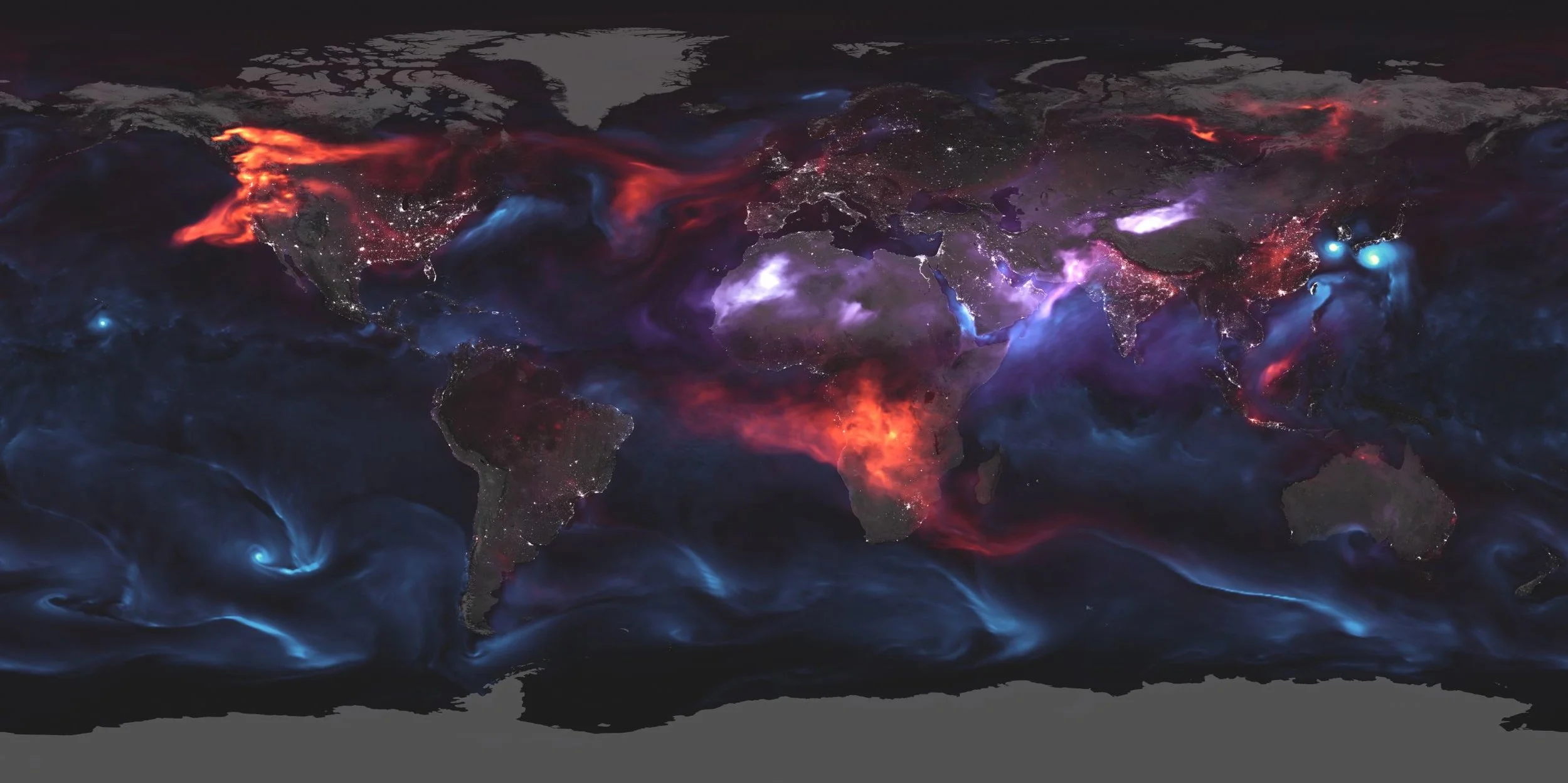
Just Another Day on Aerosol Earth
Take a deep breath. Even if the air looks clear, it is nearly certain that you will inhale millions of solid particles and liquid droplets. These ubiquitous specks of matter are known as aerosols, and they can be found in the air over oceans, deserts, mountains, forests, ice and every ecosystem in between.
