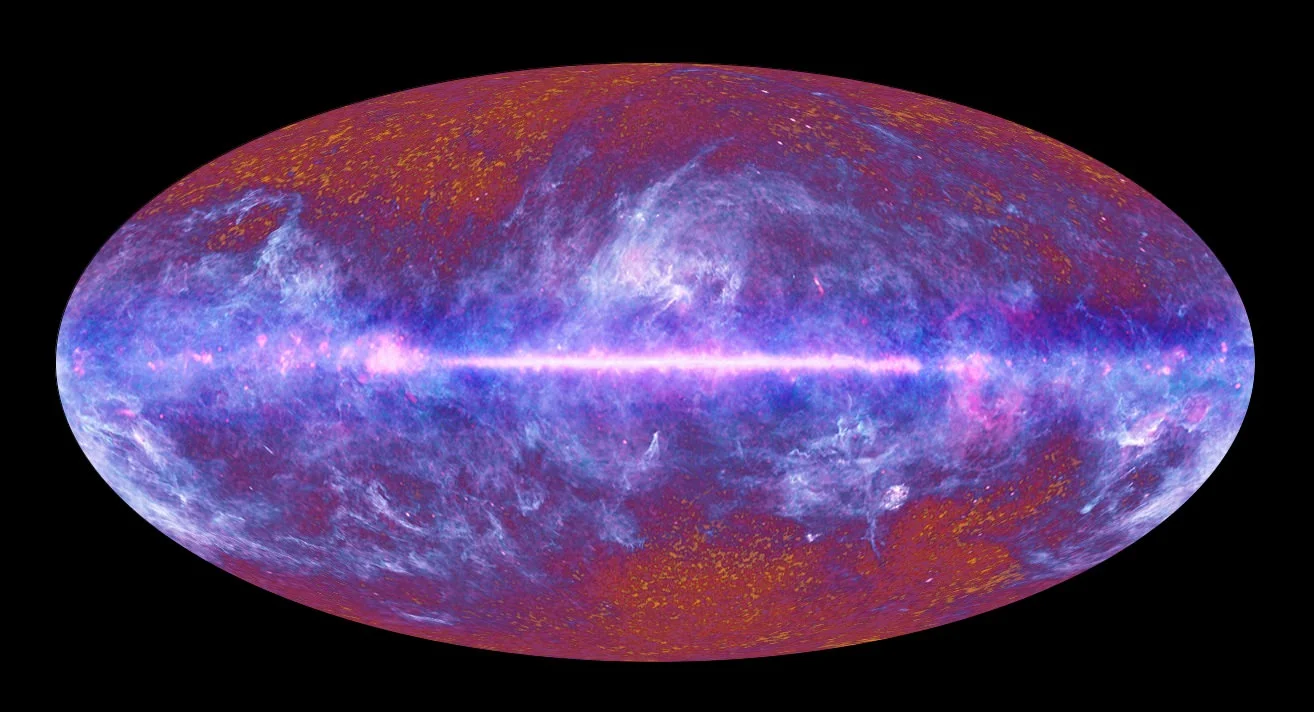
For thousands of years, human being have been contemplating the Universe and seeking to determine its true extent. And whereas ancient philosophers believed that the world consisted of a disk, a ziggurat or a cube surrounded by celestial oceans or some kind of ether, the development of modern astronomy opened their eyes to new frontiers. By the 20th century, scientists began to understand just how vast (and maybe even unending) the Universe really is.
