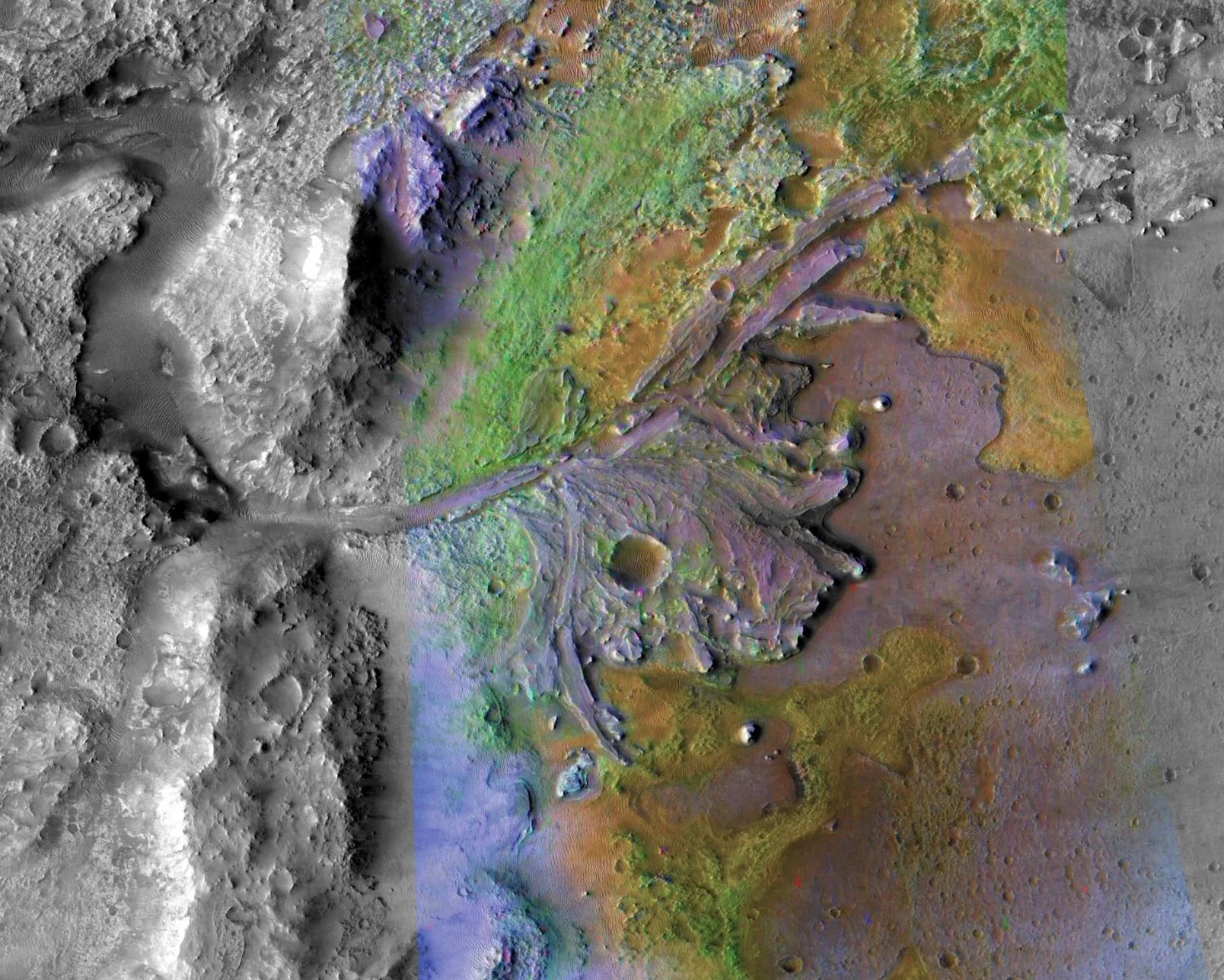
NASA has chosen Jezero Crater as the landing site for its upcoming Mars 2020 rover mission after a five year search, during which every available detail of more than 60 candidate locations on the Red Planet was scrutinized and debated by the mission team and the planetary science community.
