Somewhat ironically, cold is a hot topic these days. Occurrences such as people taking a dip in icy seawater in the middle of winter in an attempt to boost their immune system are a common sight. Cold is supposedly good for a wide variety of things. One of the claims made is that it can help you lose weight, but is this actually true?
This article will explain the effects of cold temperatures on the human body and why it can be a good idea to turn down the heat in your house a little.
It takes some getting used to… - (Image Credit: lightpoet via Shutterstock / HDR Tune by Universal-Sci)
Ancestors
If you expose yourself to low temperatures, your body will do everything it can to maintain body temperature.
Hypothermia occurs when your body temperature falls below 35 degrees Celcius (or 95 F). At this point, your heart rate slows down, and you'll take fewer breaths per minute. As a result, less oxygen-rich blood reaches your vital organs, impairing their functioning. If these circumstances are maintained, life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat) may occur.
Our ancestors were confronted with extremely low temperatures more frequently in the past. As you can imagine, they couldn't simply turn up the heating a few degrees or put on a thick sweater. This is why our body itself is equipped with useful systems to keep us warm.
What happens to your body when it's cold?
When you're out in the cold, one of the first things that happens is the contraction of the blood vessels in the skin of your arms and legs.
Blood is responsible for the spreading of warmth throughout your body, so as soon as the blood vessels in the extremities of your body contract, warm blood stays in your core, closer to vital organs. This is the reason why your hands and feet feel cold the quickest.
If you stay out in the cold for an extended period of time, you'll start shattering your teeth, and your body will begin to shiver. Those muscle movements generate heat.
But something else will happen as well; a special type of fat that we have in our body gets activated, namely brown fat. Several types of fat exist within our bodies that can generally be divided into white fat and brown fat.
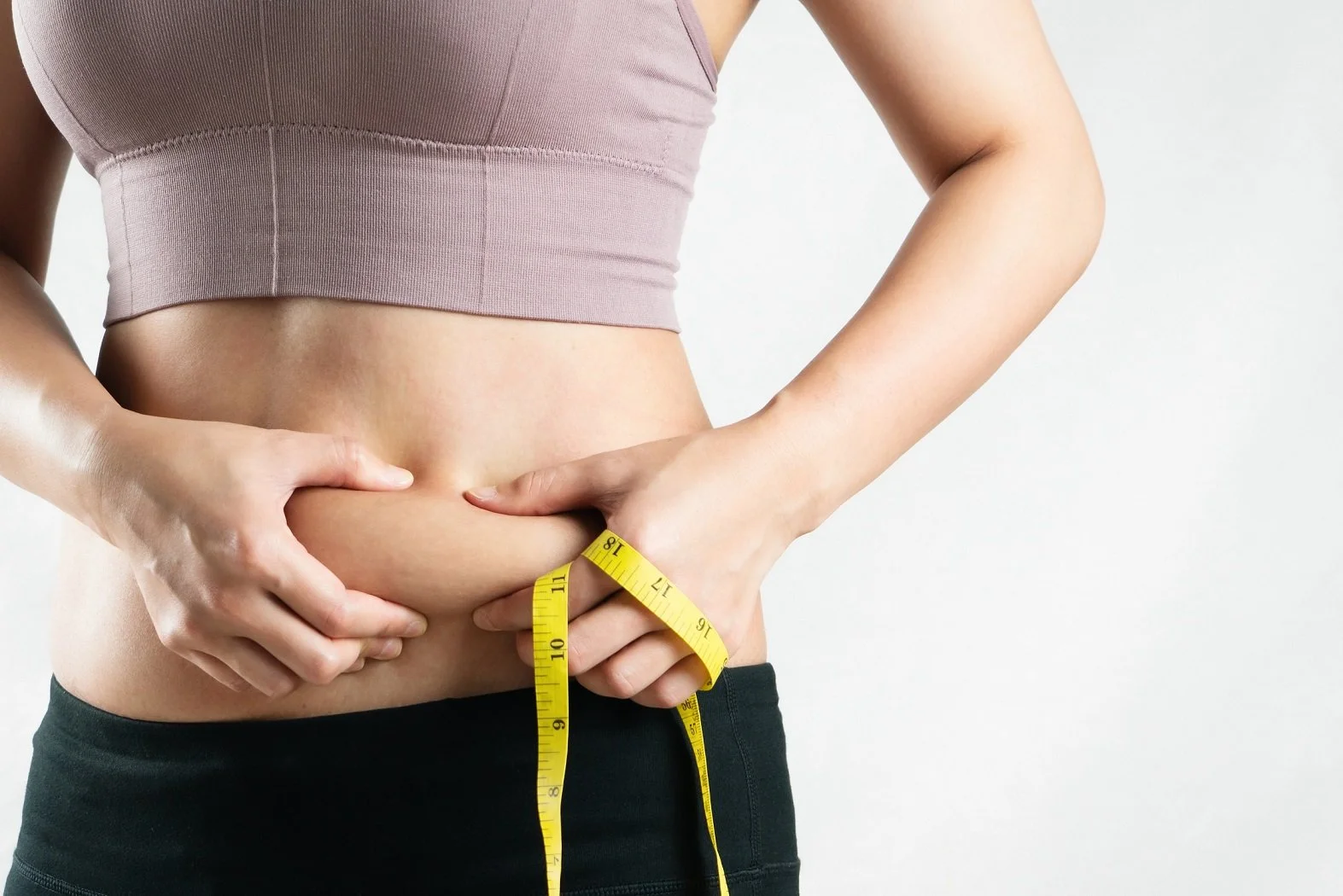
White fat
White fat cells are, among other things, responsible for storing energy. This comes in handy in times of hunger as it can swiftly release energy to supply the body. White cells are used to store a surplus of energy whenever we consume more food than is strictly necessary.