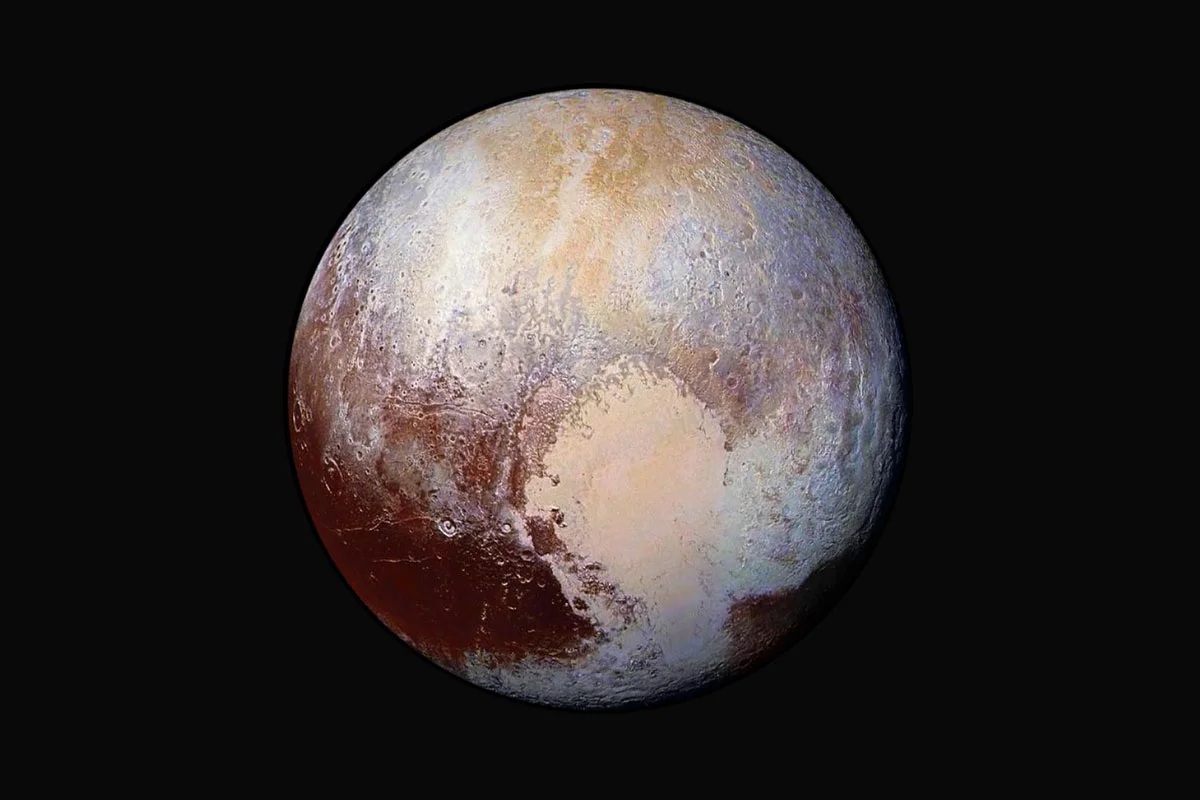
New Reasons why Pluto Should be Considered a Planet After All
In 2006, during their 26th General Assembly, the International Astronomic Union (IAU) passed a resolution to adopt a formal definition for the term “planet”. According to this definition, bodies that orbit the Sun, are spherical, do not orbit other bodies, and have cleared their orbits were designated planets. Pluto, and other such bodies that did not meet all of these requirements, would thereafter be designated as “dwarf planets”.
Europan Space Whales Anyone? Planets Covered by Deep Oceans Can Still Have Life on Them
