The electric vehicle revolution is coming, but it won’t be driven by the U.S. Instead, China will be at the forefront.
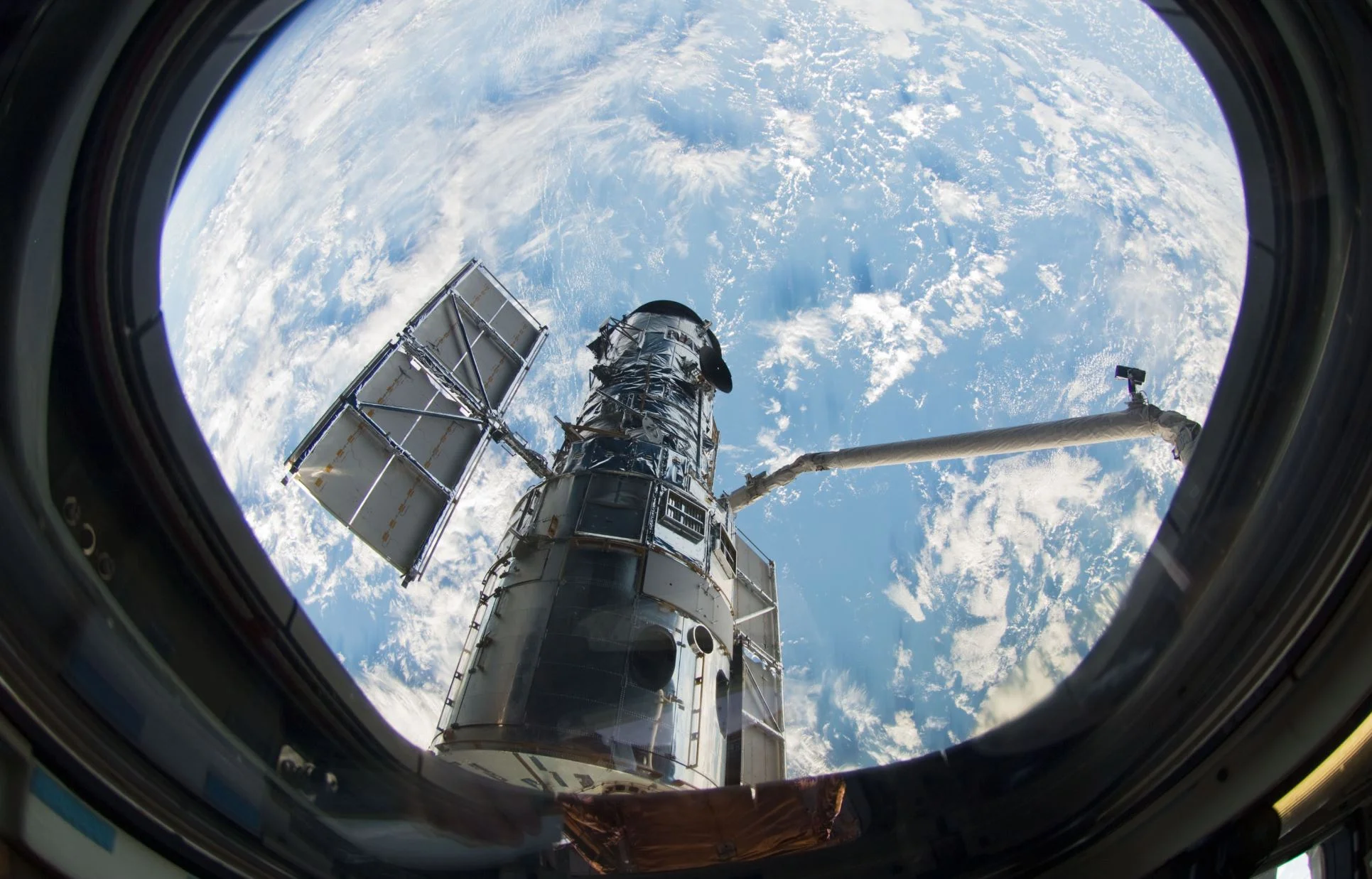
10 Years Ago, Hubble’s Final Servicing Mission Made It Better Than Ever
Astronaut Mike Massimino floated next to the Hubble Space Telescope’s cylindrical body and began to remove the screws that fastened a handrail to one of the telescope’s instrument panels. The first three screws came out easily, but when he put his power tool to the final screw, the bit began to spin.