Abell 1033: To Boldly Go into Colliding Galaxy Clusters
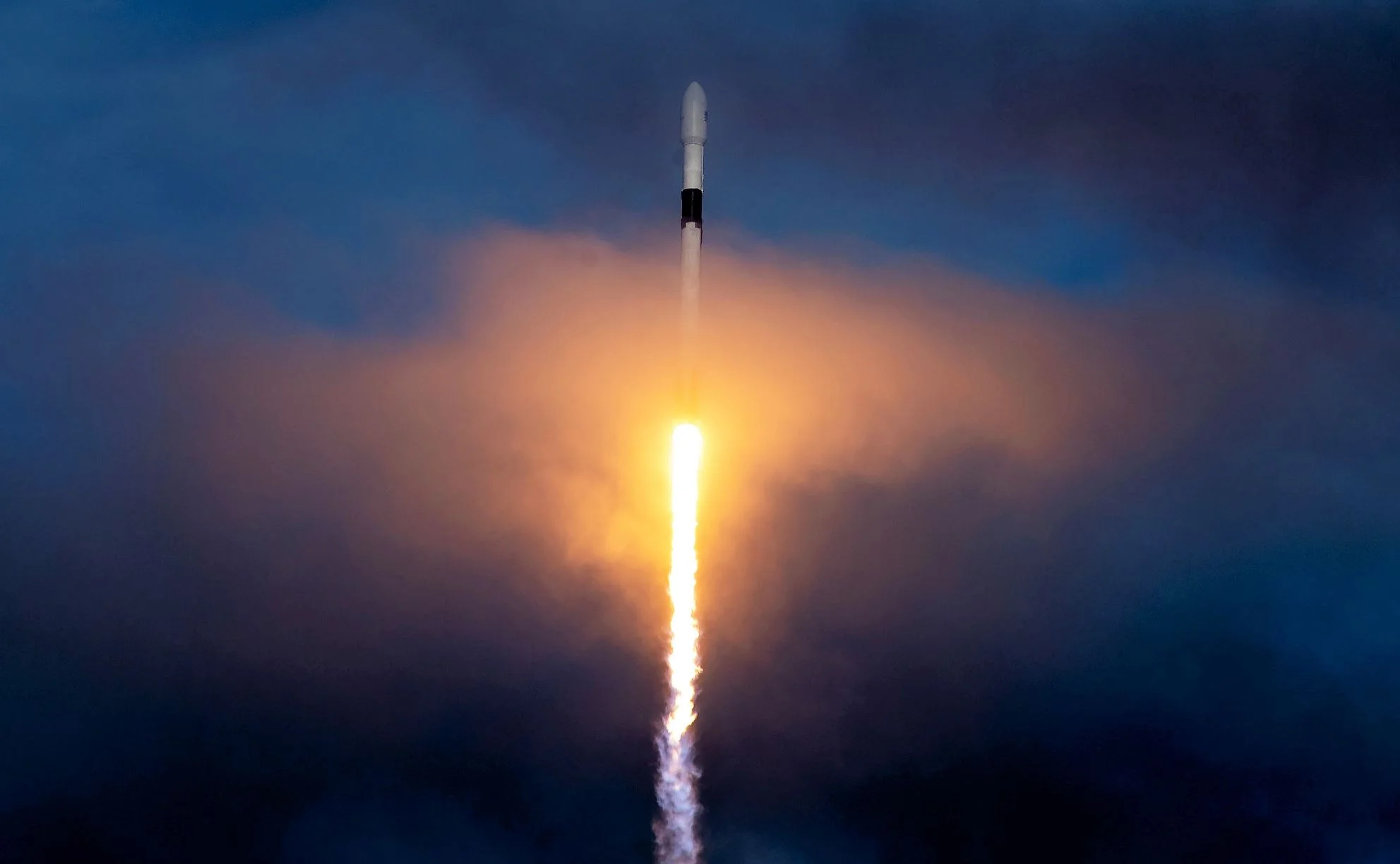
SpaceX Gives More Details on how their Starlink Internet Service Will Work
For years, Elon Musk has talked about his plans to provide broadband internet access to the world using a constellation of satellites. Known as Starlink, this constellation was originally going to of nearly 12,000 low-cost satellites providing a terabit internet service. The first batch of these satellites is scheduled to launch in June of 2019, with the full constellation being deployed by the mid-2020s
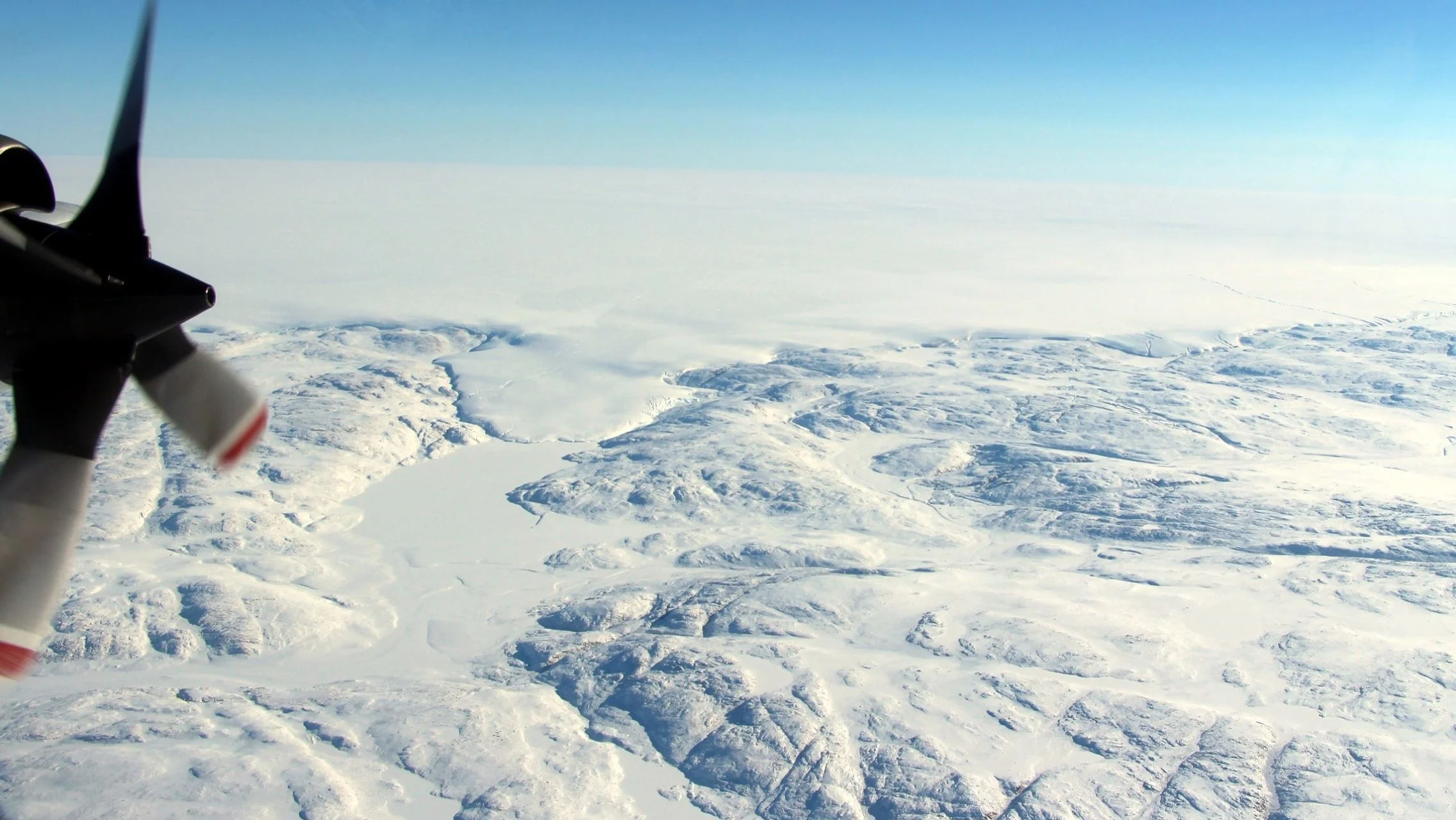
An Unexpected Discovery Under Greenland Ice!