Health Check: why do I get a headache when I haven’t had my coffee?
Oort clouds around other stars should be visible in the cosmic microwave background
For decades, scientists have theorized that beyond the edge of the Solar System, at a distance of up to 50,000 AU (0.79 ly) from the Sun, there lies a massive cloud of icy planetesimals known as the Oort Cloud. Named in honor of Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, this cloud is believed to be where long-term comets originate from. However, to date, no direct evidence has been provided to confirm the Oort Cloud’s existence.
Research Check: can sleeping too much lead to an early death?
Why the summer sound of noisy crickets is growing fainter
Designed to deceive: How gambling distorts reality and hooks your brain
To call gambling a “game of chance” evokes fun, random luck and a sense of collective engagement. These playful connotations may be part of why almost 80 percent of American adults gamble at some point in their lifetime. When I ask my psychology students why they think people gamble, the most frequent suggestions are for pleasure, money or the thrill.
Celebrating the 150th anniversary of helium’s discovery – why we need it more than ever
Watching helium gas lift balloons into the air is a lot of fun – or perhaps a tragedy if that balloon belonged to a small child who let it go. And, who hasn’t sipped the helium gas from a balloon and then quacked like Donald Duck? Although, that’s not the smartest thing to do since helium can displace the air in our lungs, or cause other problems with respiration.
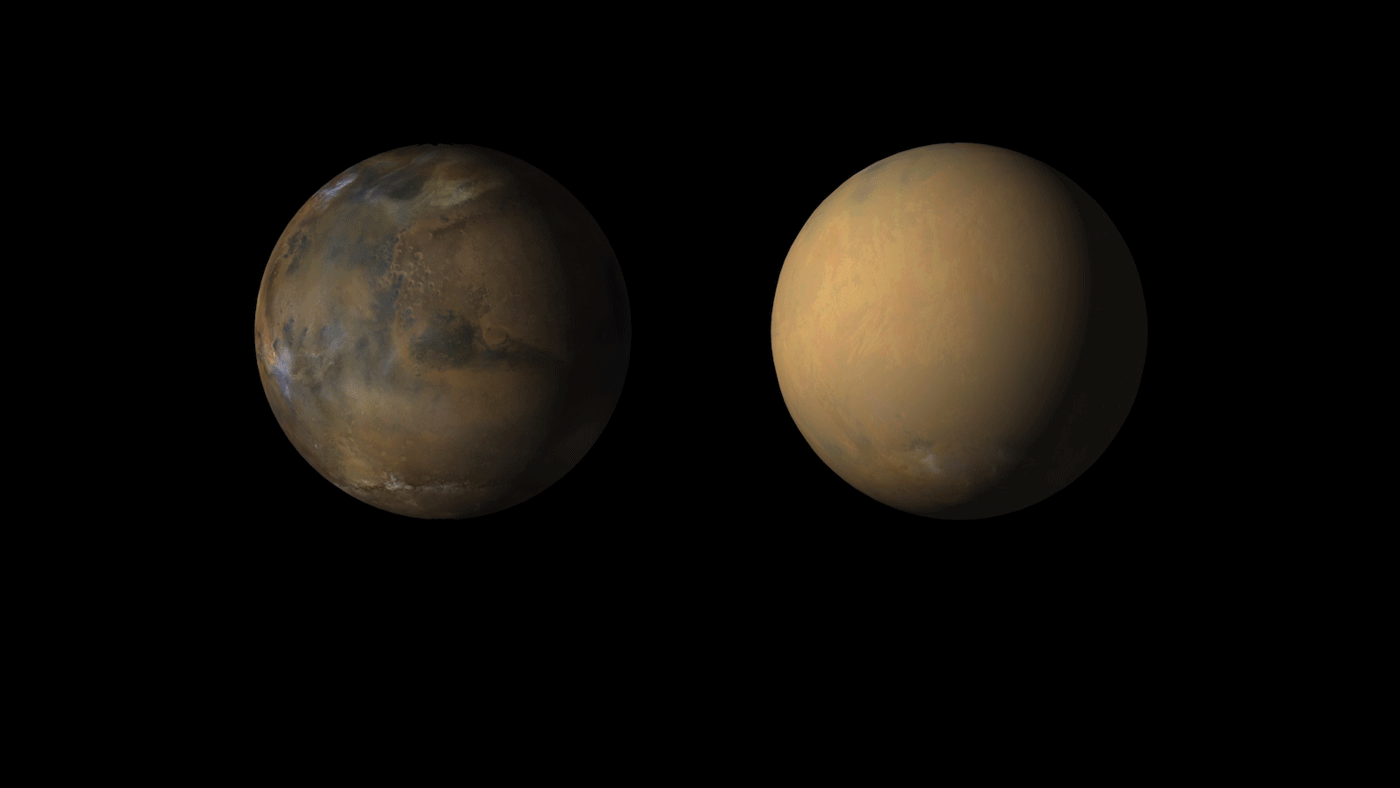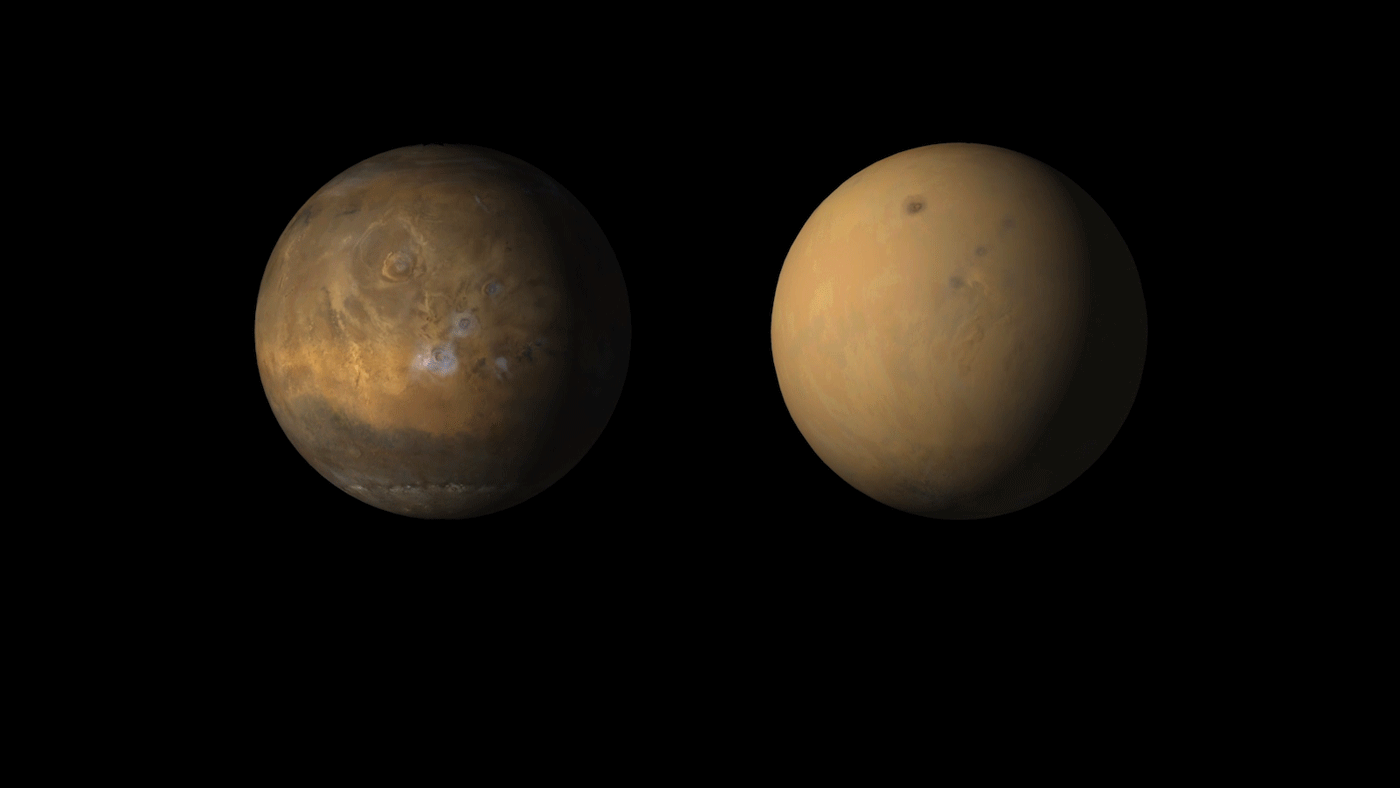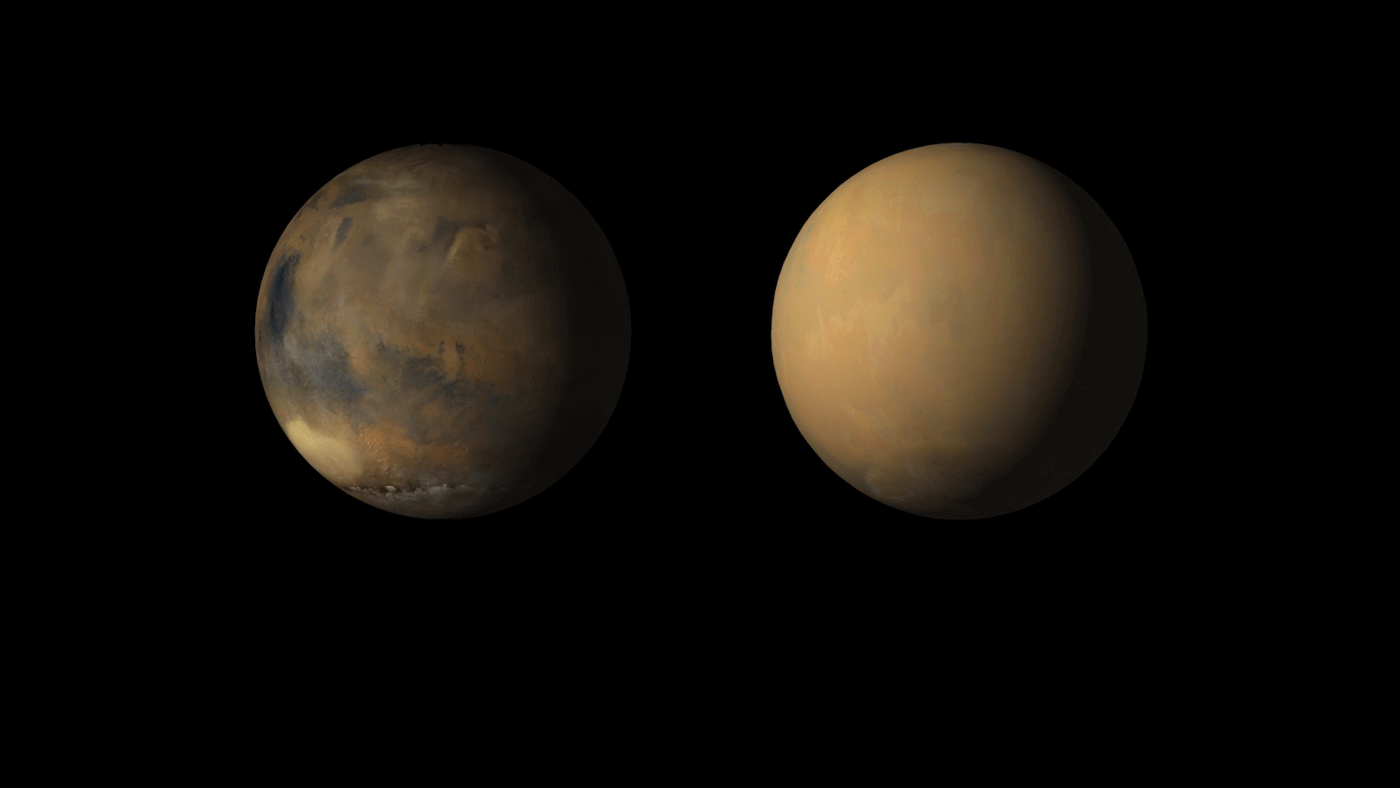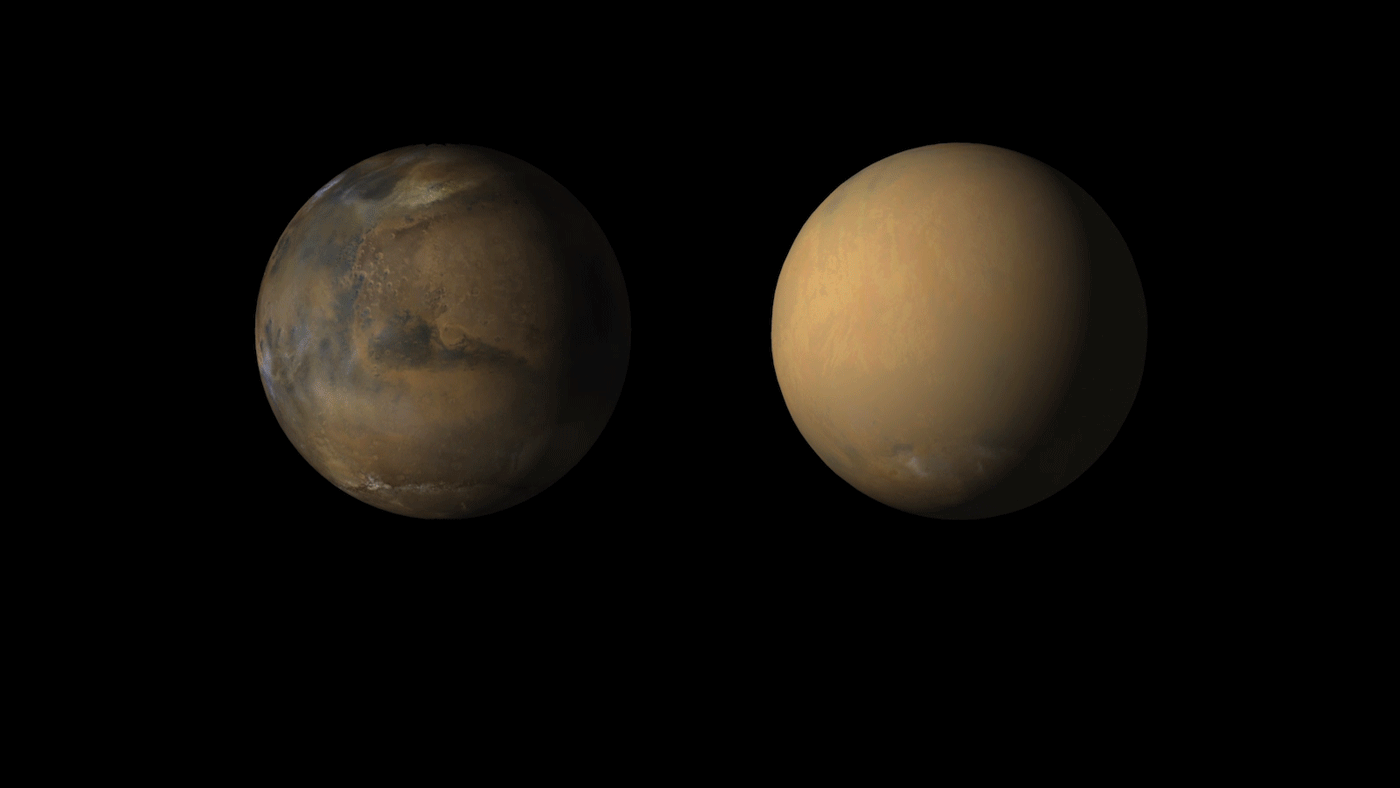
Six Things About Opportunity's Recovery Efforts
NASA's Opportunity rover has been silent since June 10, when a planet-encircling dust storm cut off solar power for the nearly-15-year-old rover. Now that scientists think the global dust storm is "decaying" -- meaning more dust is falling out of the atmosphere than is being raised back into it -- skies might soon clear enough for the solar-powered rover to recharge and attempt to "phone home."
Hubble Paints Picture of the Evolving Universe
Astronomers using the ultraviolet vision of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have captured one of the largest panoramic views of the fire and fury of star birth in the distant universe. The field features approximately 15,000 galaxies, about 12,000 of which are forming stars. Hubble’s ultraviolet vision opens a new window on the evolving universe, tracking the birth of stars over the last 11 billion years back to the cosmos’ busiest star-forming period, which happened about 3 billion years after the big bang.