Why hasn’t evolution dealt with the inefficiency of ageing?
Life pits the order and intricacy of biology against the ceaseless chaos of physics. The second law of thermodynamics, or the thermodynamic arrow of time, states that any natural system will always tend towards increasing disorder. Biological ageing is no different, making death inevitable. However, one of the least-addressed questions of ageing is the apparent paradox between the optimizing drive of evolution, and the inevitable deterioration of the body.
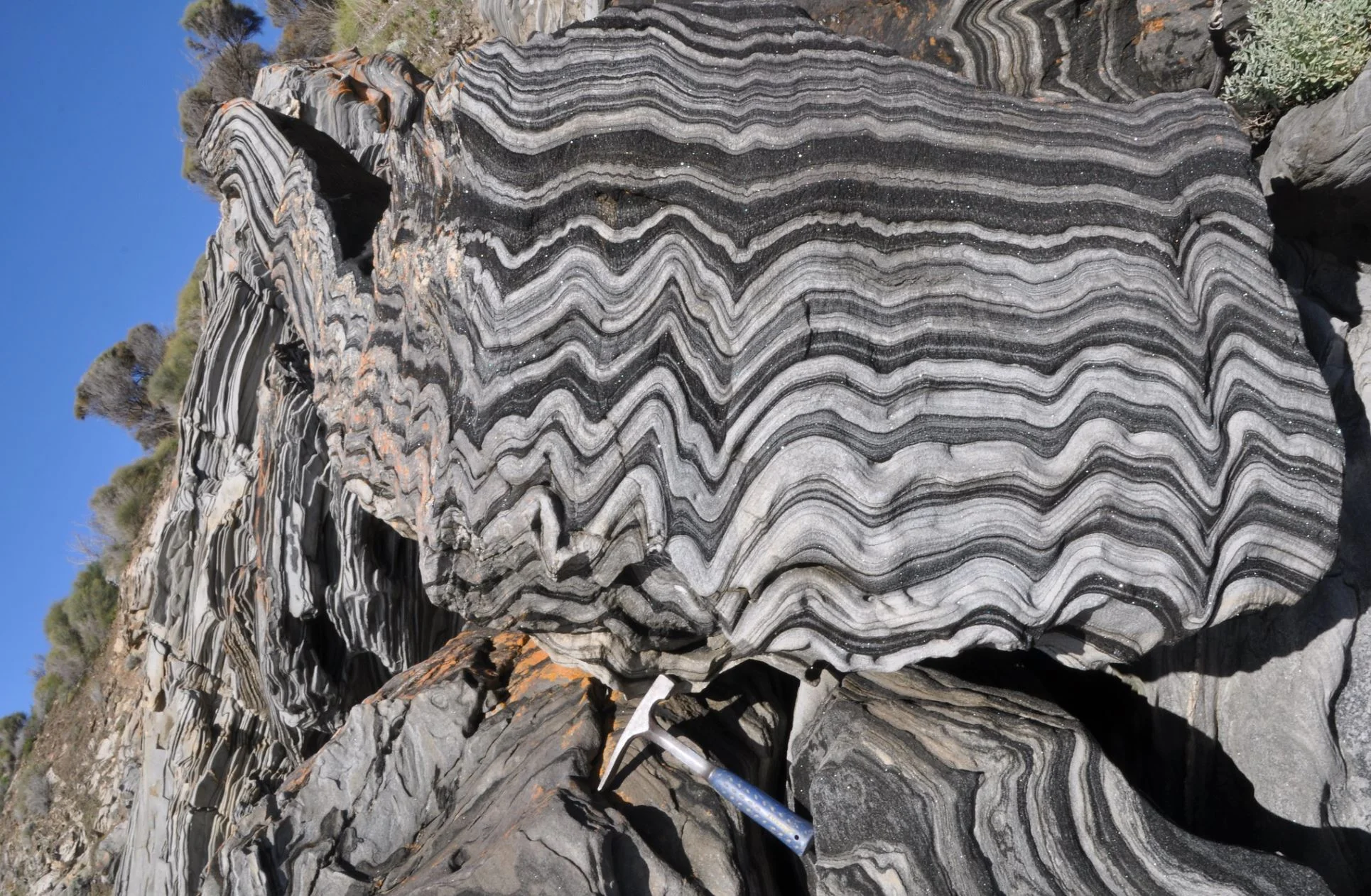
How Earth’s continents became twisted and contorted over millions of years
We are pretty sure the continental parts of plates are not uniform, nor are they rigid. The giant forces that slowly move continents across the viscous mantle layer underneath, like biscuits gliding over a warm toffee ocean, stress the continents, and twist and contort the crust. This is a process that has taken place over millions of years.