In recent decades, astronomers have discovered many planets that they believe are “Earth-like” in nature, meaning that they appear to be terrestrial (i.e. rocky) and orbit their stars at the right distance to support the existence of liquid water on their surfaces. Unfortunately, recent research has indicated that many of these planets may in fact be “water worlds“, where water makes up a significant proportion of the planet’s mass.
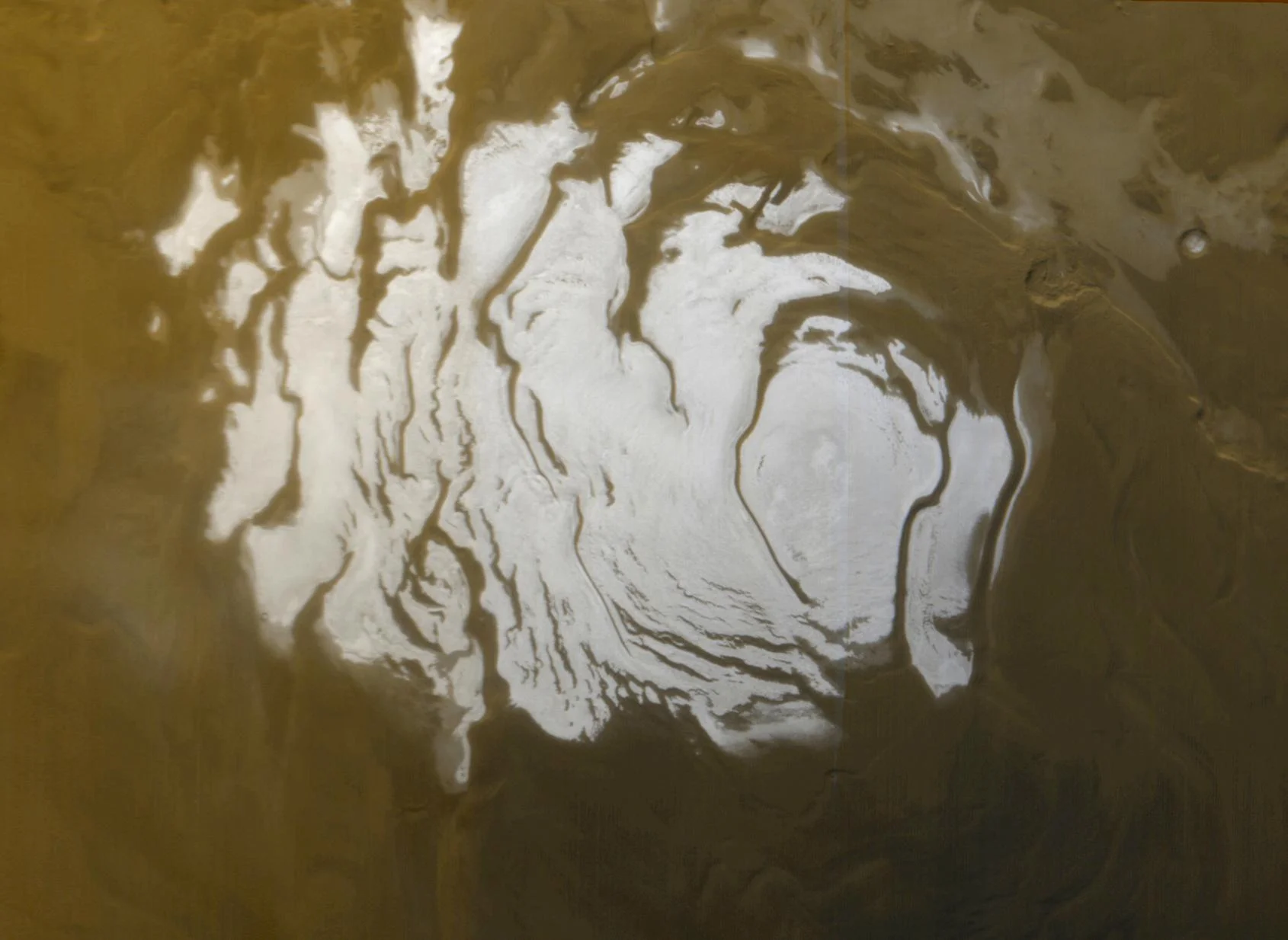
What on Earth could live in a salt water lake on Mars? An expert explains
Tantalizing new evidence has suggested that there may be a salty lake below a glacier on Mars. While brine at freezing temperatures does not sound like the most hospitable of environments, it is difficult to resist pondering whether organic life could survive – or even make some kind of living – there