An international team of researchers, including a NASA glaciologist, has discovered a large meteorite impact crater hiding beneath more than a half-mile of ice in northwest Greenland. The crater — the first of any size found under the Greenland ice sheet — is one of the 25 largest impact craters on Earth, measuring roughly 1,000 feet deep and more than 19 miles in diameter, an area slightly larger than that inside Washington’s Capital Beltway
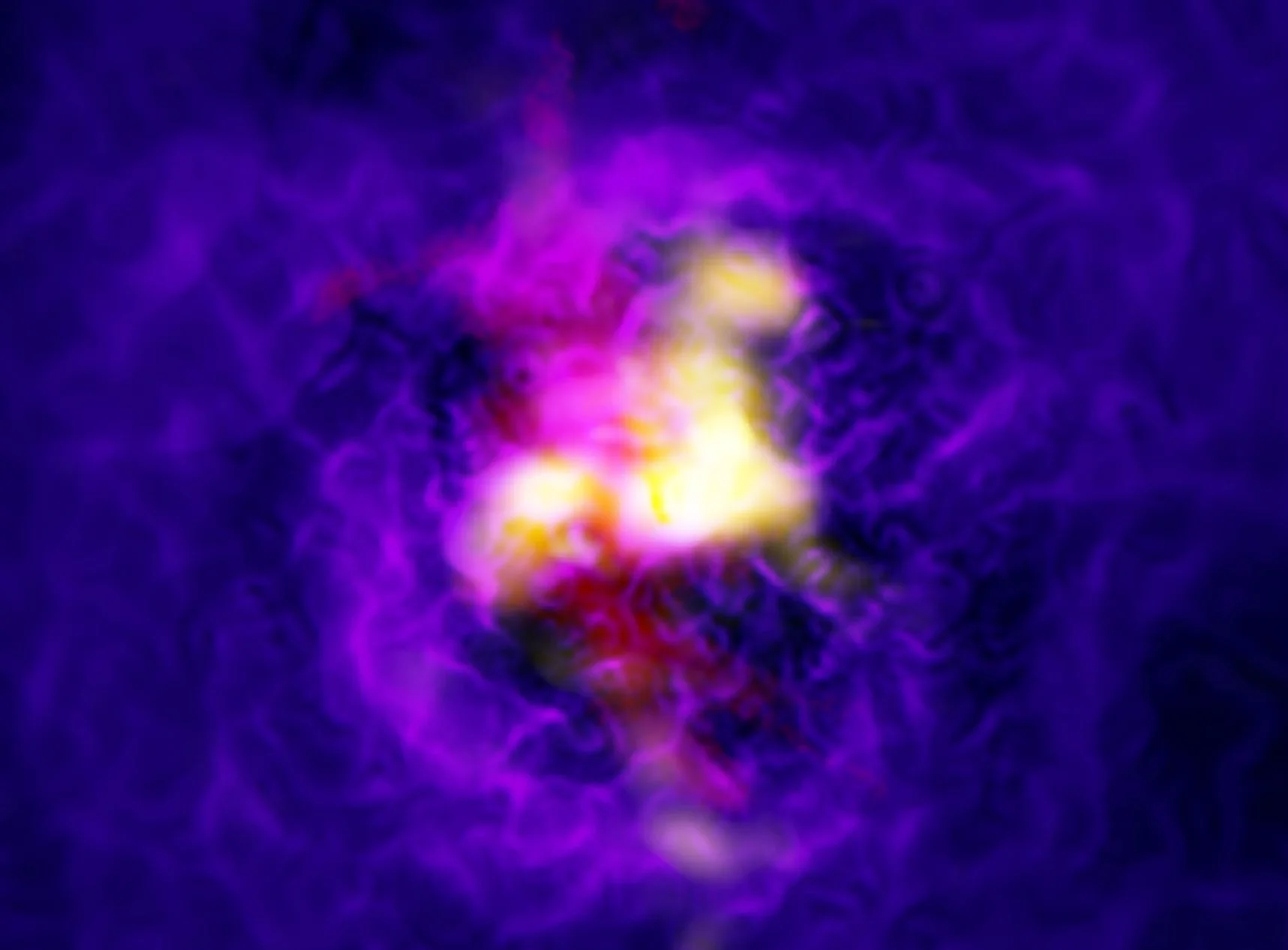
Here’s how the ‘brightest’ object in the universe formed
Active galaxies are some of the most luminous and impressive objects in the sky. They tend to be massive, distant and emit extraordinary amounts of energy as material falls into the supermassive black hole that lurks at their centre. Astronomers have recently discovered that some of them are also hidden from plain view by huge amounts of gas and smoke-like dust. But it is unclear how these rare objects form and feed.
Digging into the ice on Europa with lasers
Ever since the Pioneer and Voyager probes passed through the Jovian system in the 1970s, NASA and other space agencies have dreamed of one-day sending a mission to Europa. Beyond Earth, it is considered one of the most promising candidates for finding life, which could exist in the subsurface ocean that lies beneath the moon’s icy crust.
The Most Luminous Galaxy Is Eating Its Neighbors
The most luminous galaxy ever discovered is cannibalizing not one, not two, but at least three of its smaller neighbors, according to a new study published today (Nov. 15) in the journal Science and coauthored by scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The material that the galaxy is stealing from its neighbors is likely contributing to its uber-brightness, the study shows.
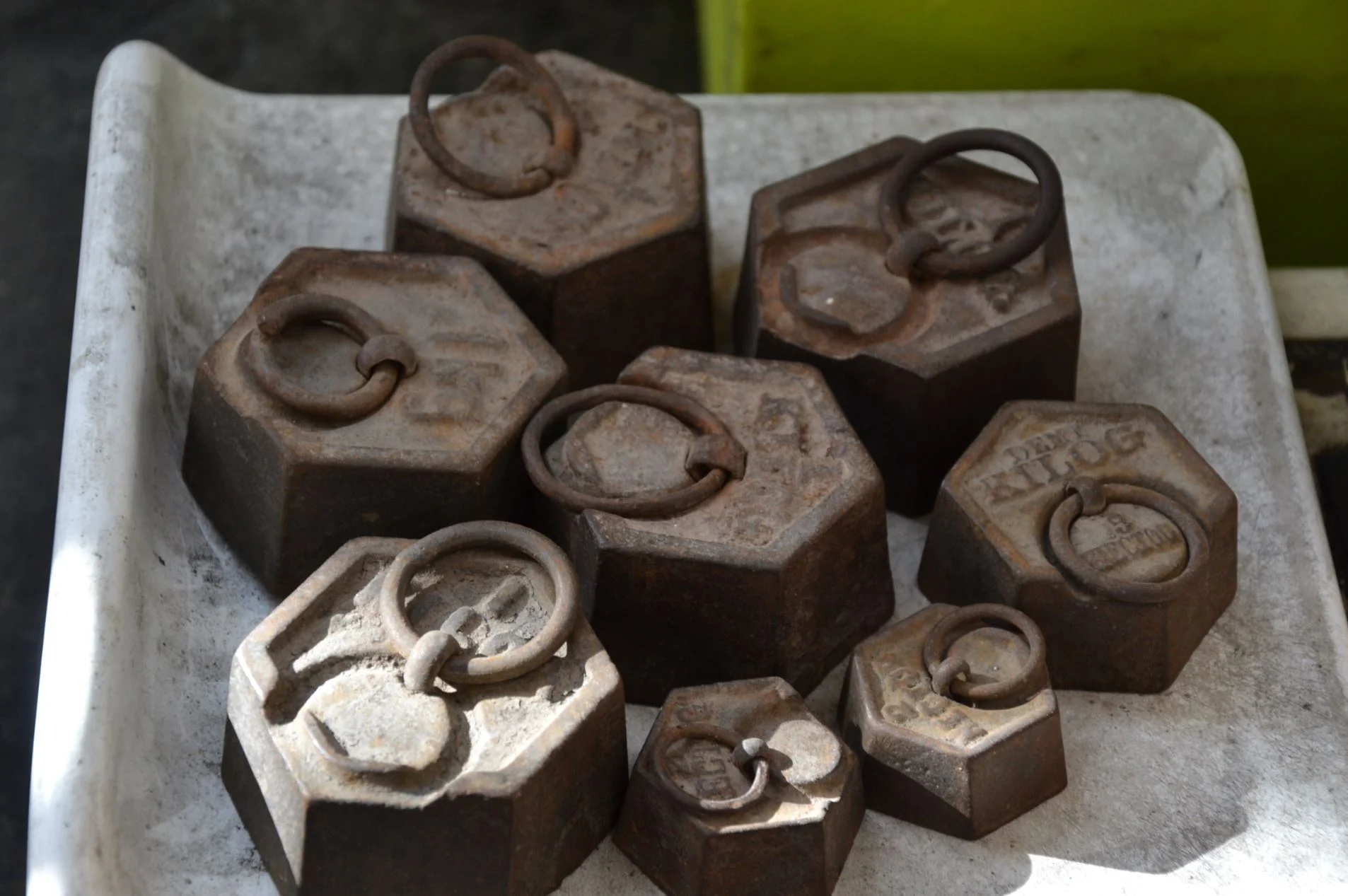
The kilogram is being redefined – a physicist explains
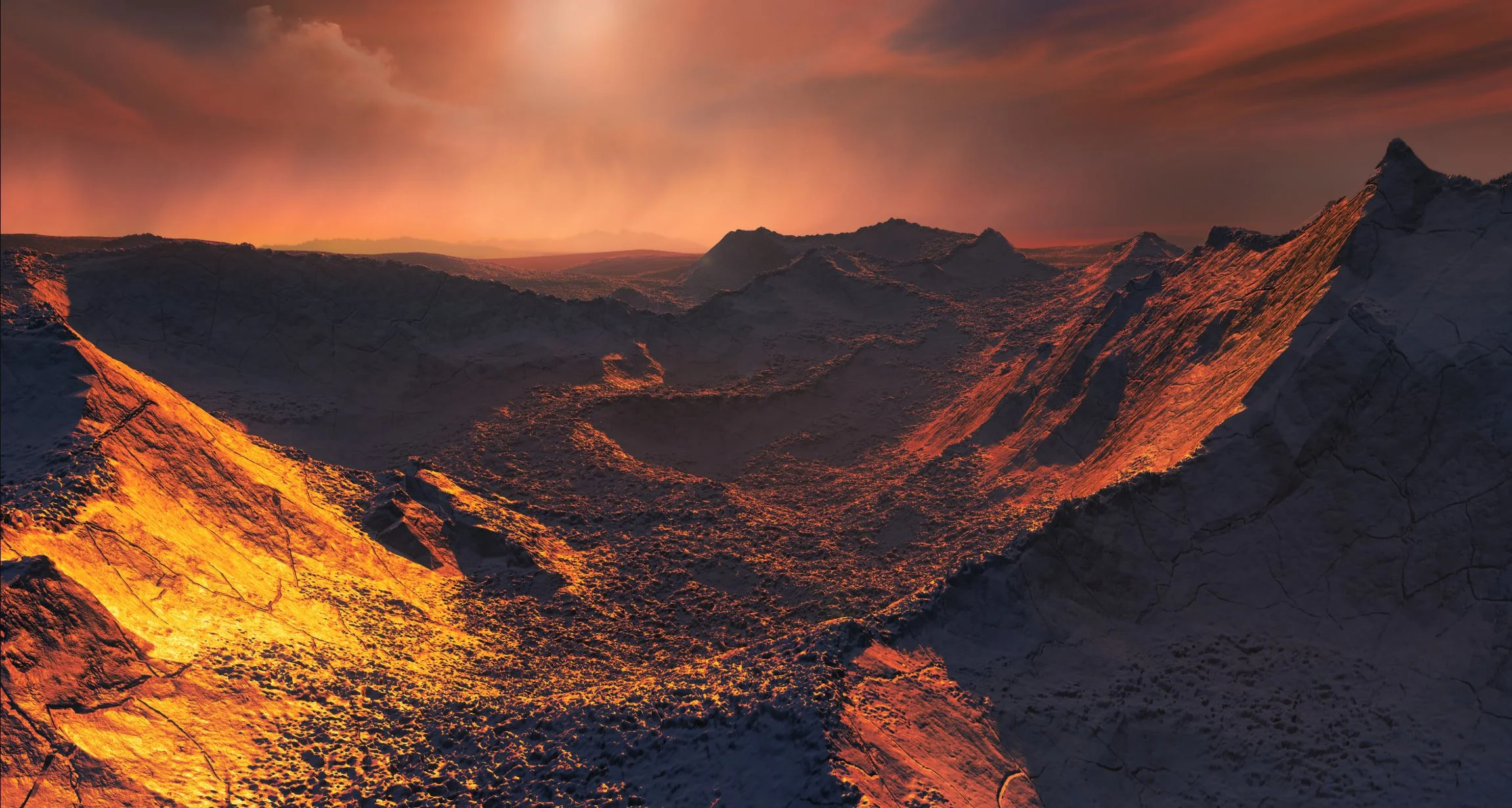
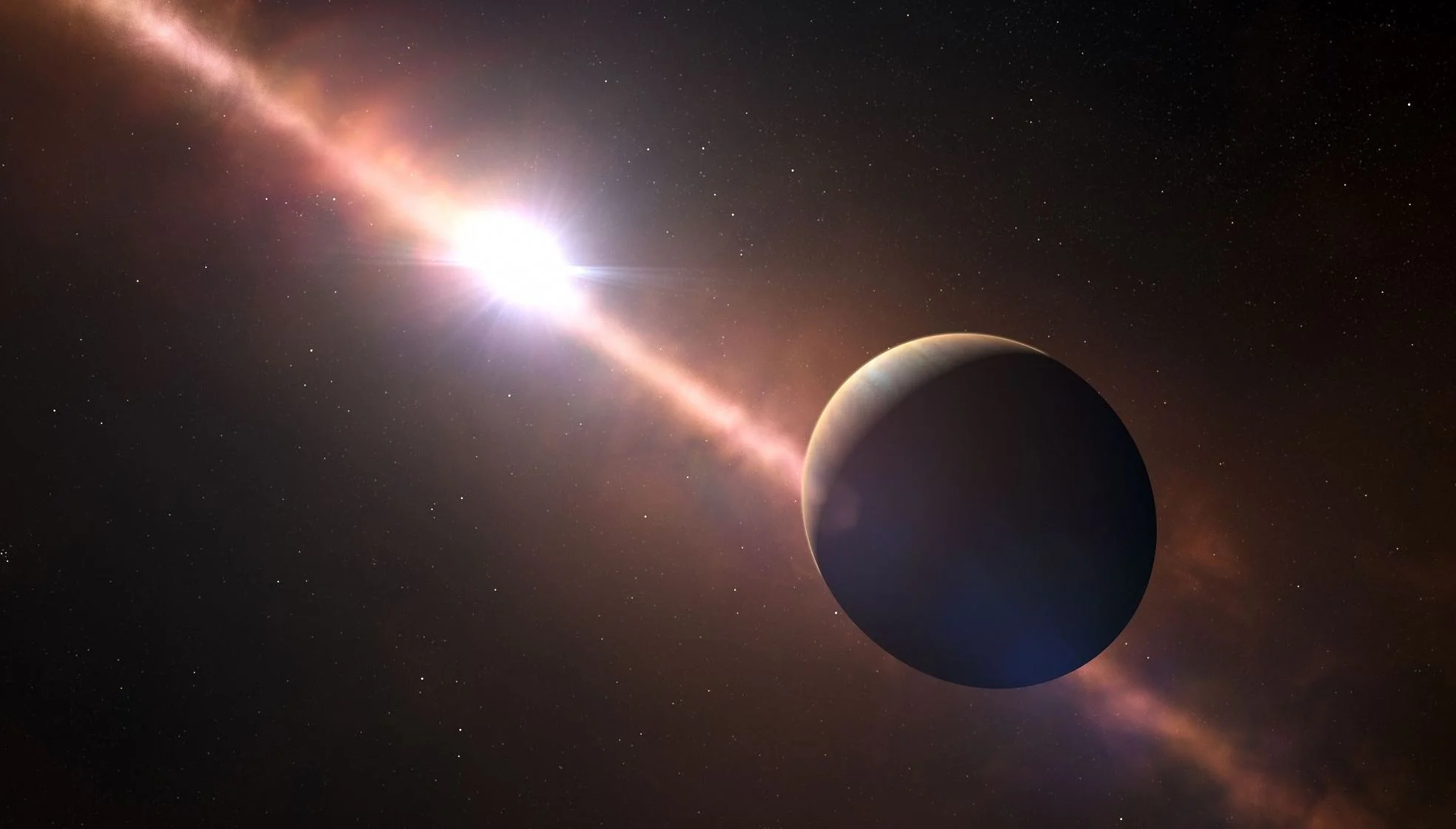
A super-Earth found in our stellar back yard!
Direct Observations of a Planet Orbiting a Star 63 Light-Years Away
In the past thirty years, the number of planets discovered beyond our Solar System has grown exponentially. Unfortunately, due to the limitations of our technology, the vast majority of these exoplanets have been discovered by indirect means, often by detecting the transits of planets in front of their stars (the Transit Method) or by the gravitational influence they exert on their star (the Radial Velocity Method)
Not all the Earth’s Water Came From Comets
Small Tissue Chips in Space a Big Leap Forward for Research
Ancient Star Found that’s Only Slightly Younger than the Universe Itself
According to the most widely-accepted cosmological theory, the first stars in our Universe formed roughly 150 to 1 billion years after the Big Bang. Over time, these stars began to come together to form globular clusters, which slowly coalesced to form the first galaxies – including our very own Milky Way. For some time, astronomers have held that this process began for our galaxy some 13.51 billion years ago.
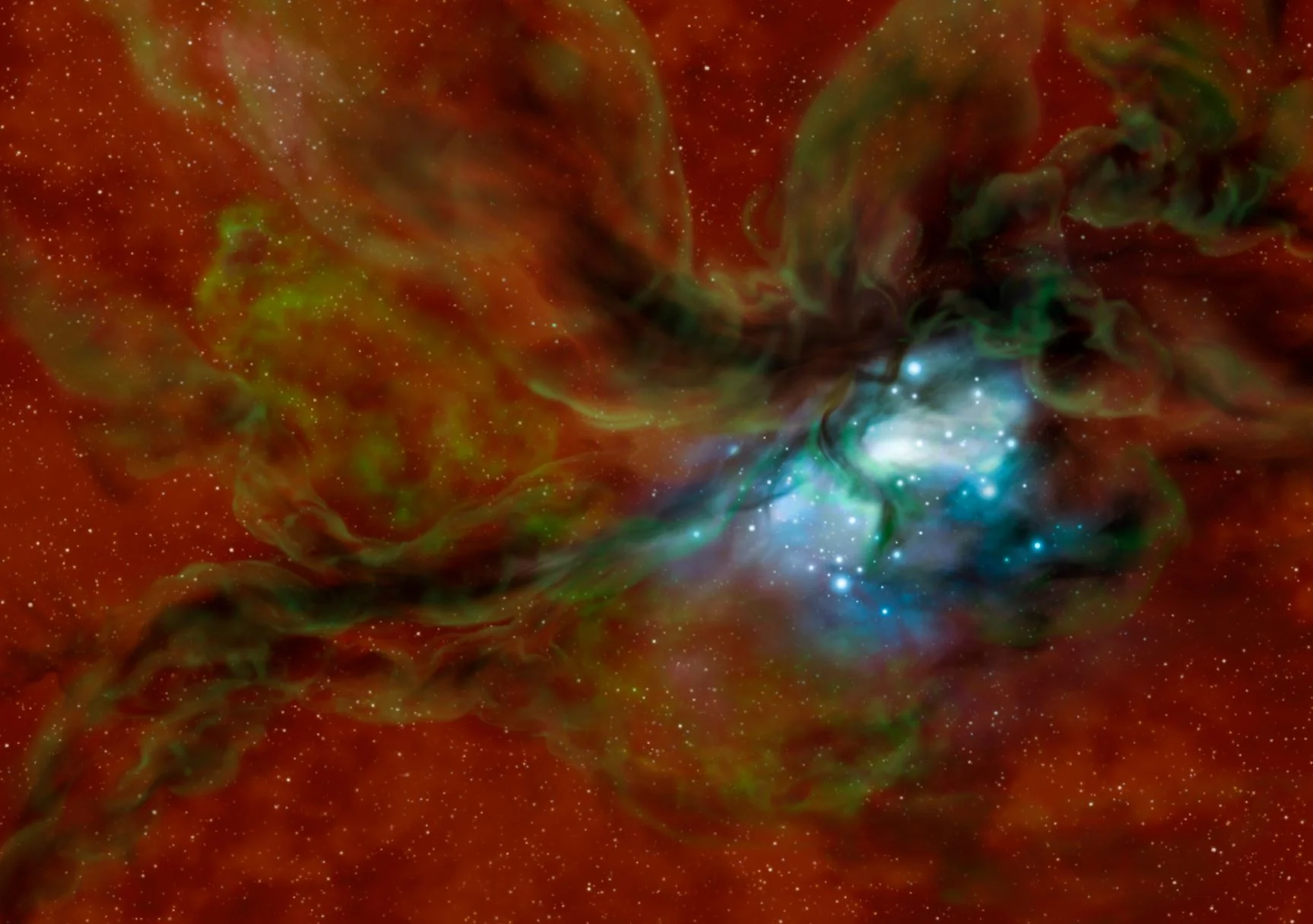
Cosmic Collisions: SOFIA Unravels the Mysterious Formation of Star Clusters
Great Pyramid: how my research on ancient Egyptian poetry led to an amazing discovery
What began as an expedition to record the inscriptions of ancient Egyptian quarry workers produced a remarkable discovery about the Great Pyramid at Giza. My colleagues and I in the Anglo-French joint archaeological mission to the ancient quarry site of Hatnub recently revealed the existence of a well-preserved haulage ramp dating to the time of the Great Pyramid, roughly 4,500 years ago.
ALMA and MUSE Detect Galactic Fountain
Observations by ALMA and data from the MUSE spectrograph on ESO’s VLT have revealed a colossal fountain of molecular gas powered by a black hole in the brightest galaxy of the Abell 2597 cluster — the full galactic cycle of inflow and outflow powering this vast cosmic fountain has never before been observed in one system.
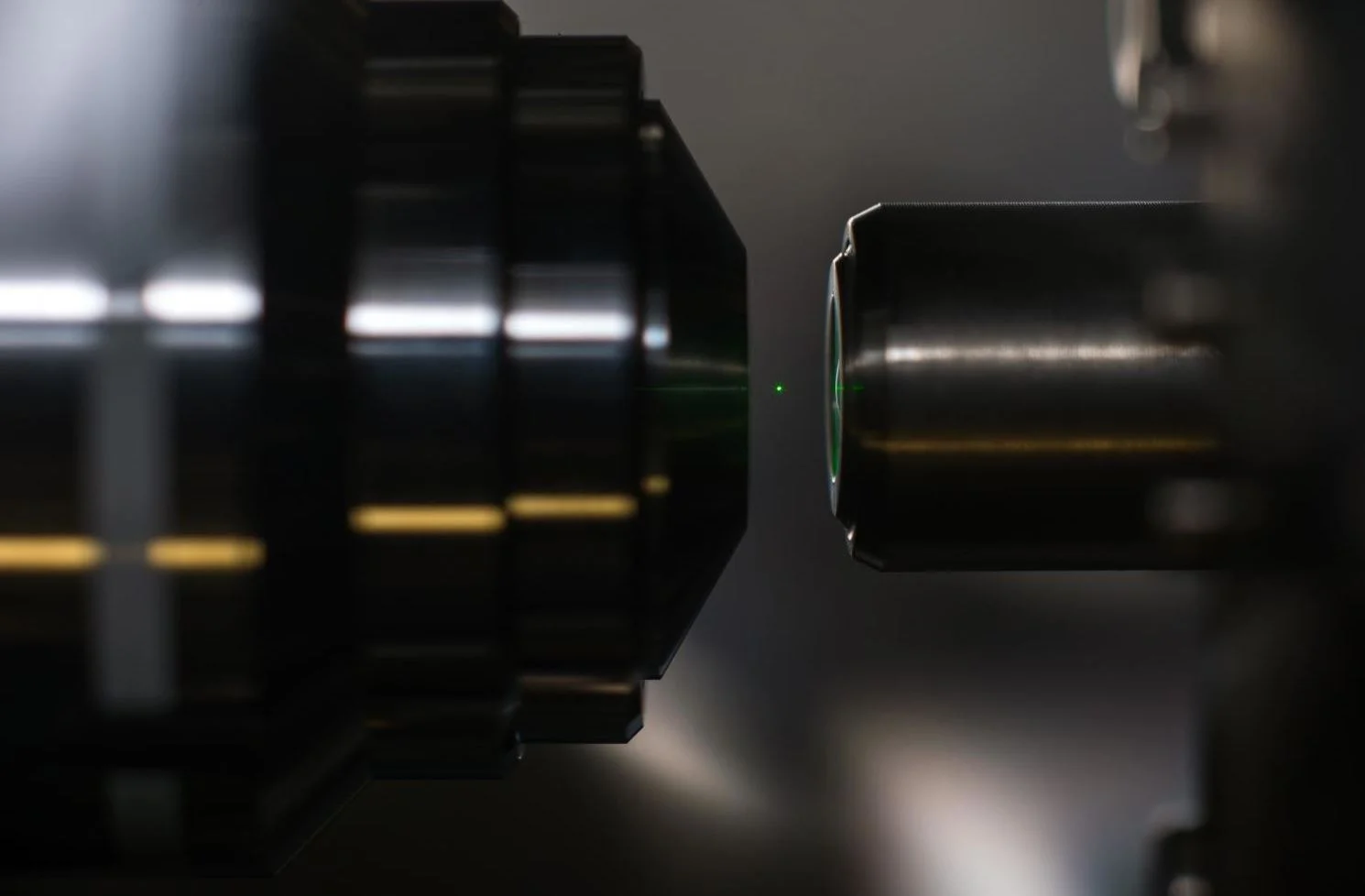
Experiments with optical tweezers race to test the laws of quantum mechanics
One might think that the optical tweezer – a focused laser beam that can trap small particles – is old hat by now. After all, the tweezer was invented by Arthur Ashkin in 1970. And he received the Nobel Prize for it this year - presumably after its main implications had been realized during the last half-century.
Could consciousness all come down to the way things vibrate?
Why is my awareness here, while yours is over there? Why is the universe split in two for each of us, into a subject and an infinity of objects? How is each of us our own center of experience, receiving information about the rest of the world out there? Why are some things conscious and others apparently not? Is a rat conscious? A gnat? A bacterium?
Dramatic galaxy collision filled the Milky Way with stars, astronomers discover
Imagine trying to map out your home town using only information you could gather from your window. Even with a pair of binoculars you’d find it a difficult task. Mapping out our own galaxy, the Milky Way, is a similarly daunting mission. Unlike other galaxies that we can view from a distance, we sit inside the Milky Way – around 26,000 light years from its center. This means that when we try to look at the opposite side of the galaxy, much of our view is blocked by the stars and dust in between.