Africa is splitting in two - here is why
Will we ever know the difference between a wolf and a dog?
Astronauts Could Rely on Algae as the Perfect Life Support Partner
Mankind is planning for long-duration crewed missions, one of the most important things is to make sure that the crews have enough of the bare essentials to last for a long time. This is no easy task, since a crewed spacecraft will be a crew’s entire world for months on end. That means that a sufficient amount of food, water and oxygen will need to be brought along.
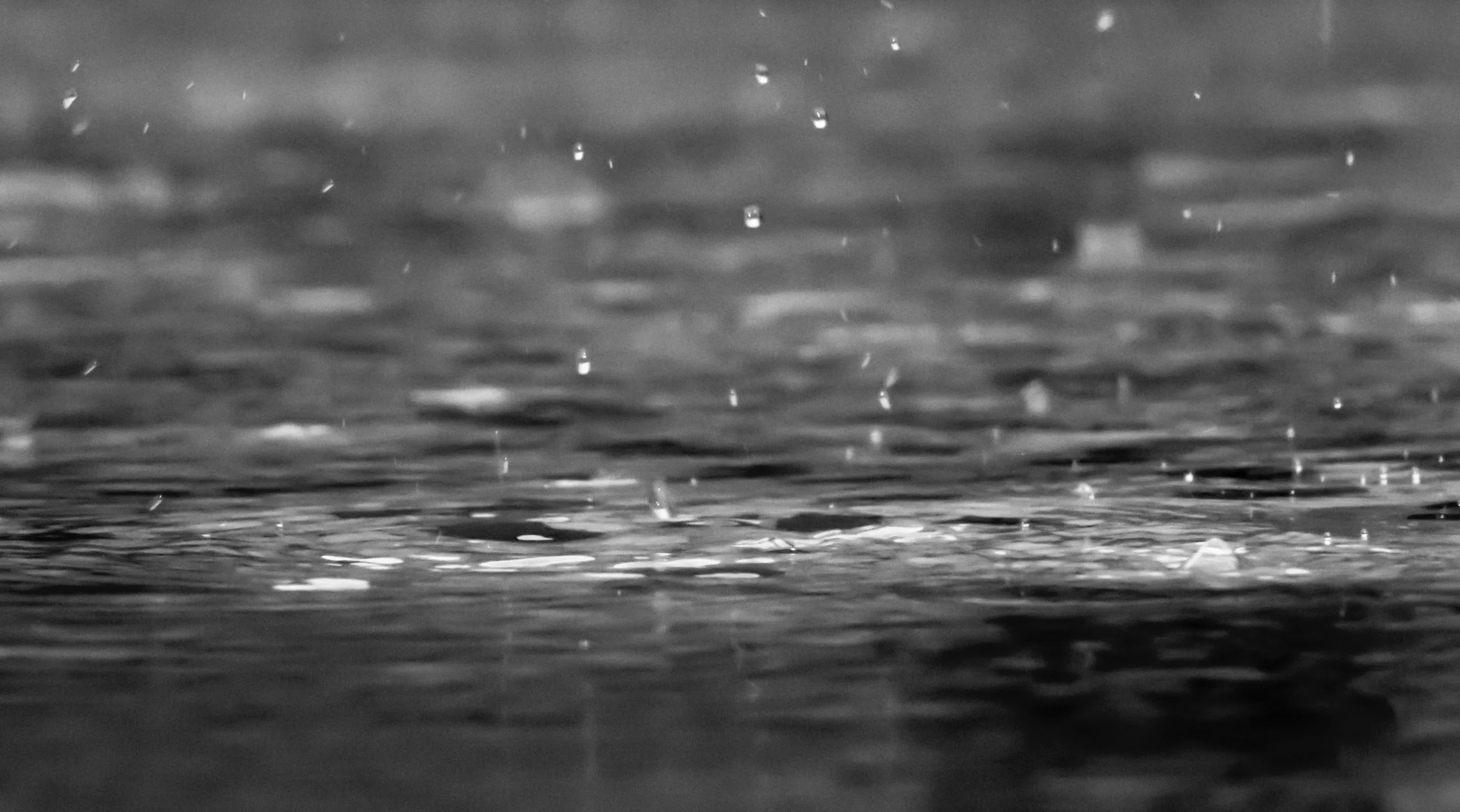
What happens when a raindrop hits a puddle?
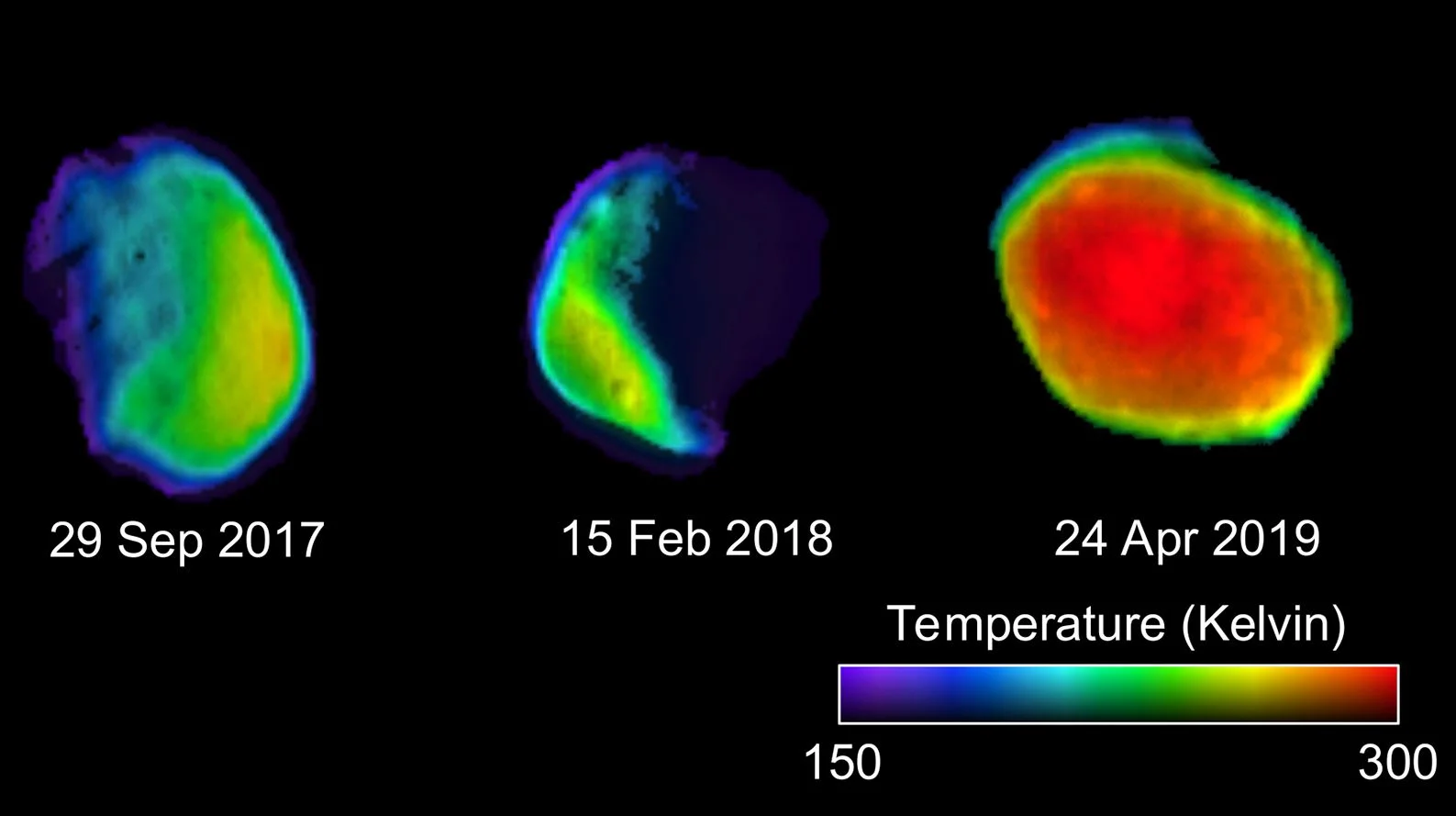
Why This Martian Full Moon Looks Like Candy
For the first time, NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter has caught the Martian moon Phobos during a full moon phase. Each color in this new image represents a temperature range detected by Odyssey's infrared camera, which has been studying the Martian moon since September of 2017. Looking like a rainbow-colored jawbreaker, these latest observations could help scientists understand what materials make up Phobos, the larger of Mars' two moons.