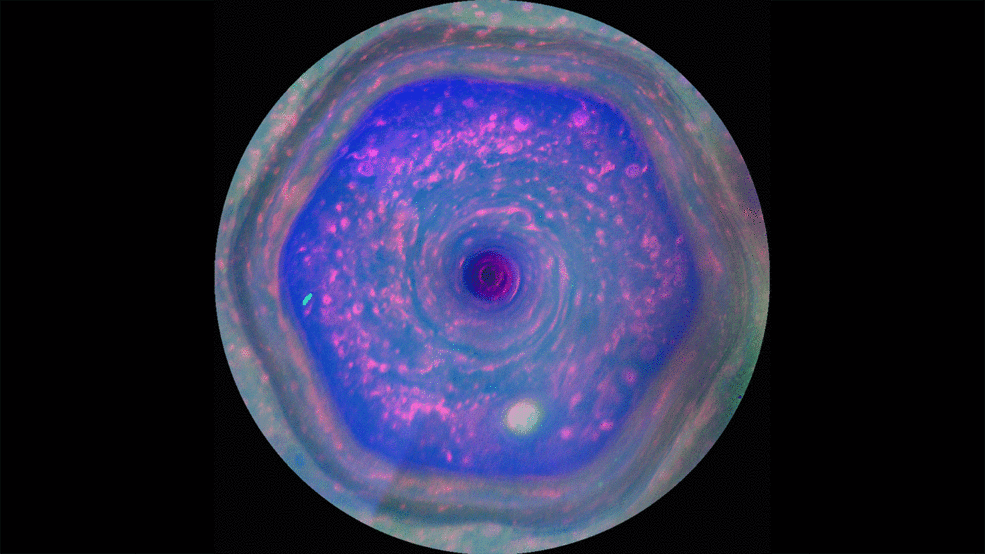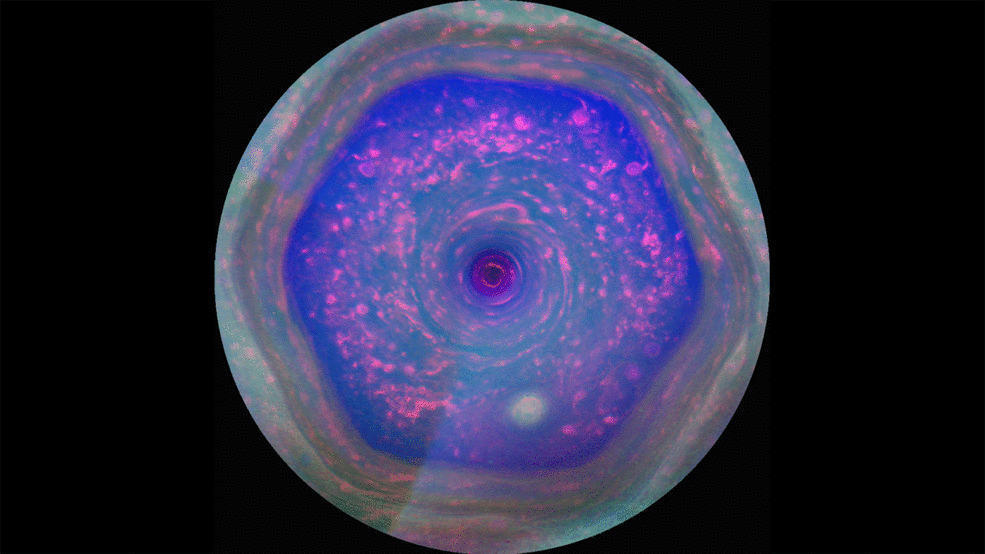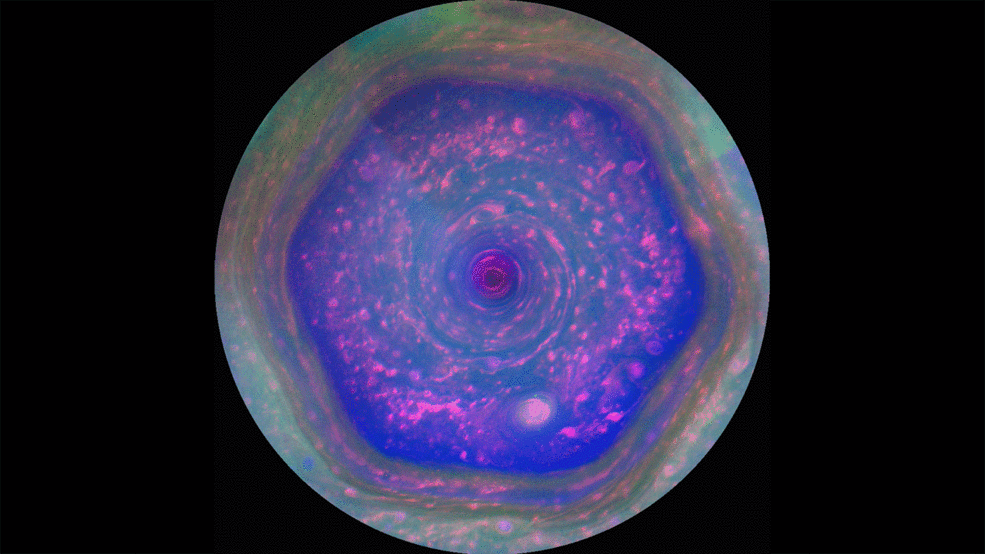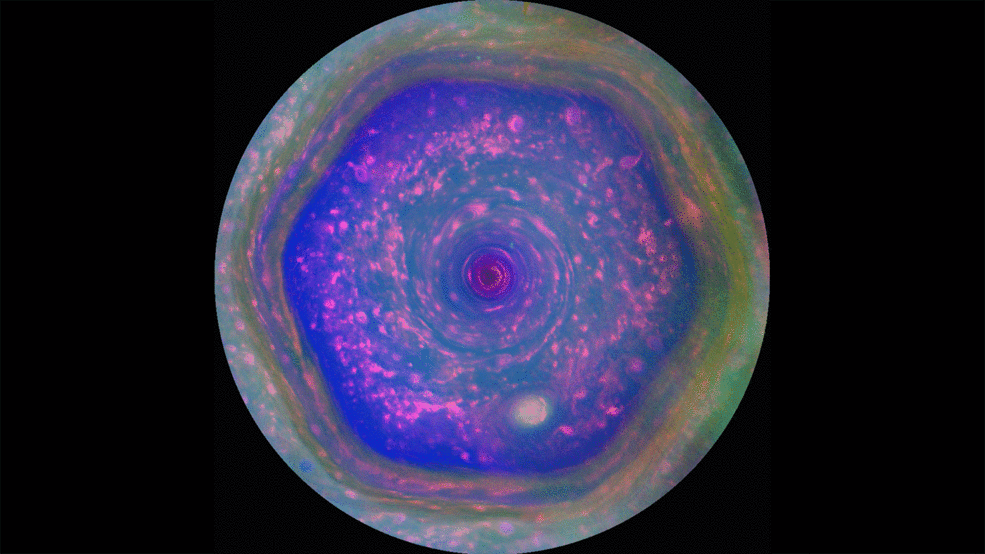
Saturn's Famous Hexagon May Tower Above the Clouds
How the next generation of ground-based super-telescopes will directly observe exoplanets
Over the past few decades, the number of extra-solar planets that have been detected and confirmed has grown exponentially. At present, the existence of 3,778 exoplanets have been confirmed in 2,818 planetary systems, with an additional 2,737 candidates awaiting confirmation. With this volume of planets available for study, the focus of exoplanet research has started to shift from detection towards characterization.