White fat is the type of fat that is subcutaneous. It can be clearly visible on, for example, your abdomen. In a way, white fat also protects you from the cold as it forms a sort of insulation layer.
Image Credit: Superstar via Shutterstock / HDR tune by Universal-Sci
We also know that this type of fat can be unhealthy. Having too much of it can increase the risk of various diseases, such as diabetes. Therefore, white fat is the type that most people would like to get rid of.
Brown fat
Brown fat cells work very differently from white fat cells. White fat cells contain a large fat 'droplet', whereas brown fat cells contain a multitude of small fat droplets that store only a tiny bit of fat as it burns fat to be converted into heat. Therefore, we consider brown fat to be healthy.
In adults, brown fat is mainly located in the neck region and in front of the vertebrae along the large blood vessels. It is a convenient location as it enables the generated heat to be transferred directly to the bloodstream, and thus it can be distributed throughout the body effectively. This is how we keep our core warm.
Image Credit: LDarin - Edited by Universal-Sci
How brown fat removes fat from places where you would like to get rid of it
Brown fat is activated when you are exposed to cold. First, a signal is sent from your skin toward your brain. Nerves connected to the brain then give off pulses towards the brown fat cells. This process takes place at a fast pace; the brown fat gets activated within minutes.
Within the brown fat exist so-called mitochondria, which act as tiny power plants. The mitochondria are equipped so that they can burn the fats from the small fat droplets within the brown fat cell and convert it into heat. At a certain point, the situation arises that fat threatens to run out in the brown fat cell. At this point, brown fat has to get its fuel from somewhere else.
Image Credit: LDarin via Shutterstock
What happens next is a very clever process where the brown cells start deriving fats from the bloodstream. The great thing about it is that white fat (which is present practically everywhere in our body) can release fats into the bloodstream, which can then be transported toward brown fat cells. In this way, brown fat removes fat from places where you would like to get rid of it.