Methane-consuming bacteria could be the future of fuel
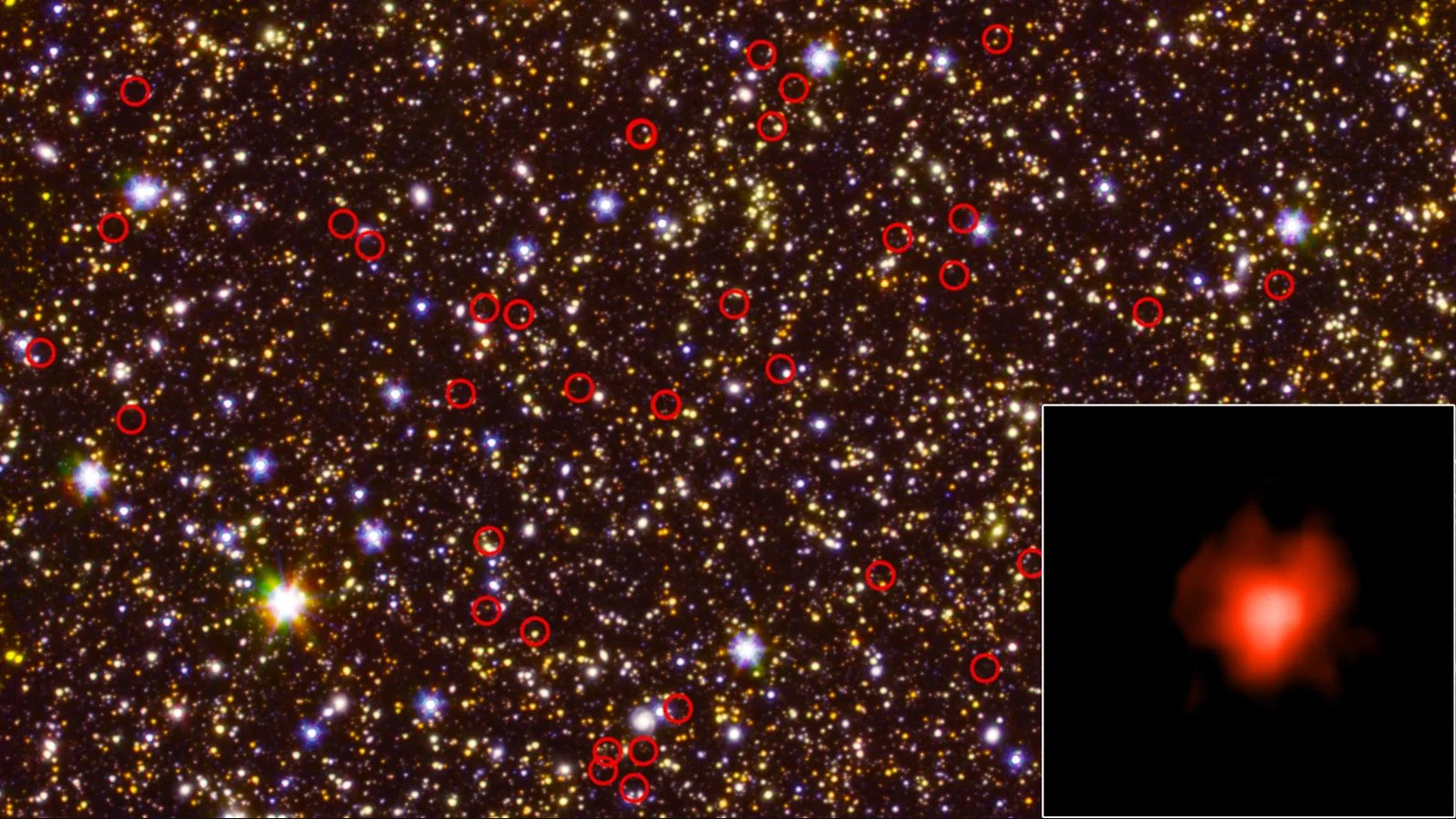
New Clues About How Ancient Galaxies Lit up the Universe
NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope has revealed that some of the universe's earliest galaxies were brighter than expected. The excess light is a byproduct of the galaxies releasing incredibly high amounts of ionizing radiation. The finding offers clues to the cause of the Epoch of Reionization, a major cosmic event that transformed the universe from being mostly opaque to the brilliant starscape seen today.
The number of electric cars sold in Europe increased by almost 85%!
Forget the Anthropocene: we’ve entered the synthetic age
One fact about our time is becoming increasingly well-known. No matter how far you travel, no matter in which direction you point, there is nowhere on Earth that remains free from the traces of human activity. The chemical and biological signatures of our species are everywhere. Transported around the globe by fierce atmospheric winds, relentless ocean currents, and the capacious cargo-holds of millions of fossil-fuel-powered vehicles, nowhere on Earth is free from humanity’s imprint. Pristine nature has permanently blinked out of existence.
Health check: why do we get motion sickness and what’s the best way to treat it?
Beyond the Metal: Investigating Soft Robots at NASA Langley
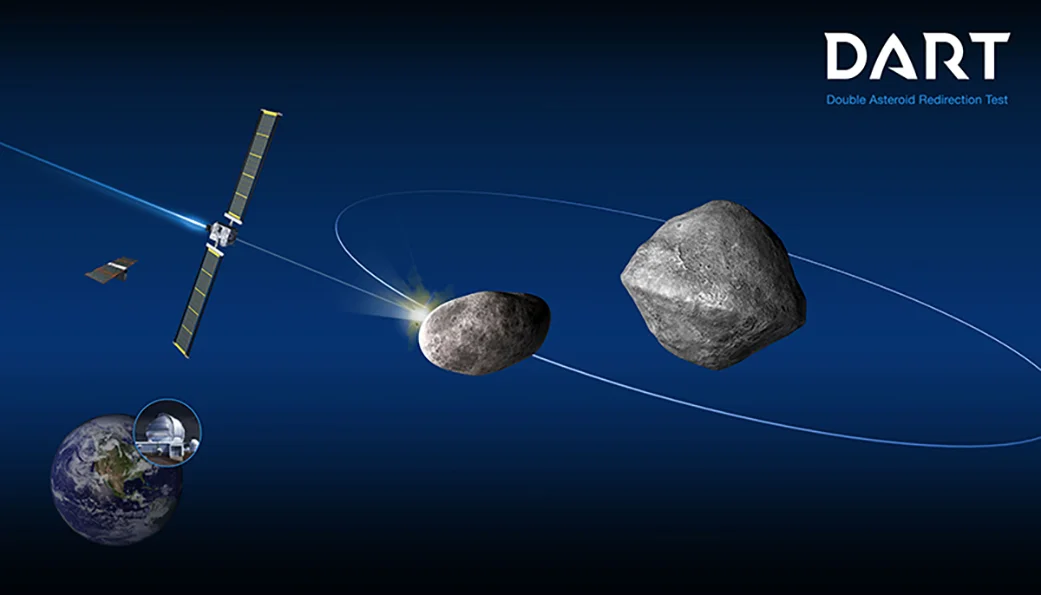
NASA’s First Planetary Defense Technology Demonstration to Collide with Asteroid in 2022
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) – NASA’s first mission to demonstrate a planetary defense technique – will get one chance to hit its target, the small moonlet in the binary asteroid system Didymos. The asteroid poses no threat to Earth and is an ideal test target: measuring the change in how the smaller asteroid orbits about the larger asteroid in a binary system is much easier than observing the change in a single asteroid's orbit around the Sun. Work is ramping up at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, and other locations across the country, as the mission heads toward its summer 2021 launch – and attempts to pull off a feat so far seen only in science fiction films.