Hubble observes energetic lightshow at Saturn’s north pole
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space telescope have taken a series of spectacular images featuring the fluttering auroras at the north pole of Saturn. The observations were taken in ultraviolet light and the resulting images provide astronomers with the most comprehensive picture so far of Saturn’s northern aurora.
Telescope pierces into one of the biggest nebulae in the milky way to reveal its newly forming (and nearly dying) stars
Located about 7500 light-years from Earth, in the constellation of Carina, lies a star-forming region known as the Carina Nebula. This dynamic, evolving cloud of interstellar gas and dust measures about 300 light-years in diameter and is one of the Milky Way’s largest star-forming regions. It is also an exercise in contrasts, consisting of bright regions of gas illuminated by intense stellar radiation and dark pillars of dust that obscure star formation.
Building bricks on the moon from lunar dust
In the coming decades, many space agencies hope to conduct crewed missions to the Moon and even establish outposts there. In fact, between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), Roscosmos, and the Indian and Chinese space agencies, there are no shortages of plans to construct lunar bases and settlements. These will not only establish a human presence on the Moon, but facilitate missions to Mars and deeper into space.
Hubble’s Lucky Observation of an Enigmatic Cloud
The little-known nebula IRAS 05437+2502 billows out among the bright stars and dark dust clouds that surround it in this striking image from the Hubble Space Telescope. It is located in the constellation of Taurus (the Bull), close to the central plane of our Milky Way galaxy. Unlike many of Hubble’s targets, this object has not been studied in detail and its exact nature is unclear.
How a NASA Scientist Looks in the Depths of the Great Red Spot to Find Water on Jupiter
For centuries, scientists have worked to understand the makeup of Jupiter. It’s no wonder: this mysterious planet is the biggest one in our solar system by far, and chemically, the closest relative to the Sun. Understanding Jupiter is key to learning more about how our solar system formed, and even about how other solar systems develop.
15 of Spitzer's Greatest Discoveries From 15 Years in Space
There are so many water-worlds out there
Ever since the first exoplanet was confirmed in 1992, astronomers have found thousands of worlds beyond our Solar System. With more and more discoveries happening all the time, the focus of exoplanet research has begun to slowly shift from exoplanet discovery to exoplanet characterization. Essentially, scientists are now looking to determine the composition of exoplanets to determine whether or not they could support life.
Oort clouds around other stars should be visible in the cosmic microwave background
For decades, scientists have theorized that beyond the edge of the Solar System, at a distance of up to 50,000 AU (0.79 ly) from the Sun, there lies a massive cloud of icy planetesimals known as the Oort Cloud. Named in honor of Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, this cloud is believed to be where long-term comets originate from. However, to date, no direct evidence has been provided to confirm the Oort Cloud’s existence.
Six Things About Opportunity's Recovery Efforts
NASA's Opportunity rover has been silent since June 10, when a planet-encircling dust storm cut off solar power for the nearly-15-year-old rover. Now that scientists think the global dust storm is "decaying" -- meaning more dust is falling out of the atmosphere than is being raised back into it -- skies might soon clear enough for the solar-powered rover to recharge and attempt to "phone home."
Hubble Paints Picture of the Evolving Universe
Astronomers using the ultraviolet vision of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have captured one of the largest panoramic views of the fire and fury of star birth in the distant universe. The field features approximately 15,000 galaxies, about 12,000 of which are forming stars. Hubble’s ultraviolet vision opens a new window on the evolving universe, tracking the birth of stars over the last 11 billion years back to the cosmos’ busiest star-forming period, which happened about 3 billion years after the big bang.
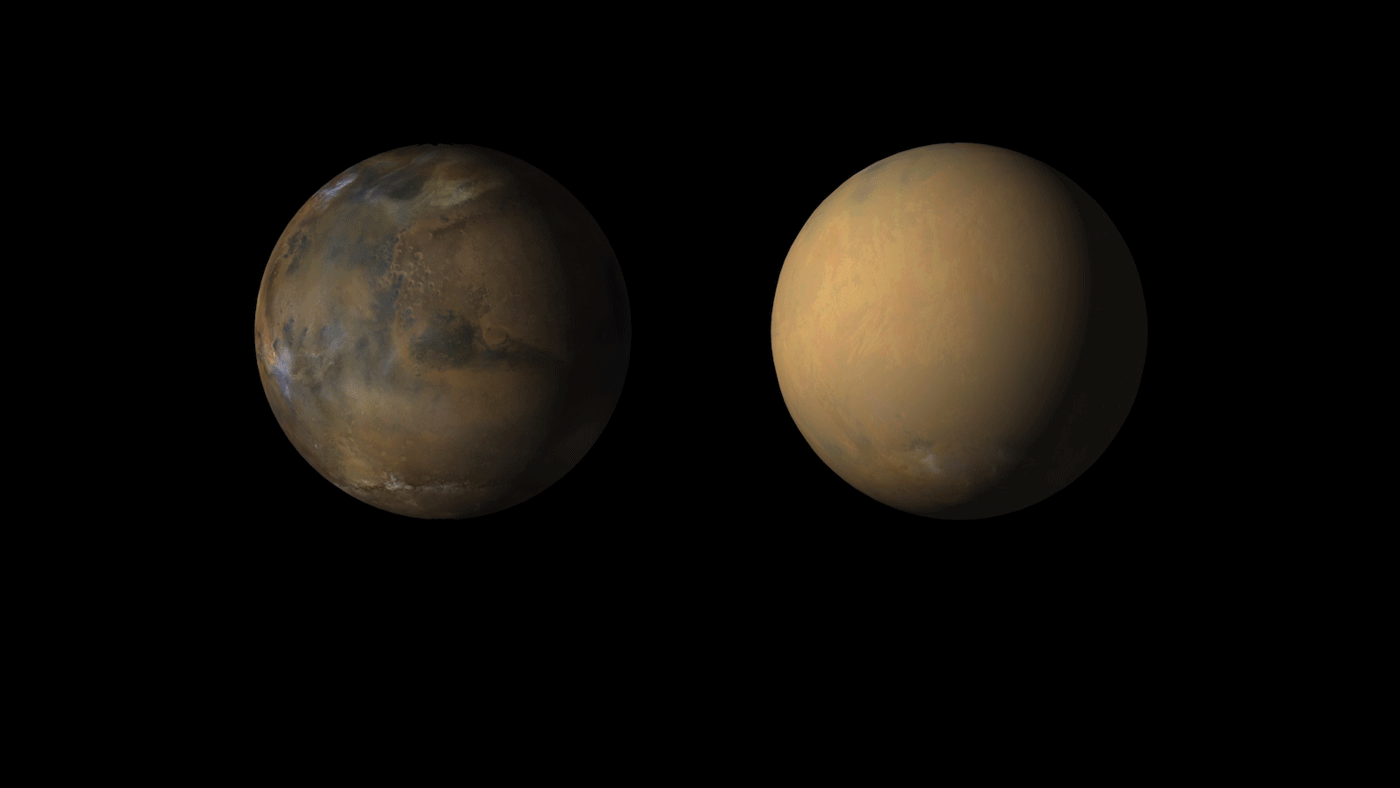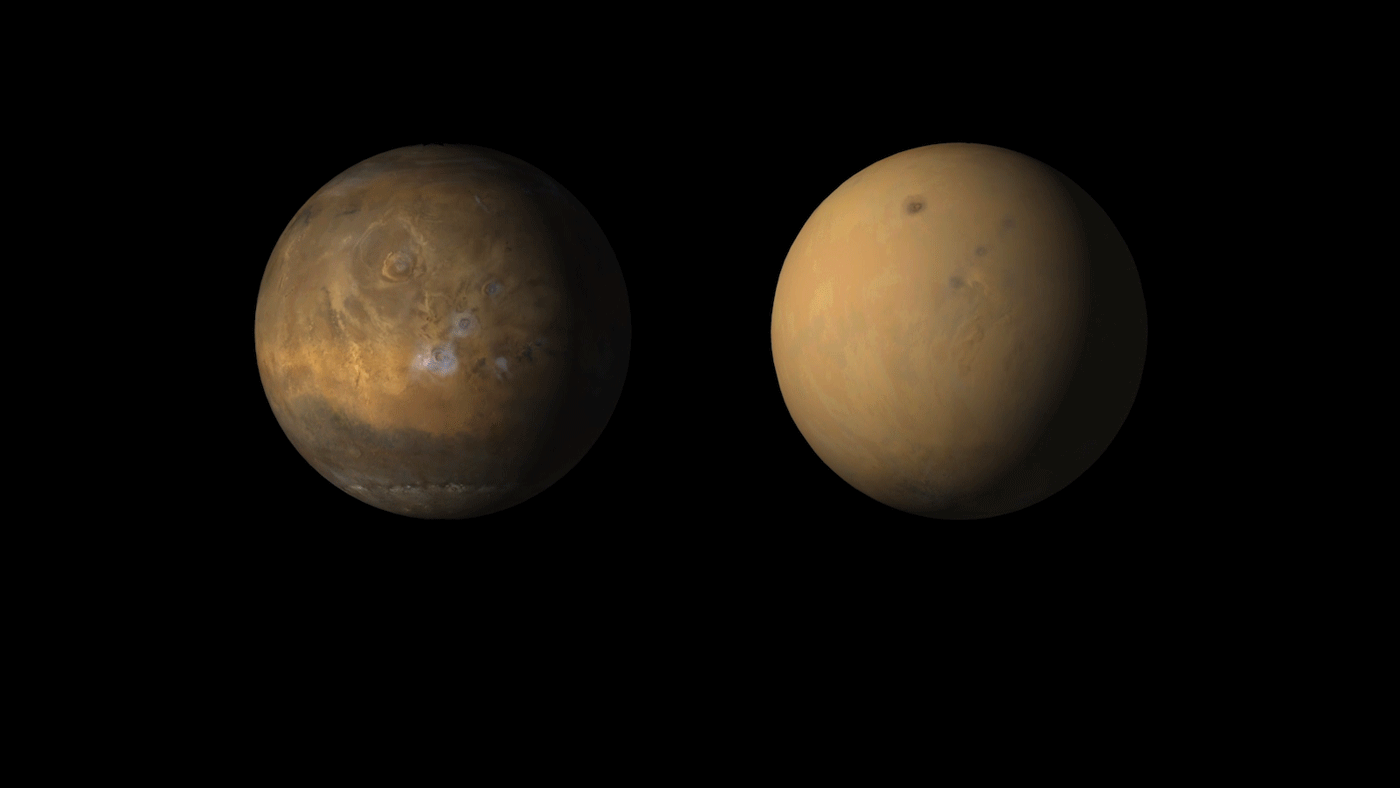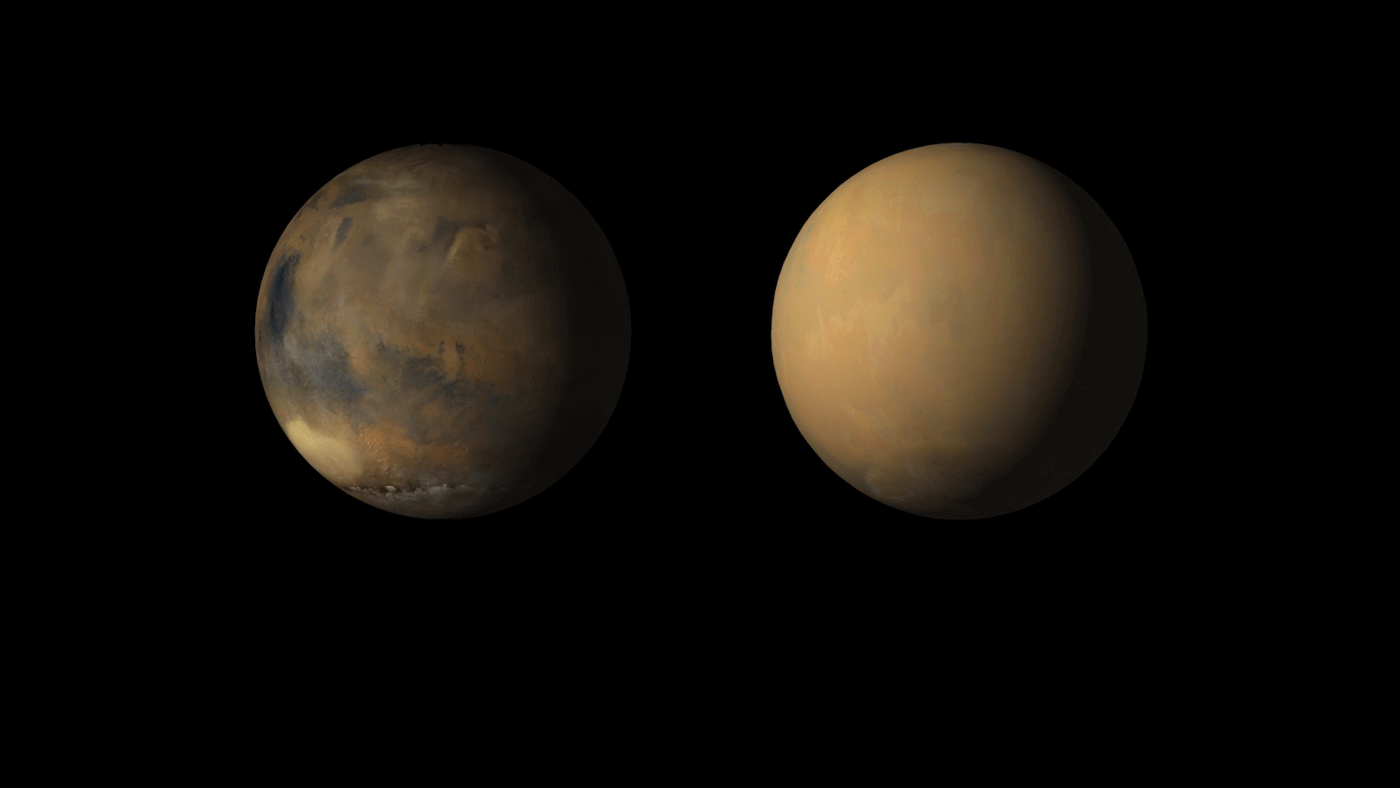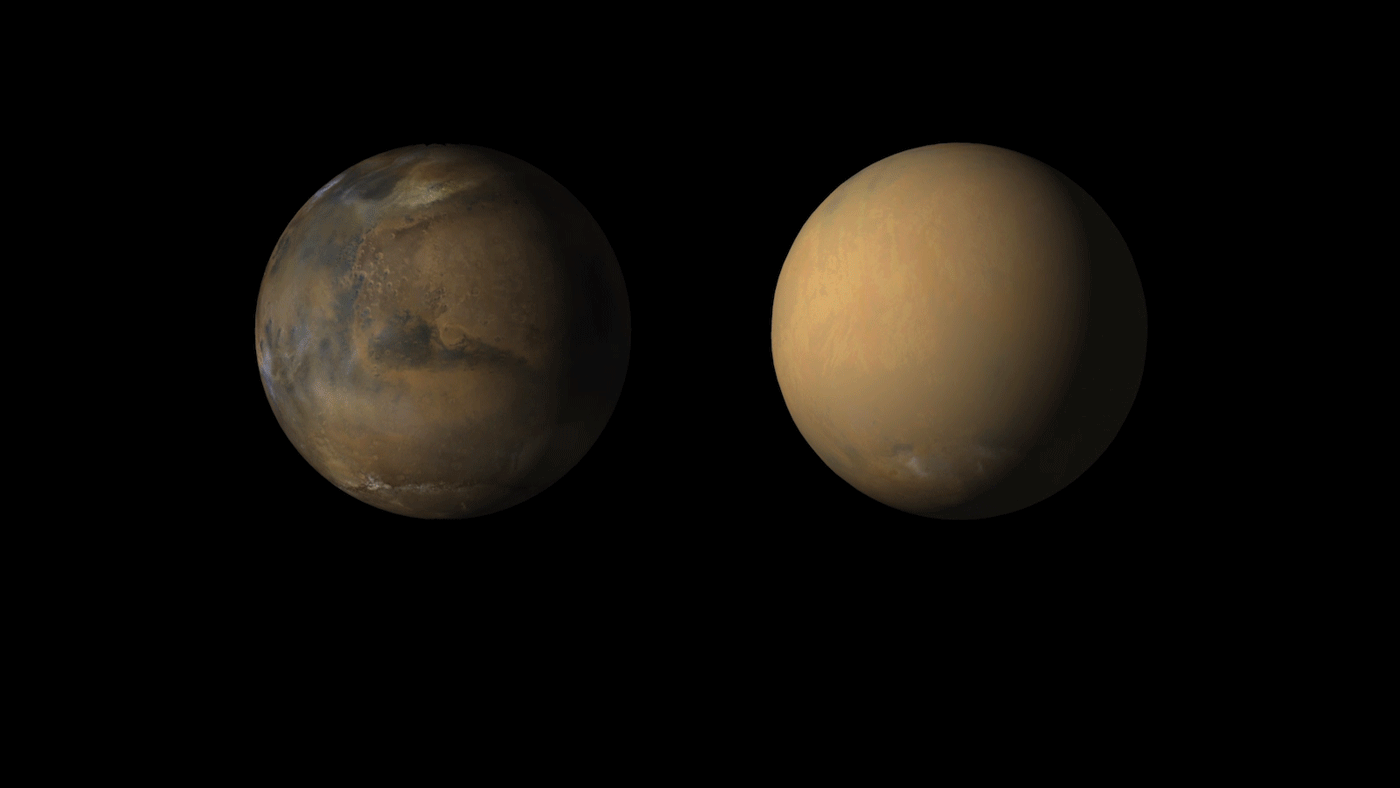
As the Martian dust storm subsides, there’s still no word from opportunity
Martian dust storms are a pretty common occurrence, and generally happen whenever the southern hemisphere is experiencing summer. Though they can begin quite suddenly, these storms typically stay contained to a local area and last only about a few weeks. However, on occasion, Martian dust storms can grow to become global phenomena, covering the entire planet.
Trees are made of human breath
Outside my office window, two skilled workers complete a hard and dirty job. They’re cutting the felled trunk of a tree into small enough pieces to be thrown into the back of a truck with the rest of the chipped remains. I know that this act was ultimately for my own safety. I, like tens of thousands of others over the past 50 years, regularly walked beneath the canopy of that tree.