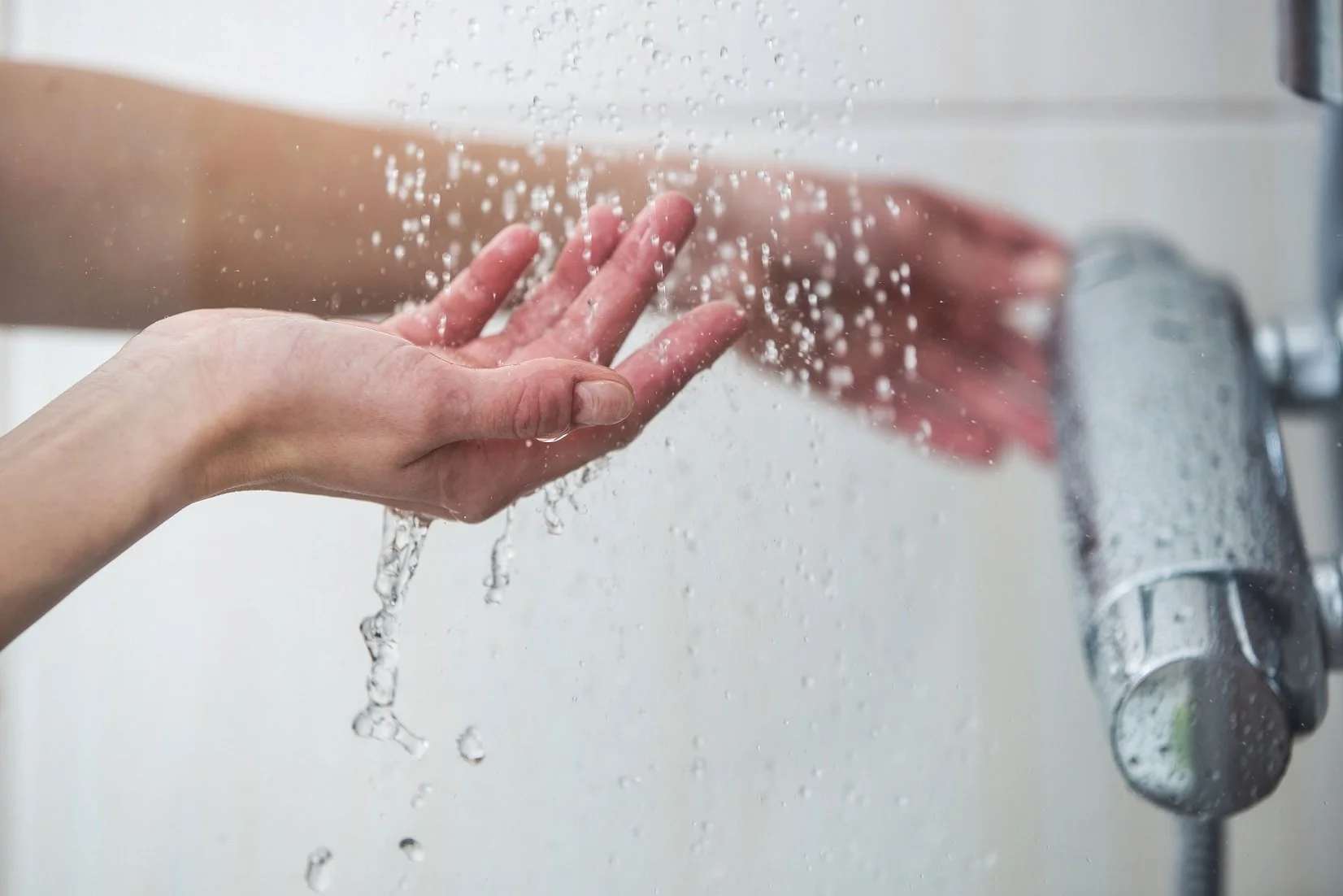
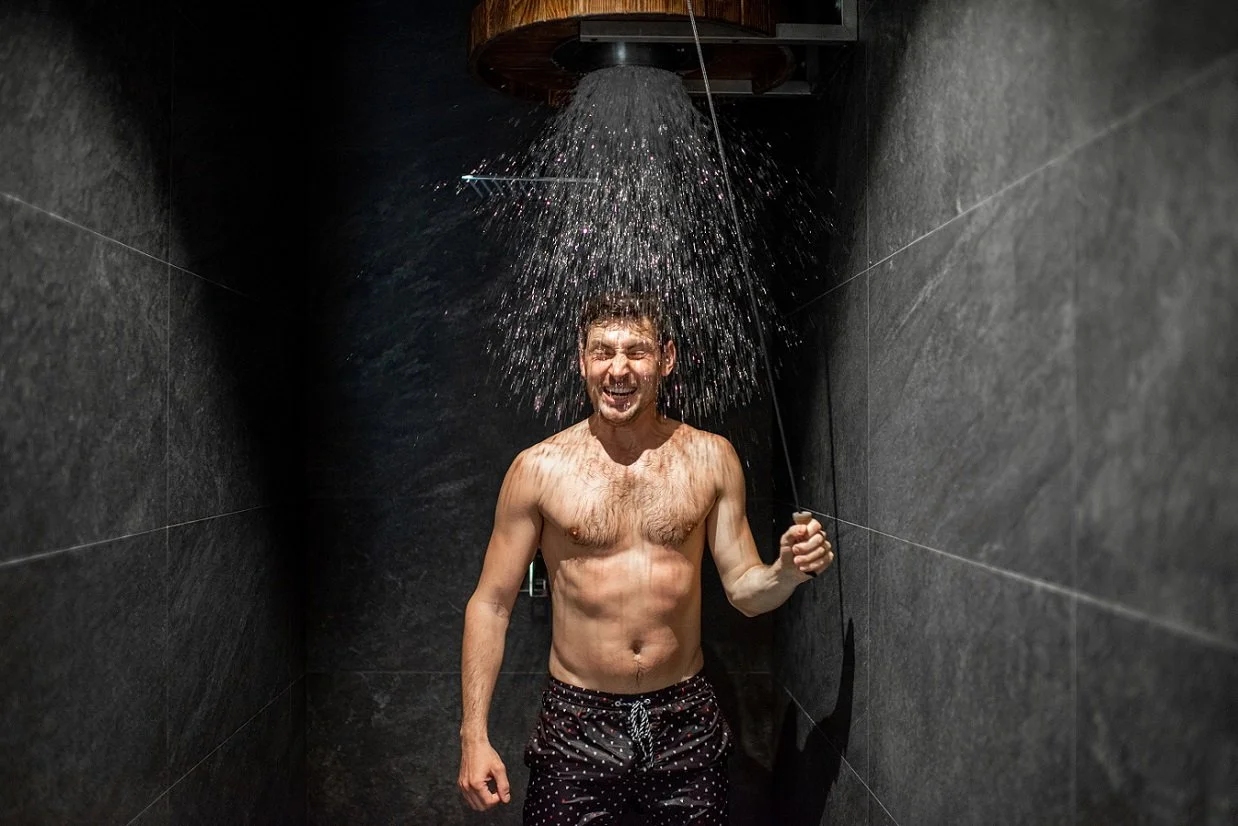
Losing weight by taking cold showers
An interesting follow-up question would be whether you can lose weight by generating and activating more brown fat cells. To answer this question, one must look at what happens when brown fat gets activated in practice.
When exposed to the right impulses, certain white fat cells can be converted into so-called beige fat cells. Beige fat cells exist between white and brown fat cells. They show similar beneficial effects to brown cells as they also contain mitochondria meaning that they are also capable of burning fat.
According to Dr. Mariëtte Boon from the Dutch Leiden University Medical Center, it is plausible that brown/beige fat cells are activated when you expose yourself to cold temperatures, like turning down your thermostat, frequently taking an ice bath, or taking a cold shower.
Image Credit: LDarin via Shutterstock
Boon and colleagues have set out to find out what happens if you expose adults to the cold for a short time. They exposed adult males to cold by putting them between mats cooled by a cold water flow. They adjusted the temperature in such a way that the men did not start shivering (so possible burned fat could not be attributed to muscle movement). The researchers found that by doing this for a relatively short period of time, the men burned off an extra 200 kcal per day.
Burning 200 kcal extra each and every day does require some patience, but it has significant effects in the long term. According to Boon, you would lose approximately 6 to 7 kilos (13 to 15 pounds) per year.
Additional health benefits of cold showers
According to Dr. Boon, cold showers enable your body to produce more endorphins which may help your general sense of well-being. However, studies have shown several additional benefits of taking a cold shower.
For example, a randomized clinical trial that also took place in the Netherlands discovered that cold showers led to an impressive 29% decrease in people calling in sick from work.
In addition, multiple scientific studies have shown that cold showers can improve sensitivity to insulin and clear glucose from the bloodstream, which can be particularly beneficial for people who have diabetes.
Image Credit: RossHelen via Shutterstock
Losing weight by lowering the thermostat
The team also discovered that when people lower their thermostat to 15 Celcius (59 Fahrenheit) for 2 hours per day for a period of six weeks, they tend to lose, on average, about 0.7kg (1.5 pounds) while maintaining muscle mass.
All in all, according to Dr. Boon, this is a healthy method of losing weight.
Sources and further reading:
The Effect of Cold Showering on Health and Work: A Randomized Controlled Trial (PLoS One)
Short-term cold acclimation improves insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus - (nature medicine)
Twelve weeks of exenatide treatment increases [ 18 F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake by brown adipose tissue without affecting oxidative resting energy expenditure in nondiabetic males (Metaboslim Journal)
Activation of Human Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT): Focus on Nutrition and Eating - (Springer)
The Changed Metabolic World with Human Brown Adipose Tissue: Therapeutic Visions - (Cell metabolism)
Brown and Beige Fat: Molecular Parts of a Thermogenic Machine - (American Diabetes Association)
Adapted cold shower as a potential treatment for depression - (national library of medicine)
If you enjoy our selection of content consider subscribing to our newsletter (Universal-Sci Weekly)
FEATURED ARTICLES: